第三章:使用 Vue 脚手架
3.1 初识脚手架
3.1.1 说明
1. Vue 脚手架是 Vue 官方提供的标准化开发工具(开发平台)
2. 最新版本 5.x (尚硅谷教程里的是 4.x,另外现在官网 Vue CLI 处于维护模式)
3. 文档:https://cli.vuejs.org/zh/
3.1.2 具体步骤
- 第一步:全局安装 @vue/cli(仅第一次执行)
npm install -g @vue/cli- 第二步:切换到你要创建项目的目录,然后使用命令创建项目
vue create xxxx // xxx 是项目的名称,注意尽可能回避主流库的名字执行完后,会出现代码执行选择 Vue 的版本:分别是 Vue 2 和 Vue 3,以及自定义选择

项目创建好会出现的界面是:

- 第三步:启动项目
npm run serve【注】
■ 在进行全局安装之前,必须要先配置 npm 淘宝镜像:
npm config set registry https://registry.npm.taobao.org/如果没配置好,会出现下载缓慢甚至中断的情况 !
■ 若全局安装过程出现以下情况,请以管理员身份运行 cmd (博主当时安装时就一直出现这个问题,后面以管理员身份运行 cmd ,才成功进行了全局安装)

■ Vue 脚手架隐藏了所有 webpack 相关的配置,若想查看具体的 webpack 配置,请执行:
vue inspect > output.js
(上面的代码在 VSCode 终端上执行,其作用是把 Vue 脚手架默认的配置整理成 .js 文件)
■ 暂停项目的快捷键:Ctrl + C
3.1.3 分析脚手架(项目)的结构
脚手架文件结构
├── node_modules
├── public
│ ├── favicon.ico: 页签图标
│ └── index.html: 主页面
├── src
│ ├── assets: 存放静态资源
│ │ └── logo.png
│ │── component: 存放组件
│ │ └── HelloWorld.vue
│ │── App.vue: 汇总所有组件
│ │── main.js: 入口文件
├── .gitignore: git版本管制忽略的配置
├── babel.config.js: babel的配置文件
├── package.json: 应用包配置文件
├── README.md: 应用描述文件
├── package-lock.json:包版本控制文件
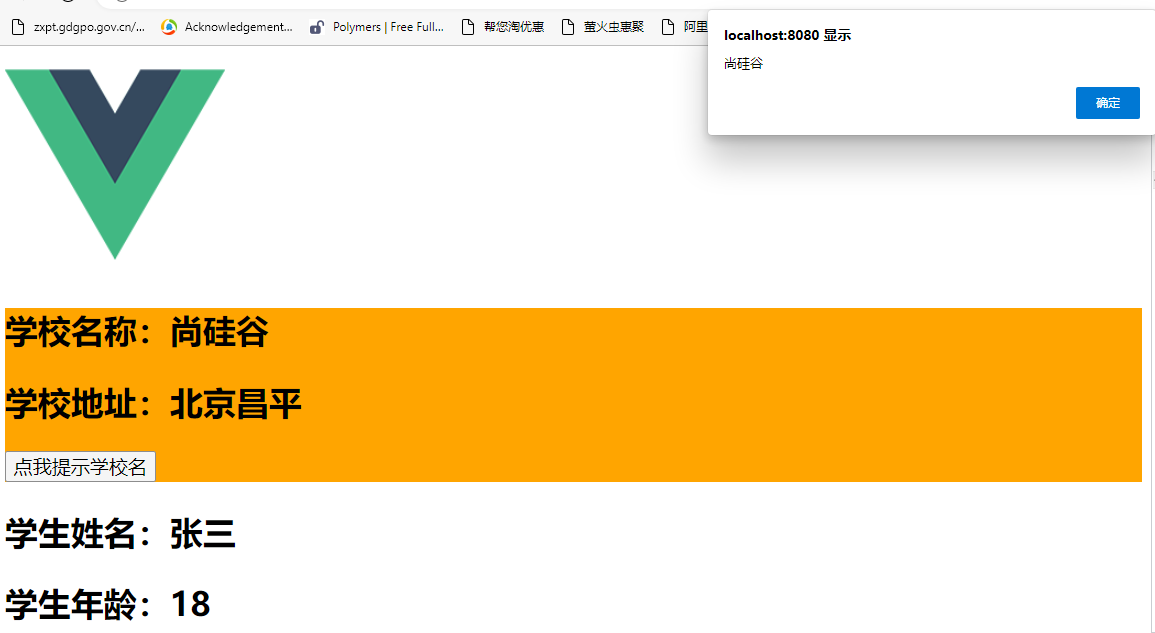
- src/components/School.vue
<template>
<div class="demo">
<h2>学校名称:{
{ name }}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{
{ address }}</h2>
<button @click="showName">点我提示学校名</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "School",
data() {
return {
name: "尚硅谷",
address: "北京昌平",
}
},
methods: {
showName() {
alert(this.name)
},
},
}
</script>
<style>
.demo {
background-color: orange;
}
</style>
- src/components/Student.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>学生姓名:{
{ name }}</h2>
<h2>学生年龄:{
{ age }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Student",
data() {
return {
name: "张三",
age: 18,
}
},
}
</script>
- src/App.vue
<template>
<div>
<img src="./assets/logo.png" alt="logo" />
<School></School>
<Student></Student>
</div>
</template>
<script>
//引入组件
import School from "./components/School"
import Student from "./components/Student"
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
School,
Student,
},
}
</script>
- src/main.js
/*
该文件是整个项目的入口文件
*/
// 引入vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入APP,它是所有组件的父组件
import App from './App.vue'
// 关闭vue的生产提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false
// 创建vue实例对象---vm
new Vue({
// el: '#app',
// 下面一行代码完成的功能是:将App组件放入容器中
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app') // 等同于在12行代码下面放 el:'#app',
// })- public/index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<!-- 针对IE浏览器的一个特殊配置,含义是让IE浏览器以最高的渲染级别渲染页面 -->
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<!-- 开启移动端的理想视口 -->
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0">
<!-- 配置页签图标 -->
<link rel="icon" href="<%= BASE_URL %>favicon.ico">
<!-- 配置网页标题 -->
<title>
<%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title %>
