目录
4-1 IoC 控制反转
- 控制反转是一种思想。
- 控制反转是为了降低程序耦合度,提高程序扩展力,达到OCP原则,达到DIP原则。
- 控制反转,反转的是什么?
- 将对象的创建权利交出去,交给第三方容器负责。
- 将对象和对象之间关系的维护权交出去,交给第三方容器负责。
- 控制反转这种思想如何实现呢?
- DI(Dependency Injection):依赖注入

- DI(Dependency Injection):依赖注入
4-2 依赖注入
依赖注入实现了控制反转的思想。
Spring通过依赖注入的方式来完成Bean管理的。
Bean管理说的是:Bean对象的创建,以及Bean对象中属性的赋值(或者叫做Bean对象之间关系的维护)。
依赖注入:
- 依赖指的是对象和对象之间的关联关系。
- 注入指的是一种数据传递行为,通过注入行为来让对象和对象产生关系。
依赖注入常见的实现方式包括两种:
- 第一种:set注入
- 第二种:构造注入
新建模块:spring6-002-dependency-injection

4-2-1 set注入

- set注入,基于set方法实现的,底层会通过反射机制调用属性对应的set方法然后给属性赋值。这种方式要求属性必须对外提供set方法。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.powernode</groupId>
<artifactId>spring6-002-dependency-injection</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>repository.spring.milestone</id>
<name>Spring Milestone Repository</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.0.0-M2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
</project>
public class UserDao {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserDao.class);
public void insert(){
//System.out.println("数据库正在保存用户信息。");
// 使用一下log4j2日志框架
logger.info("数据库正在保存用户信息。");
}
}
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import com.powernode.spring6.dao.UserDao;
import com.powernode.spring6.dao.VipDao;
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
private VipDao vipDao;
public void setAbc(VipDao vipDao){
this.vipDao = vipDao;
}
// set注入的话,必须提供一个set方法。
// Spring容器会调用这个set方法,来给userDao属性赋值。
// 我自己写一个set方法,不使用IDEA工具生成的。不符合javabean规范。
// 至少这个方法是以set单词开始的。前三个字母不能随便写,必须是“set"
/*public void setMySQLUserDao(UserDao xyz){
this.userDao = xyz;
}*/
// 这个set方法是IDEA工具生成的,符合javabean规范。
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void saveUser(){
// 保存用户信息到数据库
userDao.insert();
vipDao.insert();
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userDaoBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.dao.UserDao"/>
<bean id="userServiceBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.service.UserService">
<property name="userDao" ref="userDaoBean"/>
</bean>
</beans>
package com.powernode.spring6.test;
import com.powernode.spring6.service.UserService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className DITest
* @since 1.0
**/
public class DITest {
@Test
public void testSetDI(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean("userServiceBean", UserService.class);
userService.saveUser();
}
}
运行结果:
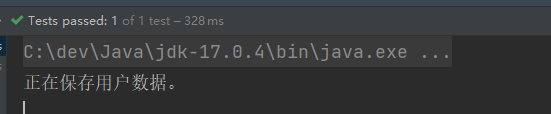
重点内容是,什么原理:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userDaoBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.dao.UserDao"/>
<bean id="userServiceBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.service.UserService">
<property name="userDao" ref="userDaoBean"/>
</bean>
</beans>
实现原理:
通过property标签获取到属性名:userDao
通过属性名推断出set方法名:setUserDao
通过反射机制调用setUserDao()方法给属性赋值
- property标签的name是属性名。
- property标签的ref是要注入的bean对象的id。(通过ref属性来完成bean的装配,这是bean最简单的一种装配方式。装配指的是:创建系统组件之间关联的动作)
可以把set方法注释掉,再测试一下:
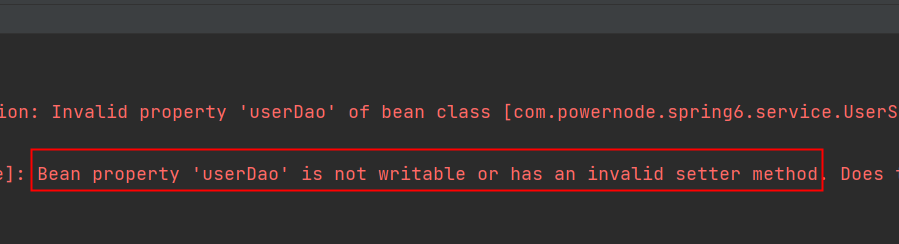
- 通过测试得知,底层实际上调用了setUserDao()方法。所以需要确保这个方法的存在。
- 我们现在把属性名修改一下,但方法名还是setUserDao(),我们来测试一下:
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import com.powernode.spring6.dao.UserDao;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className UserService
* @since 1.0
**/
public class UserService {
private UserDao aaa;
// 使用set方式注入,必须提供set方法。
// 反射机制要调用这个方法给属性赋值的。
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.aaa = userDao;
}
public void save(){
aaa.insert();
}
}
运行测试程序:

