1、复杂度
常见的时间复杂度 :
O(1) ->HashMap
O(logn) -> 二叉树
O(n) -> for 循环
O(nlogn) -> for 循环嵌套二叉树
O(n2) -> for 循环嵌套for 循环
常见的空间复杂度
O(1) ->int number=1
O(n) -> int[n]
O(n^2) -> int[n][n]
2、数组
数组:插入因为插入需要将插入位置后面的数据往后挪,删除就是往前挪,寻找如果是按下标直接为O(1),如果按内容的话则平均为时间复杂度为O(n)

3、链表
可以由拥有值和下一个节点的Node对象去构成链表

LRU缓存算法的实现

双向链表
Node对象中需要多一个prev的节点指向上一个节点
如果建立在不查询的基础上,知道上一个节点,去删除/插入一个节点,单向链表的时间复杂度可以是O(1),但往往单向链表只知道下一个节点,所以加上查询,总的时间复杂度会是O(n)
而双向链表可以解决该问题,因为它可以知道上一个节点和下个节点,将上个节点和下个节点进行连接修改,插入/删除的时间复杂度会变为O(1);

翻转链表-1
题目:将单向链表进行翻转
思路:以三个为单位进行变化,首先第一个指向null,把第二个存起来,将第二个的next指向第一个,然后第三个存起来,将第三个的指向第二个,依次进行
public class ReverseLinkedList{
public Node reverseLinkedList(Node node){
if(node==null){
return node;
}
//上一个节点
Node prev=null;
//当前节点
Node cur=node;
//下一个节点
Node next=node.next;
while(next!=null){
cur.next=prev;
prev=cur;
cur=next;
next=next.next;
}
cur.next=prev;
return cur;
}
}
public class Node{
int value;
Node next;
public Node(int value){
this.value=value;
}
}
翻转链表-2
题目将第n和第m之间
思路:首先得把第n个Node和第m个Node取出来,还有nNode的上一个Node,mNode的下一个Node,取出来后再进行中间部分的翻转。
public class ReverseLinkedList{
public Node reverseLinkedList(Node node,int m,int n){
if(node==null || m>=n){
return node;
}
//返回用的起始节点
Node head=new Node(-1);
head.next=node;
//获取mNode和其前一个
Node mNode=node;
Node prevNode=head;
for(int i=1;i<m;i++){
prevNode=prevNode.next;
mNode=mNode.next;
}
//获取nNode和其后一个
Node nNode=node;
Node postNode=node.next;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
nNode=nNode.next;
postNode=postNode.next;
}
//用来调换顺序的数据
Node cur=mNode.next;
Node prev=mNode;
Node next=cur.next;
//最前和最后的指向调换
prevNode.next=nNode;
mNode.next=postNode;
//进行中间顺序的调换
for(int i=0;i<(n-m);i++){
cur.next=prev;
prev=cur;
//此处不能用cur.next,因为在第一步就换成了prev
cur=next;
next=cur.next;
}
return head.next;
}
}
深度拷贝带随机指针的链表
题目:其进行深拷贝
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-RJx8a3xr-1646055152123)(C:\Users\76532\Desktop\面试复习\算法\深拷贝链表图.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/330cf77603724862b9e931272621f9dd.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBAR29pbmdfbWFu,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
思路:该题有两只解法,①利用Map的结构区去进行深拷贝②利用链表的结构,由next结构进行拷贝插入,然后再一步一步分离开

