一、排序
资料:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_72499901/article/details/136592073
正排序
import java.util.Arrays;
public class SortArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] citations = {5, 3, 8, 2, 1, 4};
// 打印原数组
System.out.println("原数组: " + Arrays.toString(citations));
// 使用 Arrays.sort() 进行排序
Arrays.sort(citations);
// 打印排序后的数组
System.out.println("排序后的数组: " + Arrays.toString(citations));
}
}
降序排序
这个只能处理包装,处理Integer,不能处理int
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] citations = {5, 3, 8, 2, 1, 4};
// 打印原数组
System.out.println("原数组: " + Arrays.toString(citations));
// 使用 Arrays.sort() 进行降序排序
Arrays.sort(citations, Collections.reverseOrder());
// 打印排序后的数组
System.out.println("排序后的数组: " + Arrays.toString(citations));
}
处理数组
Integer[] arr = {5,4,7,9,2,12,54,21,1};
//降序
Arrays.sort(arr, new Comparator<Integer>() {
//重写compare方法,最好加注解,不加也没事
public int compare(Integer a, Integer b) {
//返回值>0交换
return b-a;
}
});
二、初始化
自己对于列表,数组的初始化还是不太熟悉
1. 数组的初始化
int[] a = {1,2,3,4};
2. Java List的初始化
用数组初始化List
Integer [] a = {1,2,34};
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(a);
list.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
直接初始化
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4));
list.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
数组增加在指定位置
List<Integer> list= new LinkedList<>(Arrays.asList(1,3,4));
list.add(2,5);
list.stream().forEach(System.out::println);
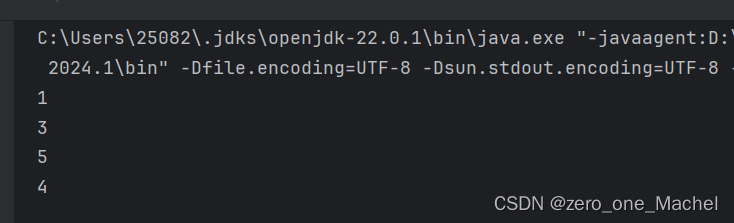
3. 数组转为List
citations 是int数组
List<Integer> citationList = IntStream.of(citations)
.boxed()
.toList();
切片
数组的切片
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[]{1,2,3,4};
int[] subArr = Arrays.copyOfRange(arr,1,3);//左闭右开
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(subArr));
}
String切片
public static void main(String[] args) {
String test_string = "12345";
test_string = test_string.substring(1, 4);
System.out.println(test_string);
}
List切片
List<Integer> test_list = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5));
System.out.println(test_list.subList(1,3));
Java stream语法
int[][] intervals = {
{1, 3},
{2, 4},
{5, 7},
{6, 8}
};
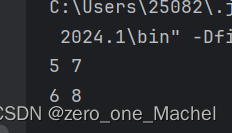
Arrays.stream(intervals).skip(2).limit(2).forEach(a -> System.out.println(a[0] +" "+ a[1]));
skip 就是跳过前两个,limit 表示只输出两个,所以输出的是
数据结构
1. queue
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<String>();
//添加元素
queue.offer("a");
queue.poll() // 删除并返回
queue.peek()//只返回

https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/1252599548343744/1265121791832960
https://www.runoob.com/java/data-queue.html
2. stack
压入元素 (push):
弹出元素 (pop):从栈顶移除并返回元素。
查看栈顶元素 (peek):查看栈顶元素但不移除它。
查找元素 (search):
import java.util.Stack;
public class StackExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个 Stack
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
// 压入元素
stack.push(10);
stack.push(20);
stack.push(30);
System.out.println("Stack after pushing: " + stack);
// 查看栈顶元素
System.out.println("Top element is: " + stack.peek());
// 弹出元素
System.out.println("Popped element: " + stack.pop());
System.out.println("Stack after popping: " + stack);
// 查找元素
int position = stack.search(10);
if (position != -1) {
System.out.println("Element 10 found at position: " + position);
} else {
System.out.println("Element 10 not found.");
}
// 检查是否为空
System.out.println("Is stack empty? " + stack.isEmpty());
}
}
stack 转化list
List list = stack.stream().toList();
stack 循环
Iterator<Integer> iterator = stack.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(iterator.next() + " ");
}
数学
- 平方
double pow = Math.pow(2, 3); // 2的3次方
输入输出
public class PrintfExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double number = 123.456789;
// 控制小数位数为2位
System.out.printf("Formatted number: %.2f%n", number); // 输出: Formatted number: 123.46
// 控制小数位数为4位
System.out.printf("Formatted number: %.4f%n", number); // 输出: Formatted number: 123.4568
}
}
读取时空格
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNextInt()){
int a = scanner.nextInt();
int b = scanner.nextInt();
String str = scanner.nextLine(); // 现在可以正确读取下一行的字符串了
System.out.println(a + b);
System.out.println(str);
}
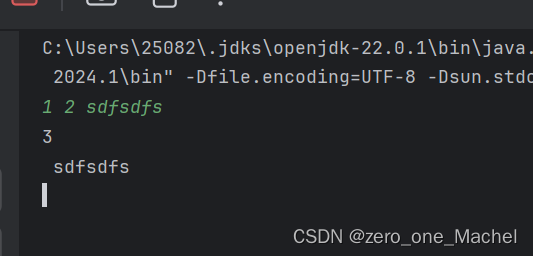
或者 需要多加一个nextLine 读取换行






















 924
924











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