通过测试看到程序仍然可以正常执行,说明property标签的name是:setUserDao()方法名演变得到的。演变的规律是:
- setUsername() 演变为 username
- setPassword() 演变为 password
- setUserDao() 演变为 userDao
- setUserService() 演变为 userService
另外,对于property标签来说,ref属性也可以采用标签的方式,但使用ref属性是多数的:
<bean id="userServiceBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.service.UserService">
<property name="userDao">
<ref bean="userDaoBean"/>
</property>
</bean>
总结:set注入的核心实现原理:通过反射机制调用set方法来给属性赋值,让两个对象之间产生关系。
如果构造方法有两个参数:
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
private VipDao vipDao;
public void setAbc(VipDao vipDao){
this.vipDao = vipDao;
}
// set注入的话,必须提供一个set方法。
// Spring容器会调用这个set方法,来给userDao属性赋值。
// 我自己写一个set方法,不使用IDEA工具生成的。不符合javabean规范。
// 至少这个方法是以set单词开始的。前三个字母不能随便写,必须是“set"
/*public void setMySQLUserDao(UserDao xyz){
this.userDao = xyz;
}*/
// 这个set方法是IDEA工具生成的,符合javabean规范。
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void saveUser(){
// 保存用户信息到数据库
userDao.insert();
vipDao.insert();
}
}
spring配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--配置dao-->
<bean id="userDaoBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.dao.UserDao"/>
<!--配置service-->
<bean id="userServiceBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.service.UserService">
<!-- 想让Spring调用对应的set方法,需要配置property标签 -->
<!-- name属性怎么指定值:set方法的方法名,去掉set,然后把剩下的单词首字母变小写,写到这里。-->
<!-- ref翻译为引用。英语单词:references。ref后面指定的是要注入的bean的id。-->
<!--<property name="mySQLUserDao" ref="userDaoBean"/>-->
<!--set方法起名的时候,不要为难自己,按照规范来。所以一般情况下name位置写属性名就行了。-->
<property name="userDao" ref="userDaoBean"/>
<property name="abc" ref="vipDaoBean"/>
</bean>
<bean id="vipDaoBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.dao.VipDao"/>
</beans>
执行测试程序:
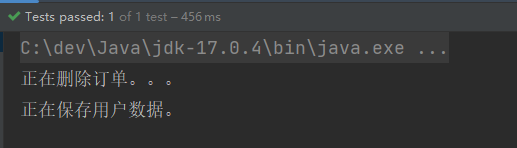
- 可以得出结论: XML 的配置文件中 property 属性的 name 是根据 set 方法 set 后面的英文字母进行命名的。
4-2-2 构造注入

