文章结构概览
本文将按一下顺序,逐一介绍。
- Arrays类介绍
- Arrays方法分类
- 排序相关
- 查找相关
- 比较相关
- 打印相关
- 计算hashCode
- 拷贝相关
- 赋值相关
- 转化为集合List
1. Arrays类介绍
This class contains various methods for manipulating arrays (such as
sorting and searching). This class also contains a static factory
that allows arrays to be viewed as lists.
该类包含用于操作数组的各种方法(例如排序和搜索)。该类还包含一个静态工厂,允许将数组视为列表。
根据注释解释,可以知道该类是一个操作数组的工具类,里面封装了常用的数组操作方法。
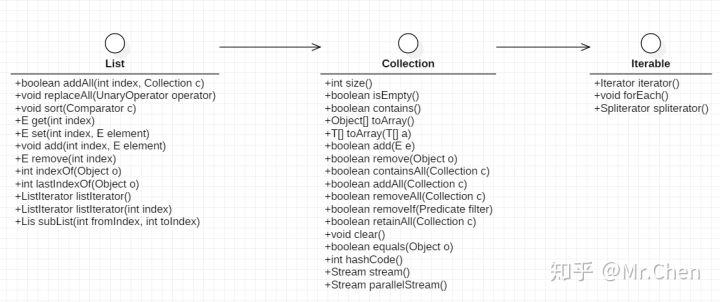
List相关类
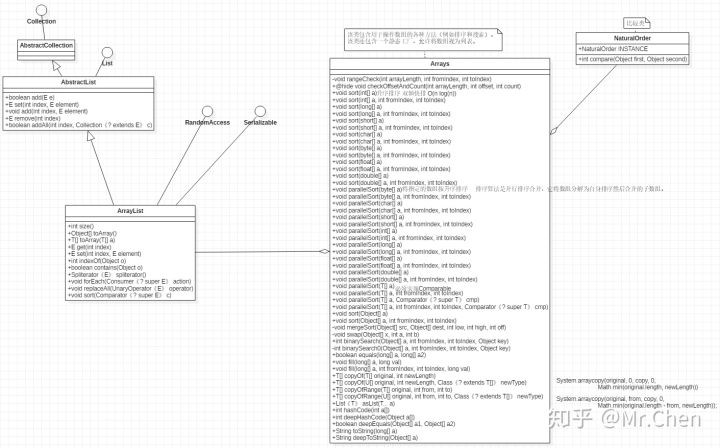
Arrays相关类图
2. Arrays方法分类
2.1 排序相关
2.1.1 普通排序
int[] numbers = new int[]{2, 8, 1};
// 整体排序
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers));
Arrays.sort(numbers);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers));
// 指定位置排序
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers));
Arrays.sort(numbers, 1, 2);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers));主要是调用静态方法 sort() ,支持基本类型数组,引用类型数组必须实现 Comparable接口。
其中的排序算法用的是Dual-Pivot Quicksort(双轴快排),升序排序,时间复杂度为O(n log(n))。
/**
* Sorts the specified range of the array using the given
* workspace array slice if possible for merging
*
* @param a the array to be sorted
* @param left the index of the first element, inclusive, to be sorted
* @param right the index of the last element, inclusive, to be sorted
* @param work a workspace array (slice)
* @param workBase origin of usable space in work array
* @param workLen usable size of work array
*/
static void sort(int[] a, int left, int right, int[] work, int workBase, int workLen) {
// 对于小规模的数组,使用快排
if (right - left < QUICKSORT_THRESHOLD) {
sort(a, left, right, true);
return;
}
/*
* Index run[i] is the start of i-th run
* 索引从i开始
* (升序或降序).
