VUE
一.快速入门
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="ann">
<!-- 引入Vue 的数据 -->
{{name}}
</div>
</body>
<!-- 引入Vue文件 -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 绑定vue元素
new Vue({
el: "#ann",
data: {
name: 'zhangsai'
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
二.语法
插值表达式
- 获取Vue对象中的属性以及方法
- 获取数组中的内容
- 获取对象中的属性
- 三目运算
- 四则运算
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="a">
1. 获取Vue对象中的属性以及方法<br />
{{name}}<br />
{{hello()}}<br />
2. 获取数组中的内容<br />
{{shuzu[4]}}<br />
3. 获取对象中的属性<br />
{{student.name}}<br />
4. 三目运算<br />
{{1<0?'yes':'no'}}<br />
5. 四则运算<br />
{{1+2-1*4/1}}<br />
</div>
</body>
<!-- 引入Vue文件 -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 绑定vue元素
new Vue({
el: "#a",
data: {
student: {
name: 'zhanghaha',
age: 33
},//测试3
shuzu: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5], //测试数组
hello() {
return "hello"
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
条件判断
- v-if
- v-else
- v-else-if
几乎等同于Java的If-else
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="a">
<!-- 当Flag为True时,代表没钱,为False时代表有钱 -->
<p v-if="flag">我好穷!!!</p>
<!-- <p v-else="flag">我有钱了!</p> -->
<!--else-if 当前一个为false时,判断后一个,如果为true执行,如果不为true 不执行 -->
<p v-else-if="rich">有钱了,出去浪!</p>
<!-- 双向绑定,点击按钮,实现Flag取反 -->
<button @click="flag=!flag">彩票中奖!</button>
</div>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript">
new Vue({
el: "#a",
data: {
flag: true,
rich: true
}
})
</script>
</html>
-
v-show
V-show跟V-if的区别,
- 在切换true跟false的状态的时候,v-if是添加或者删除标签实现的
- v-show是通过Style的显示设置实现的,所以从效率上讲 V-show的效率更高
循环
- v-for
普通的For循环
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="a">
<ul>
<!-- 用法1 : 等同于for(int a :args){a} -->
<li v-for="a in args">{{a}}</li>
<hr />
<!-- 用法2: a为取出的元素,i循环的次数-->
<li v-for="(a,i) in args" :key="i">
{{i}} == {{a}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#a",
data: {
args: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
}
})
</script>
</html>
- 用for循环取出对象属性
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="a">
<ul>
<!-- v:值,k:键,i:序号 -->
<li v-for="(v,k,i) in stu">
序号:{{i}},键:{{k}}=值:{{v}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#a",
data: {
stu:{
name:'zhang',
age:12,
sex:'男'
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
- 遍历对象数组
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
<link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@3.3.7/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<!-- 获取对象数组 -->
<body>
<div id="a">
<table class="table table-hover" align="center" border="1px" >
<tr>
<th>序号</th>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>年龄</th>
<th>性别</th>
</tr>
<tr v-for="(stu,i) in students">
<td>{{i}}</td>
<td>{{stu.name}}</td>
<td>{{stu.age}}</td>
<td>{{stu.sex}}</td>
</tr>
</table>
<!-- 测试嵌套循环 -->
<ul v-for="stu in students">
<li v-for="(v,k,i) in stu">
{{i}}:{{k}}:{{v}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<!-- jQuery (Bootstrap 的所有 JavaScript 插件都依赖 jQuery,所以必须放在前边) -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/jquery@1.12.4/dist/jquery.min.js"></script>
<!-- 加载 Bootstrap 的所有 JavaScript 插件。你也可以根据需要只加载单个插件。 -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@3.3.7/dist/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#a",
data: {
students: [{
name: '张三',
age: 11,
sex: '男'
},
{
name: '李四',
age: 11,
sex: '女'
},
{
name: '王五',
age: 11,
sex: '男'
}
]
}
})
</script>
</html>
三.属性绑定
- 简单的属性绑定
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 简单的属性绑定 -->
<div id="a">
<input type="text" v-model="title"/>{{title}}
</div>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#a",