- 实现 CustomerService 类,其包含 UserDao 和 VipDao
public class CustomerService {
private UserDao userDao;
private VipDao vipDao;
/*public CustomerService(UserDao userDao, VipDao vipDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
this.vipDao = vipDao;
}*/
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void setVipDao(VipDao vipDao) {
this.vipDao = vipDao;
}
public void save(){
userDao.insert();
vipDao.insert();
}
}
- 实现构造注入的 xml 配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--方式1:根据构造方法参数名进行注入-->
<bean id="UserDaoBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.dao.UserDao"/>
<bean id="VipDaoBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.dao.VipDao"/>
<bean id="csBean2" class="com.powernode.spring6.service.CustomerService">
<!--根据构造方法参数的名字进行注入。-->
<constructor-arg name="vipDao" ref="yyyy"/>
<constructor-arg name="userDao" ref="xxxx"/>
</bean>
<!--方式2:根据下标进行注入-->
<bean id="xxxx" class="com.powernode.spring6.dao.UserDao"/>
<bean id="yyyy" class="com.powernode.spring6.dao.VipDao"/>
<bean id="csBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.service.CustomerService">
<!--构造注入-->
<!--
index属性指定参数下标,第一个参数是0,第二个参数是1,第三个参数是2,以此类推。
ref属性用来指定注入的bean的id
-->
<!--指定构造方法的第一个参数,下标是0-->
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="xxxx"/>
<!--指定构造方法的第二个参数,下标是1-->
<constructor-arg index="1" ref="yyyy"/>
</bean>
</beans>
- 测试程序
@Test
public void testConstructorDI(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
CustomerService customerService = applicationContext.getBean("csBean", CustomerService.class);
customerService.save();
CustomerService csBean2 = applicationContext.getBean("csBean2", CustomerService.class);
csBean2.save();
}
4-3 set 注入专题
4-3-1 注入外部Bean

- 定义订单类 OrderDao
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className OrderDao
* @since 1.0
**/
public class OrderDao {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(OrderDao.class);
public void insert(){
logger.info("订单正在生成....");
}
}
- 定义 OrderService
public class OrderService {
private OrderDao orderDao;
// 通过set方法给属性赋值。
public void setOrderDao(OrderDao orderDao) {
this.orderDao = orderDao;
}
/**
* 生成订单的业务方法。。。
*/
public void generate(){
orderDao.insert();
}
}
- 配置 XML 实现外部 Bean
- 外部 Bean:使用ref属性来引入。这就是注入外部Bean
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--声明/定义Bean-->
<bean id="orderDaoBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.dao.OrderDao"></bean>
<bean id="orderServiceBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService">
<!--使用ref属性来引入。这就是注入外部Bean-->
<property name="orderDao" ref="orderDaoBean"/>
</bean>
</beans>
- 测试程序
@Test
public void testSetDI2(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("set-di.xml");
OrderService orderService = applicationContext.getBean("orderServiceBean", OrderService.class);
orderService.generate();
OrderService orderService2 = applicationContext.getBean("orderServiceBean2", OrderService.class);
orderService2.generate();
}
4-3-2 注入内部Bean
- 在 property 标签中使用嵌套的bean标签,这就是内部Bean
<bean id="orderServiceBean2" class="com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService">
<property name="orderDao">
<!--在property标签中使用嵌套的bean标签,这就是内部Bean-->
<bean class="com.powernode.spring6.dao.OrderDao"></bean>
</property>
</bean>
4-3-3 注入简单类型