*/
int[] run = new int[MAX_RUN_COUNT + 1];
int count = 0; run[0] = left;
// 检查数组是否接近有序
for (int k = left; k < right; run[count] = k) {
if (a[k] < a[k + 1]) { // 升序
while (++k <= right && a[k - 1] <= a[k]);
} else if (a[k] > a[k + 1]) { // 降序
while (++k <= right && a[k - 1] >= a[k]);
for (int lo = run[count] - 1, hi = k; ++lo < --hi; ) {
int t = a[lo]; a[lo] = a[hi]; a[hi] = t;
}
} else { // 相等
for (int m = MAX_RUN_LENGTH; ++k <= right && a[k - 1] == a[k]; ) {
if (--m == 0) {
sort(a, left, right, true);
return;
}
}
}
/*
* 如果数组的规模没有超过最大规模,
* 应该使用快排,而不是归并排序
*/
if (++count == MAX_RUN_COUNT) {
sort(a, left, right, true);
return;
}
}
// 检查特殊情况
// Implementation note: variable "right" is increased by 1.
if (run[count] == right++) { // 最后一次运行只包含一个元素
run[++count] = right;
} else if (count == 1) { // 数组已经有序
return;
}
// Determine alternation base for merge
byte odd = 0;
for (int n = 1; (n <<= 1) < count; odd ^= 1);
// 创建或使用临时数组b
int[] b; // temp array; alternates with a
int ao, bo; // array offsets from 'left' 相对于left的偏移
int blen = right - left; // space needed for b b所需要的空间
if (work == null || workLen < blen || workBase + blen > work.length) {
work = new int[blen];
workBase = 0;
}
if (odd == 0) {
System.arraycopy(a, left, work, workBase, blen);
b = a;
bo = 0;
a = work;
ao = workBase - left;
} else {
b = work;
ao = 0;
bo = workBase - left;
}
// 合并排序
for (int last; count > 1; count = last) {
for (int k = (last = 0) + 2; k <= count; k += 2) {
int hi = run[k], mi = run[k - 1];
for (int i = run[k - 2], p = i, q = mi; i < hi; ++i) {
if (q >= hi || p < mi && a[p + ao] <= a[q + ao]) {
b[i + bo] = a[p++ + ao];
} else {
b[i + bo] = a[q++ + ao];
}
}
run[++last] = hi;
}
if ((count & 1) != 0) {
for (int i = right, lo = run[count - 1]; --i >= lo;
b[i + bo] = a[i + ao]
);
run[++last] = right;
}
int[] t = a; a = b; b = t;
int o = ao; ao = bo; bo = o;
}
}2.1.2 并行排序
int[] numbers = new int[]{2, 8, 1};
// 整体排序
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers));
Arrays.parallelSort(numbers);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers));
// 指定位置排序
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers));
Arrays.parallelSort(numbers, 1, 2);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers));主要是调用静态方法 parallelSort() ,支持基本数据类型数组,引用类型的数组需要实现Comparable接口,或者调用方法时传入指定的比较器。
这种排序方式,会去判断当前数组的大小是否 小于最小的并行排序长度 MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN,或者并行池的数量为1,如果满足条件,还会调用Dual-Pivot Quicksort(双轴快排)方法来排序,否则才去执行并行排序。
public static void parallelSort(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
rangeCheck(a.length, fromIndex, toIndex);
int n = toIndex - fromIndex, p, g;
if (n <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN || (p = ForkJoinPool.getCommonPoolParallelism()) == 1) {
DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, fromIndex, toIndex - 1, null, 0, 0);
} else {
new ArraysParallelSortHelpers.FJInt.Sorter
(null, a, new int[n], fromIndex, n, 0,
((g = n / (p << 2)) <= MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN) ?
