1、Java新IO简介


2、缓冲区与Buffer

2.1、Buffer的基本操作


//缓冲区的操作流程
@Test
public void nioMethod() {
//开启10个大小的缓冲区
IntBuffer buf=IntBuffer.allocate(10);
//postion:操作位置、limit:缓冲区的限制、capacity:缓冲区的容量
System.out.println("1、写入数据前的postion、limit、capacity:");
System.out.println(buf.position()+"、"+buf.limit()+"、"+buf.capacity());
//定义整形数组
int temp[]= {1,2,3,5};
//向缓冲区写入一个数据
buf.put(3);
//向缓冲区写入一组数据
buf.put(temp);
System.out.println("2、写入数据后的postion、limit、capacity:");
System.out.println(buf.position()+"、"+buf.limit()+"、"+buf.capacity());
//重设缓冲区 将操作位置设置为0
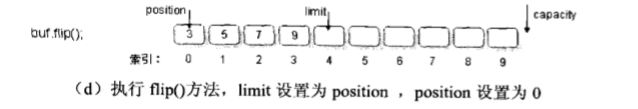
buf.flip();
System.out.println("3、准备输出数据时的postion、limit、capacity:");
System.out.println(buf.position()+"、"+buf.limit()+"、"+buf.capacity());
System.out.println("缓冲区内的内容:");
while(buf.hasRemaining()) {
int x=buf.get();
System.out.print(x+"、");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("4、输出数据后的postion、limit、capacity:");
System.out.println(buf.position()+"、"+buf.limit()+"、"+buf.capacity());
}
结果:

2.2、深入缓冲区操作

2.3、 创建子缓冲区

测试:
//创建子缓冲区
@Test
public void sliceTest() {
//1、开辟十个大小的缓冲区
CharBuffer buf=CharBuffer.allocate(10);
//定义缓冲区对象
CharBuffer read=null;
//向缓冲区中加入数据
buf.put('g');
buf.put('u');
buf.put('a');
buf.put('i');
//创建只读缓冲区
read=buf.asReadOnlyBuffer();
//重设缓冲区
read.flip();
System.out.println("缓冲区的内容:");
//读取缓冲区数据
while(read.hasRemaining()) {
char x=read.get();
System.out.print(x);
}
System.out.println();
try {
read.put("f");
}catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
结果:

2.4、创建直接缓冲区

测试:
//创建直接缓冲区
@Test
public void ByteBufTest() {
//声明对象
ByteBuffer buf=null;
//开辟直接缓冲区
buf=ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(10);
//定义byte数组
byte temp[]= {'g','u','a','i'};
//向缓冲区写入一组数据
buf.put(temp);
//重设缓冲区
buf.flip();
System.out.println("缓冲区的内容:");
// hasRemaining(): 判断当前位置到限制位置之间是否内容
while(buf.hasRemaining()) {
byte x=buf.get();
System.out.print((char)x);
}
}
结果:

3、通道

3.1、FileChannel

// 4、使用通道输入输出内容
@Test
public void channelTest() throws IOException {
// 带输出的数据
String info[] = { "hello", " guai" };
// 创建文件对象
File file = new File("e:/test.txt");
// 实例化输出流
FileOutputStream output = new FileOutputStream(file);
//实例化输入流
FileInputStream input=new FileInputStream(file);
//1)输出数据到文件
// 声明输出的通道对象
FileChannel fileChannel = null;
// 的到输出的文件通道
fileChannel = output.getChannel();
// 开辟缓冲
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 将输出内容写入缓冲
for (int i = 0; i < info.length; i++) {
buf.put(info[i].getBytes());
}
// 重设缓冲区
buf.flip();
// 使用管道输出内容到文件
fileChannel .write(buf);
//2)从文件中读取内容
//清空缓冲区
buf.clear();
fileChannel =null;
//实例化输入管道
fileChannel =input.getChannel();
//声明变量接收内容
int temp=0;
//将文件中的内容读取到缓冲区
while((temp=fileChannel.read(buf))!=-1) {
}
//重设缓冲区
buf.flip();
//输出缓冲区中的内容
System.out.println("从文件中读取的内容");
while(buf.hasRemaining()) {
byte x=buf.get();
System.out.print((char)x);
}
//关闭
fileChannel .close();
output.close();
input.close();
}
结果:

3.2、内存映射

测试;
//5、内存映射,提高文件读写速度
@Test
public void mapTest() throws IOException {
//创建文件对象
File file=new File("e:/test.txt");
//初始化文件输入流对象
FileInputStream input=new FileInputStream(file);
//实例化文件管道
FileChannel fileChannel=input.getChannel();
//声明文件的映射
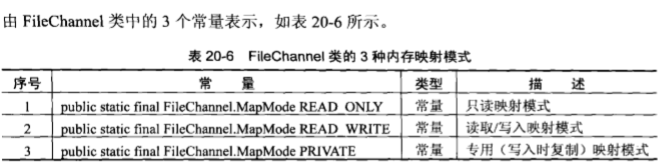
MappedByteBuffer mbb=fileChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY,0,file.length());
//定义数组接收数据
byte data[]=new byte[(int)file.length()];
//定义下标
int foot=0;
//判断是否有数据
while(mbb.hasRemaining()) {
data[foot++]=mbb.get();
}
System.out.println(new String(data));
//关闭
fileChannel.close();
input.close();
}
结果:

3.3、文件锁


测试练习:
//6、文件锁
@Test
public void fileLockTest() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//实例化一个文件对象
File file =new File("e:/test.txt");
//创建文件输入流
FileOutputStream output=new FileOutputStream(file);
//创建文件通道
FileChannel fChannel=output.getChannel();
//试图获得此通道的文件锁
FileLock lock=fChannel.lock();
if(lock!=null) {
System.out.println(file.getName()+"文件锁定1秒");
//线程休眠,模拟该线程对文件的操作过程
Thread.sleep(1000000);
//解除锁定
lock.release();
System.out.println(file.getName()+"文件解除锁定");
}
fChannel.close();
output.close();
}
5、Selector

测试练习
/**
*
* @description: 使用selector建议一个非阻塞的服务器端
* @author: guai
* @data: 2020年3月16日 下午6:45:38
*/
public class ServiceUI {
//服务器端
@Test
public void serviceTest() throws IOException {
//打开一个选择器
Selector selector=Selector.open();
//实例化ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel socketChannel=ServerSocketChannel.open();
//配置服务器为非阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 通过检索与此通道关联的服务端套接字
ServerSocket initSocket=socketChannel.socket();
//实例化监听地址与端口
InetSocketAddress address=new InetSocketAddress(9999);
//绑定地址
initSocket.bind(address);
//注册选择器
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("服务器在运行,在9999端口监听。");
int keysAdd;
//选择一组建,相应的通道已为IO准备就绪
while((keysAdd=selector.select())>0) {
//取出全部生成的key
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys=selector.selectedKeys();
//实例化Iteration 迭代器
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator=selectedKeys.iterator();
//迭代全部的key
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
//取出SelectionKey
SelectionKey key=(SelectionKey) iterator.next();
//判断客户端是否已连接上
if(key.isAcceptable()) {
System.out.println("与客户端成功连接");
//取得Channel
ServerSocketChannel server=(ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
//接收连接
SocketChannel client=server.accept();
//设置为非阻塞状态
client.configureBlocking(false);
//开启缓冲区
ByteBuffer outBuf=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//写入数据
outBuf.put(("当前时间:"+new Date()).getBytes());
//重置缓冲区
outBuf.flip();
//输出信息
client.write(outBuf);
client.close();
}
}
selectedKeys.clear();
}
}
//客户端
@Test
public void clientTest() throws Exception {
//创建socket
Socket cSocket=new Socket("localhost",9999);
//通过socket创建输入流
InputStream input=cSocket.getInputStream();
//创建缓冲流提高数据读写效率
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(input));
//读取客户端的请求数据
String str=null;
while((str=br.readLine())!=null) {
System.out.println("服务端信息为:"+str);
}
//关闭资源
br.close();
cSocket.close();
}
}
结果:























 508
508











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