- 我们之前在进行注入的时候,对象的属性是另一个对象。
- 如果对象的属性是一个 简单数据类型并非我们自定义的对象,如 String 该如何注入?
- 编写 User 类
String是简单类型int是简单类型
public class User {
private String username; // String是简单类型
private String password;
private int age; // int是简单类型
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
- 注入简单类型的 XML 文件
- 重点:如果是给简单类型赋值,就不能使用ref了。就需要使用value了
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--注入简单类型-->
<bean id="userBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.bean.User">
<!--重点:如果是给简单类型赋值,就不能使用ref了。就需要使用value了。-->
<property name="username" value="张三"/>
<property name="password" value="123"/>
<property name="age" value="20"/>
</bean>
</beans>
需要特别注意:如果给简单类型赋值,使用value属性或value标签。而不是ref。
简单类型包括哪些呢?可以通过Spring的源码来分析一下:BeanUtils类
public class BeanUtils{
//.......
/**
* Check if the given type represents a "simple" property: a simple value
* type or an array of simple value types.
* <p>See {@link #isSimpleValueType(Class)} for the definition of <em>simple
* value type</em>.
* <p>Used to determine properties to check for a "simple" dependency-check.
* @param type the type to check
* @return whether the given type represents a "simple" property
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition#DEPENDENCY_CHECK_SIMPLE
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#checkDependencies
* @see #isSimpleValueType(Class)
*/
public static boolean isSimpleProperty(Class<?> type) {
Assert.notNull(type, "'type' must not be null");
return isSimpleValueType(type) || (type.isArray() && isSimpleValueType(type.getComponentType()));
}
/**
* Check if the given type represents a "simple" value type: a primitive or
* primitive wrapper, an enum, a String or other CharSequence, a Number, a
* Date, a Temporal, a URI, a URL, a Locale, or a Class.
* <p>{@code Void} and {@code void} are not considered simple value types.
* @param type the type to check
* @return whether the given type represents a "simple" value type
* @see #isSimpleProperty(Class)
*/
public static boolean isSimpleValueType(Class<?> type) {
return (Void.class != type && void.class != type &&
(ClassUtils.isPrimitiveOrWrapper(type) ||
Enum.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
CharSequence.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
Number.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
Date.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
Temporal.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
URI.class == type ||
URL.class == type ||
Locale.class == type ||
Class.class == type));
}
//........
}
通过源码分析得知,简单类型包括:
- 基本数据类型
- 基本数据类型对应的包装类
- String或其他的CharSequence子类
- Number子类
- Date子类
- Enum子类
- URI
- URL
- Temporal子类
- Locale
- Class
- 另外还包括以上简单值类型对应的数组类型。
经典案例:给数据源的属性注入值:
- 定义一个类 SimpleValueType,为其添加简单类属性
public class SimpleValueType {
/*
public static boolean isSimpleValueType(Class<?> type) {
return (Void.class != type && void.class != type &&
(ClassUtils.isPrimitiveOrWrapper(type) ||
Enum.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
CharSequence.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
Number.class.isAssignableFrom(type) ||
Date.class.isAssignableFrom(type) || java.util.Date是简单类型
Temporal.class.isAssignableFrom(type) || Temporal是Java8提供的时间和时区类型
URI.class == type ||
URL.class == type ||
Locale.class == type || Locale是语言类,也是简单类型。
Class.class == type));
}
*/
private int age;
private Integer age2;
private boolean flag;
private Boolean flag2;
private char c;
private Character c2;
private Season season;
private String username;
private Class clazz;
// 生日
private Date birth;
public void setBirth(Date birth) {
this.birth = birth;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SimpleValueType{" +
"age=" + age +
", age2=" + age2 +
", flag=" + flag +
", flag2=" + flag2 +
", c=" + c +
", c2=" + c2 +
", season=" + season +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", clazz=" + clazz +
", birth=" + birth +
'}';
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setAge2(Integer age2) {
this.age2 = age2;
}
public void setFlag(boolean flag) {
this.flag = flag;
}
public void setFlag2(Boolean flag2) {
this.flag2 = flag2;
}
public void setC(char c) {
this.c = c;
}
public void setC2(Character c2) {
this.c2 = c2;
}
public void setSeason(Season season) {
this.season = season;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public void setClazz(Class clazz) {
this.clazz = clazz;
}
}
public enum Season {
SPRING, SUMMER, AUTUMN, WINTER
}
- XML 配置文件
<!--测试哪些类型是简单类型-->
<bean id="svt" class="com.powernode.spring6.bean.SimpleValueType">
<property name="age" value="20"/>
<property name="age2" value="20"/>
<property name="username" value="zhangsan"/>
<property name="season" value="SPRING"/>
<property name="flag" value="false"/>
<property name="flag2" value="true"/>
<property name="c" value="男"/>
<property name="c2" value="女"/>
<property name="clazz" value="java.lang.String"/>
<!--报错了,说1970-10-11这个字符串无法转换成java.util.Date类型。-->
<!--<property name="birth" value="1970-10-11"/>-->
<!--如果你硬要把Date当做简单类型的话,使用value赋值的话,这个日期字符串格式有要求-->
<!--在实际开发中,我们一般不会把Date当做简单类型,虽然它是简单类型。一般会采用ref给Date类型的属性赋值。-->
<property name="birth" value="Wed Oct 19 16:28:13 CST 2022"/>
</bean>
- 测试程序
@Test
public void testSimpleTypeSet(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("set-di.xml");
//User user = applicationContext.getBean("userBean", User.class);
//System.out.println(user);
SimpleValueType svt = applicationContext.getBean("svt", SimpleValueType.class);
System.out.println(svt);
}
4-3-4 级联属性赋值(了解)