data:{
title:'测试'
}
})
</script>
</html>
- 为标签的属性绑定Vue的值
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 简单的属性绑定 -->
<div id="a">
<input type="text" v-model="title"/>{{title}}
<!-- 在标签的属性内部不能使用插值表达式来填充进去数据,但是可以使用v-bind把数据绑定到该属性上 -->
<a v-bind:href="link">百度</a>
<!-- 也可以直接写个冒号,不写V-bind -->
<a :href="link">省略V-bind,百度</a>
</div>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#a",
data:{
title:'测试',
link:"http://www.baidu.com"
}
})
</script>
</html>
四.事件绑定
关于事件,需要把握好三个步骤: 设参,传参,和接参
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="a">
当前年龄:{{age}}
<hr />
<!-- @click => v-on:click -->
<!-- 设参 -->
<button type="button" @click="guonian(2)">过年</button>
</div>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#a",
data:{
age:1,
yeal:1
},
methods:{
// 传参
guonian:function(y){
// 接参
this.age+=y
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
扩展
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="a">
当前年龄:{{age}}
<hr />
<!-- @click => v-on:click -->
<button type="button" @click="guonian()">过年</button>
<hr />
<!-- 让用户自定义yeal的值 -->
过几年:<input type="text" v-model="yeal" />
</div>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#a",
data:{
age:1,
yeal:1
},
methods:{
guonian:function(){
// 从视图层接受到的数据是字符串格式,需要转化为数字格式
this.age+=(this.yeal-0);
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
事件修饰符:
.stop:等同于JavaScript中的event.stopPropagation(),防止事件冒泡.prevent:等同于JavaScript中的event.preventDefault(),防止执行预设的行为(如果事件可取消,则取消该事件,而不停止事件的进一步传播).capture:与事件冒泡的方向相反,事件捕获由外到内.self:只会触发自己范围内的事件,不包含子元素.once:只会触发一次
计算属性:Computed
- 简单理解,计算属性本质上是一个属性,他是把一个方法的计算结果缓存起来,作为一个Vue对象的属性来使用,这样做的好处是,减少了每次计算的运算成本,如果一个属性不经常会发生变化,就可以用这个计算属性
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="a">
{{getData()}}
{{getData2}}
</div>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var v1 = new Vue({
el: "#a",
data: {
},
methods: {
//普通方法,每次执行都将重新执行计算
getData: function() {
return Date.now();
}
},
//计算属性,把方法的返回值存为一个属性,只计算一次
computed: {
getData2: function() {
return Date.now();
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
五.Vue的组件化
1.组件的全局注册
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="a">
<!-- 使用组件 -->
<model1></model1>
</div>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
/*
参数1:组件名称
参数2:具体组件的内容
*/
Vue.component("model1", {
// 模板:就是当前组件实际的内容,并且一个组件只能包含一个根标签
template: "<div><p>{{text}}</p><input type='text' v-model='text'></input><a href='http://www.baidu.com' @click='afn()'>百度链接</a></div>",
//data必须要使用以方法的返回值的方式返回数据
data: function() {
return {
text: '测试'
}
},
// 当前组件的方法
methods: {
afn: function() {
alert("即将跳转到百度...");
}
},
//当前组件的计算属性
components:{
}
})
//使用该组件必须要先绑定一个Vue对象
new Vue({
el: "#a"
})
</script>
</html>
2.组件的本地注册
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="a">
<model1></model1>
</div>
<hr />
<div id="a1">
<model1></model1>
</div>
</body>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
new Vue({
el: "#a",
//定义本地化组件,只在当前Vue绑定的对象中有效,其他Vue绑定的元素使用无效
components: {
'model1': {
template: "<div><p>{{text}}</p><input type='text' v-model='text'></input><a href='http://www.baidu.com' @click='afn()'>百度链接</a></div>",
data: function() {
return {
text: '测试'
}
},
// 当前组件的方法
methods: {
afn: function() {
alert("即将跳转到百度...");
}
},
//当前组件的计算属性
components: {},
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
3.组件的生命周期
现在先做下一了解即可
创建一个组件之后,会在不同阶段调取钩子函数
六.使用Vue-Cli搭建Vue项目
1.什么是Vue-cli
Cli 是Vue的命令行工具,使用Vue提供的各种命令,可以拉取创建运行我们需要是用到的框架,
使用Vue-Cli需要先安装node.js
2.安装Node.js
node.js提供了前端程序的运行环境,可以把node.js理解成运行前端程序的服务器
直接在官网下载安装即可
https://nodejs.org/zh-cn/download/
测试是否安装成功
node -v
3.使用Node.js安装Vue-cli