1、利用Map结构
public class copyRandomList{
public Node copyRandomList(Node head){
if(head==null){
return null;
}
Map<Node,Node> map=new HashMap<>();
Node nextNode=head;
//复制所有节点
while(nextNode!=null){
Node copyNode=new Node(nextNode.val);
map.put(nextNode,copyNode);
nextNode=nextNode.next;
}
nextNode=head;
//复制节点内容
while(nextNode!=null){
Node copyNode=map.get(nextNode);
copyNode.next=map.get(nextNode.next);
copyNode.random=map.get(nextNode.random);
nextNode=nextNode.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
}
可以进行优化,只使用一个循环,将next和random遇到提前先创建好。
public class copyRandomList{
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head==null){
return null;
}
Map<Node,Node> map=new HashMap<>();
Node nextNode=head;
while(nextNode!=null){
//先复制,看看存不存在,不存在则创建,存在则直接取出
Node copyNode;
if(!map.containsKey(nextNode)){
copyNode=new Node(nextNode.val);
map.put(nextNode,copyNode);
}else{
copyNode=map.get(nextNode);
}
//再看看存不存在next,不存在进行拷贝创建,然后赋予给copyNext
if(map.containsKey(nextNode.next)){
copyNode.next=map.get(nextNode.next);
}else{
if(nextNode.next!=null){
Node nextCopy=new Node(nextNode.next.val);
map.put(nextNode.next,nextCopy);
copyNode.next=nextCopy;
}
}
//再看看存不存在random,不存在进行拷贝创建,然后赋予给copyNext
if(map.containsKey(nextNode.random)){
copyNode.random=map.get(nextNode.random);
}else{
if(nextNode.random!=null){
Node randomCopy=new Node(nextNode.random.val);
map.put(nextNode.random,randomCopy);
copyNode.random=randomCopy;
}
}
nextNode=nextNode.next;
}
return map.get(head);
}
}
}
2、利用链表结构
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
/**
* 特殊情况
*/
if (head==null) {
return head;
}
/**
* 本次拷贝分三个步骤
* 1、拷贝对象
* 2、赋予random
* 3、最后赋予next
*/
CopyNode(head);
CopyRandom(head);
return CopyNext(head);
}
public void CopyNode(Node head){
/**
* 该过程是把对象拷贝再插入
*/
Node next=null;
while(head!=null){
Node CopyNode =new Node(head.val);
next=head.next;
head.next=CopyNode;
CopyNode.next=next;
head=next;
}
}
public void CopyRandom(Node head){
/**
* 先判断是否拥有随机对象
* 将随机对象进行赋予
*/
Node CopyNode=null;
while(head!=null){
Node random=head.random;
CopyNode= head.next;
if (random!=null) {
CopyNode.random=random.next;
}
head=CopyNode.next;
}
}
public Node CopyNext(Node head){
/**
* 将其分开
*/
Node NewHead=head.next;
Node CopyNext=null;
while(head!=null){
CopyNext=head.next;
head.next=CopyNext.next;
head=head.next;
if(CopyNext.next!=null){
CopyNext.next=CopyNext.next.next;
}
}
return NewHead;
}
两数相加
题目:两个链表中的数进行相加
思路:首先我们要考虑到当两个链表不一样长的情况,然后进位可以用一个对象存储,依次进行相加
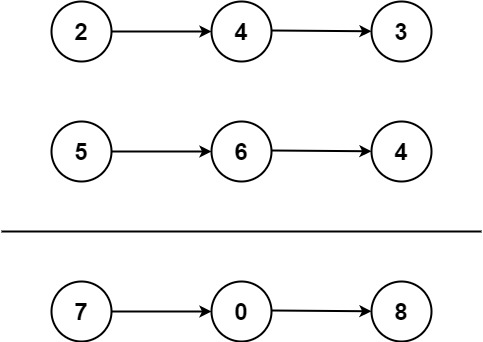
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if(l1==null){
return l2;
}
if(l2==null){
return l1;
}
//存储进位
int array=0;
//建立存储结果的listNode
ListNode sentry=new ListNode(-1);
ListNode res=sentry;
//存储和
int sum=0;
//存储余数
int value=0;
//都存在时
while(l1!=null &&l2!=null){
sum=l1.val+l2.val+array;
value=sum%10;
array=sum/10;
sentry.next=new ListNode(value);
sentry=sentry.next;
l1=l1.next;
l2=l2.next;
}
//只有l1存在时
while(l1!=null){
sum=l1.val+array;
value=sum%10;
array=sum/10;
sentry.next=new ListNode(value);
sentry=sentry.next;
l1=l1.next;
}
//只有l2存在时
while(l2!=null){
sum=l2.val+array;
value=sum%10;
array=sum/10;
sentry.next=new ListNode(value);
sentry=sentry.next;
l2=l2.next;
}
//都不存在时
if (array!=0) {
node=new ListNode(array);
sentry.next=node;
}
return res.next;
}






















 5138
5138











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