- 班级类
package com.powernode.spring6.beans;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className Clazz
* @since 1.0
**/
public class Clazz {
private String name;
public Clazz() {
}
public Clazz(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Clazz{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
- 学生对象
package com.powernode.spring6.beans;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className Student
* @since 1.0
**/
public class Student {
private String name;
private Clazz clazz;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, Clazz clazz) {
this.name = name;
this.clazz = clazz;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setClazz(Clazz clazz) {
this.clazz = clazz;
}
public Clazz getClazz() {
return clazz;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", clazz=" + clazz +
'}';
}
}
- 级联属性赋值配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="clazzBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.Clazz"/>
<bean id="student" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.Student">
<property name="name" value="张三"/>
<!--要点1:以下两行配置的顺序不能颠倒-->
<property name="clazz" ref="clazzBean"/>
<!--要点2:clazz属性必须有getter方法-->
<property name="clazz.name" value="高三一班"/>
</bean>
</beans>
4-3-5 注入数组

1- 简单数据类型的数组注入
package com.powernode.spring6.beans;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Person {
private String[] favariteFoods;
public void setFavariteFoods(String[] favariteFoods) {
this.favariteFoods = favariteFoods;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"favariteFoods=" + Arrays.toString(favariteFoods) +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="person" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.Person">
<property name="favariteFoods">
<array>
<value>鸡排</value>
<value>汉堡</value>
<value>鹅肝</value>
</array>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
@Test
public void testArraySimple(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-array-simple.xml");
Person person = applicationContext.getBean("person", Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
}
2- 非简单数据类型的数组注入
package com.powernode.spring6.beans;
/**
* @version 1.0
* @className Goods
* @since 1.0
**/
public class Goods {
private String name;
public Goods() {
}
public Goods(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Goods{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.powernode.spring6.beans;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @version 1.0
* @className Order
* @since 1.0
**/
public class Order {
// 一个订单中有多个商品
private Goods[] goods;
public Order() {
}
public Order(Goods[] goods) {
this.goods = goods;
}
public void setGoods(Goods[] goods) {
this.goods = goods;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Order{" +
"goods=" + Arrays.toString(goods) +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="goods1" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.Goods">
<property name="name" value="西瓜"/>
</bean>
<bean id="goods2" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.Goods">
<property name="name" value="苹果"/>
</bean>
<bean id="order" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.Order">
<property name="goods">
<array>
<!--这里使用ref标签即可-->
<ref bean="goods1"/>
<ref bean="goods2"/>
</array>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
@Test
public void testArray(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-array.xml");
Order order = applicationContext.getBean("order", Order.class);
System.out.println(order);
}
4-3-6 注入 List 和 Set 集合