MIN_ARRAY_SORT_GRAN : g).invoke();
}
}2.2 查找相关
int[] numbers = new int[]{2, 8, 1};
// 整体查找
int index = Arrays.binarySearch(numbers, 8);
System.out.println("8的对应下标为 " + index);
// 指定位置查找
int index2 = Arrays.binarySearch(numbers, 8, 1, 2);
System.out.println("8的对应下标为 " + index2);主要是调用静态方法 binarySearch() ,支持基本数据类型数组,引用类型的数组需要实现Comparable接口,或者调用方法时传入指定的比较器。
查找算法使用的是二分查找。
private static int binarySearch0(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex, int key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
int midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1;
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}2.3 比较相关
2.3.1 普通比较
比较数组是否相等:
int[] numbers1 = new int[]{2, 8, 1};
int[] numbers2 = new int[]{2, 6, 1};
// 比较数组是否相等
boolean result = Arrays.equals(numbers1, numbers2);
System.out.println("两个数组是否相等 " + result);支持所有数据类型,其中引用类型会调用equals方法,如果没有重写,则比较的是地址值。
2.3.2 深度比较
针对引用类型,会比较该对象里的所有基本数据类型,如果全部相等,才对比成功。
class A {
public int a;
public A(int a){
this.a = a;
}
}
A[] numbers1 = new A[]{new A(1), new A(8), new A(0)};
A[] numbers2 = new A[]{new A(2), new A(8), new A(0)};
// 比较数组是否相等
boolean result = Arrays.deepEquals(numbers1, numbers2);
System.out.println("两个数组是否相等 " + result);2.4 打印相关
2.4.1 普通打印
将数组打印出来:
int[] numbers1 = new int[]{2, 8, 1};
// 打印数组
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers1));支持所有数据类型,其中引用类型会调用 toString 方法。
2.4.2 深度打印
针对引用类型,会把该对象里的所有基本数据类型打印出来。
class A {
public int a;
public A(int a){
this.a = a;
}
}
A[] numbers = new A[]{new A(1), new A(8), new A(0)};
// 打印数组
System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(numbers));2.5 计算hashCode
2.5.1 普通计算
int[] numbers1 = new int[]{2, 8, 1};
// 打印数组的hash值
System.out.println("hashCode " + Arrays.hashCode(numbers1));支持所有数据类型,其中引用类型会调用 hashCode 方法。
2.5.2 深度计算
针对引用类型,会计算该对象里的所有基本数据类型的hashCode。
class A {
public int a;
public A(int a){
this.a = a;
}
}
A[] numbers = new A[]{new A(1), new A(8), new A(0)};
// 打印数组的hash值
System.out.println("hashCode " + Arrays.deepHashCode(numbers));2.6 拷贝相关
// 整体拷贝
int[] numbers = new int[]{2, 8, 1};
int[] numbers2 = Arrays.copyOf(numbers, 8);
// 打印拷贝的数组
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers2));
// 局部拷贝
int[] numbers3 = Arrays.copyOfRange(numbers, 1, 8);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers3));其中 copyOf 和 copyOfRange 都会调用 System的一个静态方法 arraycopy,如下所示。
public static void arraycopy(int[] src, int srcPos, int[] dst, int dstPos, int length) {
if (src == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("src == null");
}
if (dst == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("dst == null");
}
if (srcPos < 0 || dstPos < 0 || length < 0 ||
srcPos > src.length - length || dstPos > dst.length - length) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(
"src.length=" + src.length + " srcPos=" + srcPos +
" dst.length=" + dst.length + " dstPos=" + dstPos + " length=" + length);
}
if (length <= ARRAYCOPY_SHORT_INT_ARRAY_THRESHOLD) {
// Copy int by int for shorter arrays.
if (src == dst && srcPos < dstPos && dstPos < srcPos + length) {
// Copy backward (to avoid overwriting elements before
// they are copied in case of an overlap on the same
// array.)
for (int i = length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
dst[dstPos + i] = src[srcPos + i];
}
} else {
// Copy forward.
for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) {
dst[dstPos + i] = src[srcPos + i];
}
}
} else {
// Call the native version for longer arrays.
arraycopyIntUnchecked(src, srcPos, dst, dstPos, length);
}
}2.7 赋值相关
可以为一个数组赋上初始值。
// 整体赋值
int[] numbers = new int[9];
Arrays.fill(numbers, 8);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers));
// 局部赋值
int[] numbers2 = new int[9];
int value = 9;
Arrays.fill(numbers2, 5, 8, value);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(numbers2));2.8 转换为集合List
将一个数组转换成一个List。
class A {
public int a;
public A(int a){
this.a = a;
}
}
A[] numbers = new A[]{new A(1), new A(2)};
List<A> list = Arrays.asList(numbers);需要注意的是 该List是 Arrays的一个内部类,并不是我们常用的 ArrayList。
并且其只实现了部分方法:

Arrays内部的List中实现的方法
调用其他方法 会抛出异常 UnsupportedOperationException。






















 1227
1227











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