npm install -g cnpm --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org # 替换成淘宝的镜像
cnpm install vue-cli -g # 安装Vue-cli
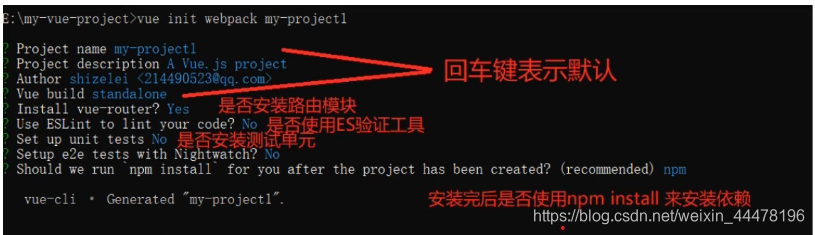
4.使用Vue-Cli下载项目骨架搭建项目
vue list # 列出支持的框架
先创建项目目录
mkdir myVue #创建?myVue目录 cd myVue #进入目录 vue init webpack myVueDemo1 #使用Webpack创建一个项目名为MyVueDemo1的项目 #执行完成之后 cd myVue #进入项目目录 npm run dev #以开发模式执行
5.目录结构
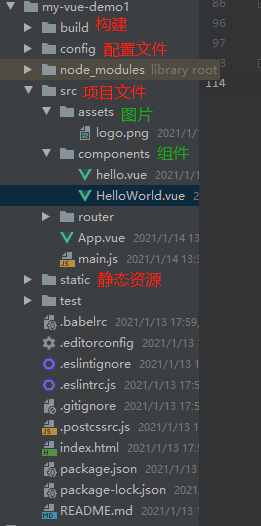
七.Vue组件之间的传递
参数传递:
1,如何在App.vue中使用子组件
创建子组件
<template> <div>我是一个子组件,Hello,Vue !!!</div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'hello' } </script> <style scoped> </style>把组件注册到Main.js
import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App' import router from './router' //导入组件 import hello from './components/hello' Vue.config.productionTip = false //定义全局组件 Vue.component(hello) /* eslint-disable no-new */ new Vue({ el: '#app', router, components: { App }, template: '<App/>' })在App.vue中使用组件
<template> <div id="app"> <!-- 使用组件--> <hello></hello> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'App' } </script> <style> #app { font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; -webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; -moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale; text-align: center; color: #2c3e50; margin-top: 60px; } </style>
2.子组件如何接受父组件的传参
1.在子组件中添加一个属性:props然后再其中写上需要接受的参数类型,如数组,对象等
<template> <div>我是一个子组件,Hello,Vue !!! <hr/> <a href="www.baidu.com">百度</a> {{MyTitle}} </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'Hello', // 数组类型传参 // props: ['MyTitle'] props: { // 对象类型传参 MyTitle: { // 类型为String type: String, // 是否必须传参 required: true, // 默认值 default: '没有接受到传参' } } } </script> <style scoped> </style>2.在App.vue中传入参数
<template> <div id="app"> <!-- 使用组件--> <!-- 传入子组件的my-title的值--> <Hello :my-title="msg"></Hello> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: 'App', data () { return { // 设置值 msg: 'you good!' } } } </script> <style> #app { font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; -webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; -moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale; text-align: center; color: #2c3e50; margin-top: 60px; } </style>
3.子组件如何传递参数给到父组件
- 子组件中设置一个返回对象为方法属性传参
<script> export default { name: 'Hello', props: { 'btnfun': { 'type': Function } }
- 在模板中添加一个按钮,设置点击事件为此方法,并传递参数
<button @click="btnfun('这是传到父组件的数据')"> 点我体验子传父</button>
- 在父组件中,设置方法
methods:{ fun: function (m) { this.msg = m; } }
- 并且父组件中使用子组件时,指定子组件调用的方法为fun()
<Hello :MyTitle="msg" :btnfun="fun"></Hello>以上,当点击子组件的按钮时,子组件中的方法参数会被传入父组件中对应的方法中,并改变父组件中,msg的值,以改变页面的显示内容
事件传递:
举例:点击事件,子组件中的按钮的点击事件需要更改来自父组件传递过来的参数
- 在父组件中引用子组件时,需要自定义一个@属性,然后引向父组件中一个方法
<template> <div id="app"> <!-- 使用子组件,自定义增加和删除的方法--> <zizujian :num="shuzi" @incr="addnum" @decr="del"></zizujian> </div> </template> <script> import Zizujian from "./components/Zizujian"; export default { name: 'App', components: {Zizujian}, data() { return { shuzi: 1 } }, //定义增加和删除的方法 methods: { addnum() { this.shuzi++; }, del() { this.shuzi-- } } } </script> <style> #app { font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif; -webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; -moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale; text-align: center; color: #2c3e50; margin-top: 60px; } </style>
在子组件中,需要编写按钮,并指定点击事件触发的方法
八.路由
路由(Vue Router)是Vue的官方的路由管理器,使页面构建更加简单
路由:是一种映射关系,是 “path =>组件”的映射
路由器:管理路由的,在路由器里配置路由
1.基础使用
.1.先创建两个组件