1- List 集合注入
- 有序可重复
package com.powernode.spring6.beans;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className People
* @since 1.0
**/
public class People {
// 一个人有多个名字
private List<String> names;
public void setNames(List<String> names) {
this.names = names;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"names=" + names +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.People">
<property name="names">
<list>
<value>铁锤</value>
<value>张三</value>
<value>张三</value>
<value>张三</value>
<value>狼</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
@Test
public void testCollection(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-collection.xml");
People peopleBean = applicationContext.getBean("peopleBean", People.class);
System.out.println(peopleBean);
}
2- Set 集合注入
- 无序不可重复
package com.powernode.spring6.beans;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className People
* @since 1.0
**/
public class People {
// 一个人有多个电话
private Set<String> phones;
public void setPhones(Set<String> phones) {
this.phones = phones;
}
//......
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"phones=" + phones +
", names=" + names +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.People">
<property name="phones">
<set>
<!--非简单类型可以使用ref,简单类型使用value-->
<value>110</value>
<value>110</value>
<value>120</value>
<value>120</value>
<value>119</value>
<value>119</value>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
4-3-7 注入 Map 和 Properties 集合

1- Map 集合注入
package com.powernode.spring6.beans;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className People
* @since 1.0
**/
public class People {
// 一个人有多个住址
private Map<Integer, String> addrs;
public void setAddrs(Map<Integer, String> addrs) {
this.addrs = addrs;
}
//......
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"addrs=" + addrs +
", phones=" + phones +
", names=" + names +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.People">
<property name="addrs">
<map>
<!--如果key不是简单类型,使用 key-ref 属性-->
<!--如果value不是简单类型,使用 value-ref 属性-->
<entry key="1" value="北京大兴区"/>
<entry key="2" value="上海浦东区"/>
<entry key="3" value="深圳宝安区"/>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
2- Properties 注入
java.util.Properties继承java.util.Hashtable,所以Properties也是一个Map集合。
package com.powernode.spring6.beans;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className People
* @since 1.0
**/
public class People {
private Properties properties;
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
//......
@Override
public String toString() {
return "People{" +
"properties=" + properties +
", addrs=" + addrs +
", phones=" + phones +
", names=" + names +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="peopleBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.People">
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="driver">com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver</prop>
<prop key="url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring</prop>
<prop key="username">root</prop>
<prop key="password">123456</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
4-3-8 注入 null 和 空字符串