</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 当浏览器不支持js时 ,noscript中的元素就会被渲染 -->
<noscript>
<strong>We're sorry but <%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title %> doesn't work properly without JavaScript enabled.
Please enable it to continue.</strong>
</noscript>
<!-- 容器 -->
<div id="app"></div>
<!-- built files will be auto injected -->
</body>
</html>效果:
3.1.4 render 函数
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
// render函数完成了这个功能:将App组件放入容器中
// 简写形式
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app') // 相当于(el:'#app')
// 完整形式
// render(createElement){
// return createElement(App)
// }
/* --------------------------------------------*/
/* new Vue({
el:'#app'
// render函数完成了这个功能:将App组件放入容器中
// 简写形式
render: h => h(App),
})
// 完整形式
// render(createElement){
// return createElement(App)
// }
*/
总结:
关于不同版本的 Vue
1. vue.js 与 vue.runtime.xxx.js 的区别:
(1). vue.js 是完整版的 Vue,包含:核心功能+模板解析器。
(2). vue.runtime.xxx.js 是运行版的 Vue,只包含:核心功能;没有模板解析器。
2. 因为 vue.runtime.xxx.js 没有模板解析器,所以不能使用 template 配置项,需要使用 render 函数接收到的 createElement 函数去指定具体内容。
3.1.5 修改默认配置
vue.config.js是一个可选的配置文件,如果项目的 (和package.json同级的) 根目录中存在这个文件,那么它会被@vue/cli-service自动加载。也可以使用package.json中的vue字段,但是注意这种写法需要你严格遵照 JSON 的格式。- 使用 vue inspect > output.js 可以查看到 vue 脚手架的默认配置。
- 使用 vue.config.js 可以对脚手架进行个性化定制,详情见:配置参考 | Vue CLI。
vue.config.js:↓ ↓ ↓
module.exports ={ // →CommonJS 是 node.js 默认的模块化方案
pages: {
index: {
// page 的入口
entry: 'src/main.js',
},
/* 当使用只有入口的字符串格式时,
模板会被推导为 `public/subpage.html`
并且如果找不到的话,就回退到 `public/index.html`。
输出文件名会被推导为 `subpage.html`。
subpage: 'src/subpage/main.js'
*/
},
lintOnSave: false // 关闭语法检查
}【注】若修改了 vue.config.js ,终端必须重新 npm run serve !!!
3.2 ref 属性
- src/main.js
// 引入 vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入App
import App from './App.vue'
// 关闭Vue的生产提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false
//创建vm
new Vue({
el: '#app',
render: h => h(App)
})- src/components/School.vue
<template>
<div class="school">
<h2>学校名称:{
{name}}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{
{address}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'School',
data() {
return {
name: '尚硅谷',
address:'北京昌平'
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
.school{
background-color: gray;
}
</style>- src/App.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1 v-text="msg" ref="title"></h1>
<button ref="btn" @click="showDOM">点我输出上方的DOM元素</button>
<School ref="sch"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 引入School组件
import School from './components/School'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: { School },
data() {
return {
msg:'欢迎学习Vue!'
}
},
methods: {
showDOM() {
console.log(this.$refs.title) // 真实DOM元素
console.log(this.$refs.btn) // 真实DOM元素
console.log(this.$refs.sch) // School组件的实例对象
}
}
}
</script>效果:

总结:
ref 属性
1. 被用来给元素或子组件注册引用信息(id 的替代者)
2. 应用在 html 标签上获取的是真实 DOM 元素,应用在组件标签上是组件实例对象(vc)
3. 使用方式:
♦ 打标识:<h1 ref = "xxx">……</h1> 或 <School ref = "xxx"></School>
♦ 获取:this.$refs.xxx
3.3 props 配置项
- src/components/Student.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>{
{msg}}</h1>
<h2>学生姓名:{
{name}}</h2>
<h2>学生性别:{
{sex}}</h2>
<h2>学生年龄:{
{myAge+1}}</h2>
<button @click="updateAge">尝试修改收到的年龄</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'Student',
data() {
console.log(this);
return {
msg: '我是一个尚硅谷的学生',
myAge:this.age
}
},
methods: {
updateAge() {
this.myAge++
}
},
// 简单声明接收
props:['name','age','sex']
// 接收的同时对数据进行类型限制
/* props: {
name: String,
age: Number,
sex:String
}
*/
// 接收的同时对数据进行类型限制+默认值的指定+必要性的限制(最完整的写法)
// props: {
// name: {
// type: String, //name 的类型是字符串
// required:true // name 是必要的
// },
// age: {
// type: Number,
// default:99 // 默认值
// },
// sex: {
// type: String, //sex 的类型是字符串
// required:true
// }
// }
}
</script>- src/App.vue
<template>
<div>
<Student name= "李四" sex= "女" :age="18" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Student from './components/Student'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: { Student }
}
</script>效果:

总结:
props 配置项:
1. 功能:让组件接收外部传过来的数据
2. 传递数据:<Demo name = "xxx"/>
3. 接收数据:
◑ 第一种方式(只接收):props:['name']
◑ 第二种方式(限制类型):props:{name:String}
◑ 第三种方式(限制类型、限制必要性、指定默认值):
props:{
name:{
type:String, //类型
required:true, //必要性
default:'老王' //默认值
}
}【备注】props 是只读的,Vue 底层会监测你对 props 的修改,如果进行了修改,就会发出警告,若业务需求确实需要修改,那么请复制 props 的内容到 data 中一份,然后去修改 data 中的数据。
3.4 mixin 混入
局部混入
- src/mixin.js
export const hunhe = {
methods: {
showName() {
alert(this.name)
}
},
mounted() {
console.log('你好啊!')
},
}- src/main.js
// 引入 vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入App
import App from './App.vue'
// 关闭Vue的生产提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false
//创建vm
new Vue({
el: '#app',
render: h => h(App)
})- src/components/School.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2 @click="showName">学校名称:{
{name}}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{
{address}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 引入一个hunhe
import { hunhe} from '../mixin'
export default {
name:'School',
data() {
return {
name: '尚硅谷',
address:'北京'
}
},
mixins:[hunhe]
}
</script>-
src/components/Student.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2 @click="showName">学生姓名:{
{name}}</h2>
<h2>学生性别:{
{sex}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 引入一个hunhe
import { hunhe} from '../mixin'
export default {
name:'Student',
data() {
return {
name: '张三',
sex:'男'
}
},
mixins:[hunhe]
}
</script>- src/App.vue
<template>
<div>
<School/>
<hr>
<Student/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import School from './components/School'
import Student from './components/Student'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: { School,Student }
}
</script>效果:

全局混入
除 App.vue 和 mixin.js 不变,其他稍作修改:
- src/main.js
// 引入 vue
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入App
import App from './App.vue'
import {hunhe} from './mixin'
// 关闭Vue的生产提示
Vue.config.productionTip = false
Vue.mixin(hunhe) // 所有的 vm 和 vc 都会得到 hunhe
//创建vm
new Vue({
el: '#app',
render: h => h(App)
})- src/components/School.vue





 本文详细介绍了使用Vue脚手架进行项目开发的过程,包括脚手架的安装、项目结构分析、render函数、配置修改、ref属性、props配置、mixin混入、插件、scoped样式、Todo-list案例、浏览器本地存储、自定义事件、全局事件总线、消息订阅与发布,以及Vue封装的过渡和动画。内容覆盖Vue2.0和Vue3.0,适合前端开发者学习进阶。
本文详细介绍了使用Vue脚手架进行项目开发的过程,包括脚手架的安装、项目结构分析、render函数、配置修改、ref属性、props配置、mixin混入、插件、scoped样式、Todo-list案例、浏览器本地存储、自定义事件、全局事件总线、消息订阅与发布,以及Vue封装的过渡和动画。内容覆盖Vue2.0和Vue3.0,适合前端开发者学习进阶。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 3536
3536

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