<!--Home组件 --> <template> <div>首页</div> </template> <script> export default { name: "Home" } </script> <style scoped> </style><!--Product组件 --> <template> <div>商品列表:商品ID:{{id}}</div> </template> <script> export default { name: "Product", data(){ return{ id:this.$route.params.id } } } </script> <style scoped> </style>2.绑定路由规则
import Vue from 'vue' import Router from 'vue-router' import Home from "../components/Home"; Vue.use(Router) export default new Router({ routes: [ { path: '/Home', component: Home //启动时加载 }, { path: '/Product/:id', component: () => import("../components/Product") //应用时加载 } ] })3.在App.vue中使用路由
<template> <div id="app"> <ul class="nav nav-tabs"> <!-- <router-link>标签的作用可以理解为把这个变成一个a标签,然后经过路由在view标签内展示对应的组件--> <oi role="presentation" class="active"><router-link to="/Home">首页</router-link></oi> <oi role="presentation"><router-link to="/Product/3"> 商品列表</router-link></oi> </ul> <!-- 此标签的作用是展示被路由的组件--> <router-view/> </div> </template>
2.路由的参数传递
设参
设定路由规则时,指定后面携带的参数
{ //:id就是后面应该携带的参数名字 path: '/Product/:id', component: () => import("../components/Product") }传参
在实现路由跳转时,给定参数
<oi role="presentation"><router-link to="/Product/3"> 商品列表</router-link></oi>接参
接受来自路由传递过来的参数的值
<script> export default { name: "Product", data(){ return{ // 设置id为当前路由对象传过来的名为ID的参数的值 id:this.$route.params.id } } } </script>
3.程序式路由
methods:{
btnfn:function () { //设定按钮点击方法,实现路由
this.$router.push("/Product/9999")
}
}
九.使用Axios发送请求
Axios的作用可以等同于AJAX,可以在浏览器中个实现异步向后端服务器发送请求
1.Axiox的使用
安装Axiox
npm install --save axios vue-axios在main.js 中引用
import axios from "axios"; import VueAxios from "vue-axios"; Vue.use(VueAxios,axios)发送Axios
//使用get请求向后端发送axios registfn() { this.axios({ method: 'get', url: "http://localhost:8080/sMVC01_war_exploded/regist?name=" + this.name + "&password=" + this.password }).then(function (resp) { console(resp) }) },//使用Post请求发送axios
registfn() {
this.axios({
method: “post”,
url: “http://localhost:8080/sMVC01_war_exploded/regist”,
data: {
name: this.name,
password: this.password
}
}).then(function (resp) {
console.log(resp)
})
注意:解决MVC的跨域问题:
<mvc:cors>
<mvc:mapping path="/**"
allowed-origins="*"
allowed-methods="POST,GET,OPTIONS,DELETE,PUT,PATCH"
allowed-headers="Content-Type,Access-Control-Allow-Headers,Authorization,X-Requested-With"
allow-credentials="true"/>
</mvc:cors>
解决SpringBoot的跨域问题:
@CrossOrigin(origins = "http://localhost:8080", maxAge = 3600) //接受来自Localhost:8080的请求,加在Controller 或者对应的方法上
十.Axios实现简单的前后端交互
- 前端做一个登录页面
<template>
<!-- login-box指定样式-->
<div class="login-box">
<!-- 登录表单-->
<el-form ref="form" :rules="rules" :model="form" label-width="80px">
<h3>欢迎登录</h3>
<!-- 用户名-->
<el-form-item label="用户名:" prop="name">
<el-input v-model="form.name"></el-input>
</el-form-item>
<!-- 密码-->
<el-form-item label="密码:" prop="password">
<el-input type="password" v-model="form.password"></el-input>
</el-form-item>
<!-- 表单提交按钮-->
<el-form-item>
<el-button type="primary" @click="submitForm('form')">登录</el-button>
</el-form-item>
</el-form>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "login",
//数据
data() {
return {
//表单数据
form: {
name: "",
password: ""
},
//表单验证
rules: {
name: [
{required: true, message: '请输入用户名', trigger: 'blur'},
{min: 5, max: 20, message: '长度为5-20个字符', trigger: 'blur'}
],
password: [
{required: true, message: '请输入密码', trigger: 'blur'},
{min: 8, max: 20, message: '长度为8-20个字符', trigger: 'blur'}
]
}
}
},
//方法
methods: {
//提交方法
submitForm(formName) {
var vm = this
//检测当前表单是否有未填的数据项
this.$refs[formName].validate((valid) => {
if (valid) {
//都填好了则使用Axios发送到后台进行验证
this.axios({
method: "post",
url: "http://localhost:8081/login",
data: {
name: vm.form.name,
password: vm.form.password
}
// 验证成功则执行这里的操作
}).then(function (resp) {
console.log(resp.data)