1- 注入空字符串
package com.powernode.spring6.beans;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className Vip
* @since 1.0
**/
public class Vip {
private String email;
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Vip{" +
"email='" + email + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="vipBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.Vip">
<!--空串的第一种方式-->
<!--<property name="email" value=""/>-->
<!--空串的第二种方式-->
<property name="email">
<value/>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
@Test
public void testNull(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-null.xml");
Vip vipBean = applicationContext.getBean("vipBean", Vip.class);
System.out.println(vipBean);
}
4-3-9 注入特殊符号
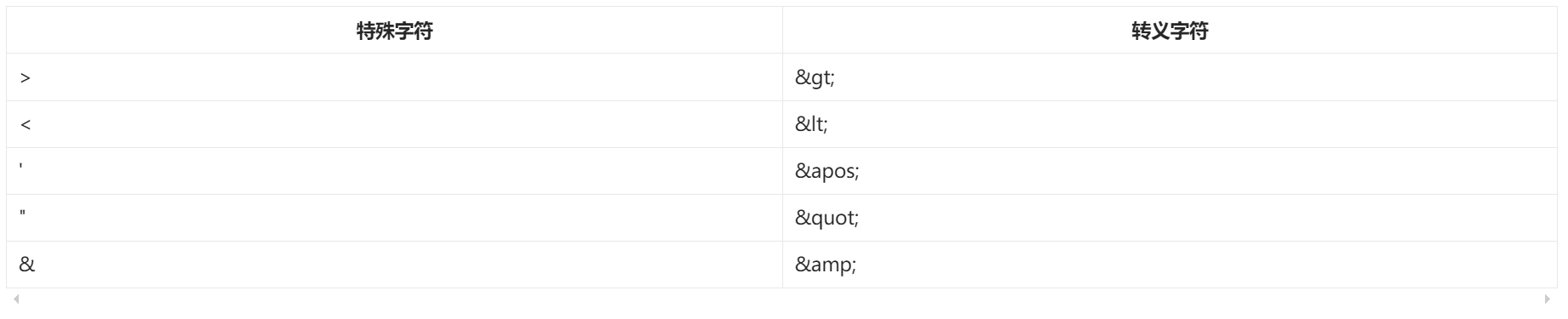
- XML中有5个特殊字符,分别是:
<、>、'、"、& - 以上 5 个特殊符号在 XML 中会被特殊对待,会被当做 XML 语法的一部分进行解析,如果这些特殊符号直接出现在注入的字符串当中,会报错。
解决方案包括两种:
- 第一种:特殊符号使用转义字符代替。
- 第二种:将含有特殊符号的字符串放到:
<![CDATA[]]>当中。因为放在CDATA区中的数据不会被 XML 文件解析器解析。
5个特殊字符对应的转义字符分别是:
1- 转义字符代替
package com.powernode.spring6.beans;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className Math
* @since 1.0
**/
public class Math {
private String result;
public void setResult(String result) {
this.result = result;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Math{" +
"result='" + result + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="mathBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.Math">
<property name="result" value="2 < 3"/>
</bean>
</beans>
@Test
public void testSpecial(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-special.xml");
Math mathBean = applicationContext.getBean("mathBean", Math.class);
System.out.println(mathBean);
}
2- 使用 CDATA 注入
- 注意:使用CDATA时,不能使用value属性,只能使用value标签。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="mathBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.Math">
<property name="result">
<!--只能使用value标签-->
<value><![CDATA[2 < 3]]></value>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
4-4 p命名空间注入
package com.powernode.spring6.beans;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className Customer
* @since 1.0
**/
public class Customer {
private String name;
private int age;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Customer{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="customerBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.Customer" p:name="zhangsan" p:age="20"/>
</beans>
4-5 c命名空间注入

package com.powernode.spring6.beans;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className MyTime
* @since 1.0
**/
public class MyTime {
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
public MyTime(int year, int month, int day) {
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyTime{" +
"year=" + year +
", month=" + month +
", day=" + day +
'}';
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--<bean id="myTimeBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.MyTime" c:year="1970" c:month="1" c:day="1"/>-->
<bean id="myTimeBean" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.MyTime" c:_0="2008" c:_1="8" c:_2="8"/>
</beans>
@Test
public void testC(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-c.xml");
MyTime myTimeBean = applicationContext.getBean("myTimeBean", MyTime.class);
System.out.println(myTimeBean);
}
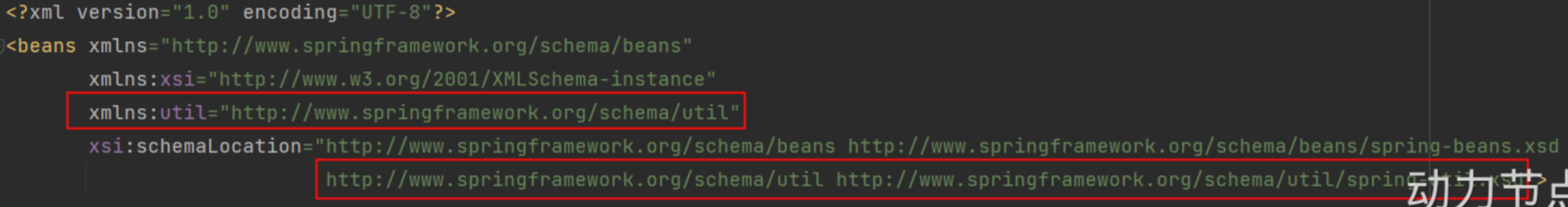
4-6 util 命名空间复用