if (resp.data == "ok") {
vm.$alert('登录成功,即将跳转到首页', '提示', {
confirmButtonText: '确定',
callback: action => {
//点击确定跳转到Home
vm.$router.push("/Home")
}
})
// 验证失败,则执行这里的操作
} else {
vm.$message.error('用户名或密码错误');
}
})
//如果用户名或密码没填完 则执行这里
} else {
this.$message.error('请检查用户名或密码');
return false;
}
});
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.login-box {
width: 500px;
height: 300px;
border: #DCDFE6 1px solid;
border-radius: 20px;
box-shadow: 0 2px 4px rgba(0, 0, 0, .12), 0 0 6px rgba(0, 0, 0, .04);
margin: 150px auto;
padding: 20px 50px 30px 20px;
}
</style>
- 创建后端Controller
@CrossOrigin(origins = "http://localhost:8080", maxAge = 3600) //使用此注解以解决跨域问题
@RestController
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/login", method = RequestMethod.POST)
// 封装RequestBody 为一个对象
public String Login(@RequestBody LoginUser lu) {
if ("admin".equals(lu.getName()) && "password".equals(lu.getPassword())) {
return "ok"; //验证成功返回ok
}
return "用户名或密码错误"; //验证失败返回"用户名密码错误
}
}
十一.Vuex
1.安装Vuex
在根目录下使用命令安装Vuex
cnpm install vuex --save
修改
main.js,导入Vuex
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
创建store.index.js
import Vue from "vue"
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex);
//创建全局的state对象,用于保存所有组件的公共数据
const state = sessionStorage.getItem('state') ? JSON.parse(sessionStorage.getItem('state')) : {
//定义一个uesr对象
//在组件中是通过this.$state.user 来获取
user: {
name: ''
}
};
//实时监听state值得最新状态,注意这里的getters可以理解为计算属性
const getters = {
//在组件中是通过 this.$store.getters.getUser来获取
getUser(state) {
return state.user;
}
};
//定义改变state初始值的方法,这里是唯一可以改变state的地方,缺点是只能同步执行
const mutations = {
updateUser(state, user) {
state.user = user;
}
};
//定义触发(mutations)函数的方法,可以异步执行mutations里的函数
const actions = {
//在组件中通过 this.$store.dispatch('asyncUpdateUser',user)来调用函数
asyncUpdateUser(context, user) {
context.commit('updateUser', user);
}
};
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
getters,
mutations,
actions
})
2.使用Vuex
组件往state中存值
vm.$store.dispatch('asyncUpdateUser', user); //往state中存值
组件从state中取值
user: this.$store.getters.getUser
3.解决刷新即失效的问题
//为页面添加监听器,监听刷新动作,在刷新之前,把state存入浏览器的sessionStorage
//为app.vue添加
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
mounted() {
window.addEventListener('unload', this.saveState)
},
methods: {
saveState() {
sessionStorage.setItem('state', JSON.stringify(this.$store.state))
}
}
}
</script>
N.parse(sessionStorage.getItem(‘state’)) : {
//定义一个uesr对象
//在组件中是通过this.$state.user 来获取
user: {
name: ‘’
}
};
//实时监听state值得最新状态,注意这里的getters可以理解为计算属性
const getters = {
//在组件中是通过 this.$store.getters.getUser来获取
getUser(state) {
return state.user;
}
};
//定义改变state初始值的方法,这里是唯一可以改变state的地方,缺点是只能同步执行
const mutations = {
updateUser(state, user) {
state.user = user;
}
};
//定义触发(mutations)函数的方法,可以异步执行mutations里的函数
const actions = {
//在组件中通过 this.$store.dispatch(‘asyncUpdateUser’,user)来调用函数
asyncUpdateUser(context, user) {
context.commit(‘updateUser’, user);
}
};
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
getters,
mutations,
actions
})
### 2.使用Vuex
> 组件往state中存值
>
> ```js
> vm.$store.dispatch('asyncUpdateUser', user); //往state中存值
> ```
> 组件从state中取值
>
> ```js
> user: this.$store.getters.getUser
> ```
### 3.解决刷新即失效的问题
```js
//为页面添加监听器,监听刷新动作,在刷新之前,把state存入浏览器的sessionStorage
//为app.vue添加
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
mounted() {
window.addEventListener('unload', this.saveState)
},
methods: {
saveState() {
sessionStorage.setItem('state', JSON.stringify(this.$store.state))
}
}
}
</script>





















 144
144











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