package com.powernode.spring6.beans;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className MyDataSource1
* @since 1.0
**/
public class MyDataSource1 {
private Properties properties;
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyDataSource1{" +
"properties=" + properties +
'}';
}
}
package com.powernode.spring6.beans;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className MyDataSource2
* @since 1.0
**/
public class MyDataSource2 {
private Properties properties;
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyDataSource2{" +
"properties=" + properties +
'}';
}
}
- 使用了
util命名空间可以实现属性的服用,这样可以在dataSource1和dataSource2中复用prop
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd">
<util:properties id="prop">
<prop key="driver">com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver</prop>
<prop key="url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring</prop>
<prop key="username">root</prop>
<prop key="password">123456</prop>
</util:properties>
<bean id="dataSource1" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.MyDataSource1">
<property name="properties" ref="prop"/>
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource2" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.MyDataSource2">
<property name="properties" ref="prop"/>
</bean>
</beans>
4-7 基于 XML 的自动装配

Spring还可以完成自动化的注入,自动化注入又被称为自动装配。它可以根据名字进行自动装配,也可以根据类型进行自动装配。
4-7-1 根据名字进行自动装配
package com.powernode.spring6.dao;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className UserDao
* @since 1.0
**/
public class UserDao {
public void insert(){
System.out.println("正在保存用户数据。");
}
}
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import com.powernode.spring6.dao.UserDao;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className UserService
* @since 1.0
**/
public class UserService {
private UserDao aaa;
// 这个set方法非常关键
public void setAaa(UserDao aaa) {
this.aaa = aaa;
}
public void save(){
aaa.insert();
}
}
Spring的配置文件这样配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="userService" class="com.powernode.spring6.service.UserService" autowire="byName"/>
<bean id="aaa" class="com.powernode.spring6.dao.UserDao"/>
</beans>
这个配置起到关键作用:
- UserService Bean中需要添加autowire=“byName”,表示通过名称进行装配。
- UserService类中有一个UserDao属性,而UserDao属性的名字是aaa,对应的set方法是setAaa(),正好和UserDao Bean的id是一样的。这就是根据名称自动装配。
@Test
public void testAutowireByName(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-autowire.xml");
UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
userService.save();
}
4-7-2 根据类型进行自动装配
package com.powernode.spring6.dao;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className AccountDao
* @since 1.0
**/
public class AccountDao {
public void insert(){
System.out.println("正在保存账户信息");
}
}
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import com.powernode.spring6.dao.AccountDao;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className AccountService
* @since 1.0
**/
public class AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
public void save(){
accountDao.insert();
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--byType表示根据类型自动装配-->
<bean id="accountService" class="com.powernode.spring6.service.AccountService" autowire="byType"/>
<bean class="com.powernode.spring6.dao.AccountDao"/>
</beans>
4-8 Spring 引入外部属性配置文件
我们都知道编写数据源的时候是需要连接数据库的信息的,例如:driver url username password等信息。这些信息可以单独写到一个属性配置文件中吗,这样用户修改起来会更加的方便。当然可以。
1- 第一步:写一个数据源类,提供相关属性。
package com.powernode.spring6.beans;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLFeatureNotSupportedException;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className MyDataSource
* @since 1.0
**/
public class MyDataSource implements DataSource {
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyDataSource{" +
"driver='" + driver + '\'' +
", url='" + url + '\'' +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
private String driver;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
public void setDriver(String driver) {
this.driver = driver;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
//......
}
2-第二步:在类路径下新建jdbc.properties文件,并配置信息。
driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring
username=root
password=root123
3-第三步:在spring配置文件中引入context命名空间。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
</beans>
4-第四步:在spring中配置使用jdbc.properties文件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.powernode.spring6.beans.MyDataSource">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</bean>
</beans>























 783
783

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








