1.封装
属性的封装
1.对属性加一个修饰符 private(私有的)
2.只能写属性对应的setter(赋值)和getter(取值)方法
class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public void setName (String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName () {
return name;
}
}
class Demo1 {
public static void main (String[] args) {
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("狗子");
System.out.println(person.getName());
}
}
今天的内容
1.this关键字
2.类对象作为方法的参数【重点】
3.类对象作为另外一个类的属性【重点】
4.继承【重点】
1.this关键字
字面意思:
这个
1.在一个类中表示的是当前对象
2.使用this在哪使用
1、构造方法中
2、普通方法
3.this可以调用属性和方法
this.name===>对象.name
4.this 可以调用构造方法(很少用)
this();//调用无参构造
this(“狗蛋”,12);//调用有参构造
调用构造方法的时候,只能写在构造方法中。
1.在一个构造方法中调用另外一个构造方法的时候,只能写在首行
2.在一个构造不能调用自身
package com.qf.a_test;
class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person (String name, int age) {
//this可以调用属性
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void setName (String sb) {
//this.name 就是对象调用属性
//this可以调用属性
name = sb;
}
public String getName () {
return this.name;
}
public void test () {
System.out.println("嘻嘻测试呢");
}
public void xixi() {
test();
}
public Person () {
//this代表当前的对象
System.out.println("这个是构造方法中的this:"+this);//@15db9742
}
}
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//实例化的是谁,实体类中this就代表谁 this 很强的机动性灵活性
Person person1 = new Person();
System.out.println("person1:" + person1);
Person person2 = new Person();
System.out.println("person2:" + person2);
person2.xixi();
person2.test();
}
}
package com.qf.a_test;
class Car {
String name;
public Car () {
//this();
//this("五菱神车");
this.name = "狗蛋";
//在无参的构造方法 调用了有参的构造方法
//Constructor call must be the first statement in a constructor
}
public Car (String name) {
this();
this.name = name;
}
}
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car car = new Car();
System.out.println(car.name);//null
//对name 赋值 通过有参构造方法进行赋值,咋写?
Car car1 = new Car("劳斯莱斯幻影");
System.out.println(car1.name);
//要求 只能通过无参构造方法对name进行赋值,咋解决?
}
}
总结:
1.this可以调用属性和方法
2.this调用构造方法
2.类对象作为方法的参数【重点】
一个方法的参数可以有 八大基本数据类型,String, 数组
类对象也可以作为一个方法的参数
package com.qf.a_test;
//人喂狗,狗在吃
class People {
public void feed (Dog sb ) {
sb.eat();
}
}
class Dog {
public void eat () {
System.out.println("狗吃大骨头");
}
}
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog = new Dog();
People people = new People();
people.feed(dog);
}
}
案例:
老师教学生,学生敲代码
package com.qf.a_test;
//老师教学生 学生敲代码
class Teacher {
public void teach (Student stu) {
stu.coding();
}
}
class Student {
public void coding () {
System.out.println("学生敲代码");
}
}
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Student student = new Student();
Teacher teacher = new Teacher();
teacher.teach(new Student());
}
}
3.类对象作为另外一个类的属性【重点】
人有属性:
名字,年龄,猫
package com.qf.a_test;
class Man {
String name;//人的名字
int age;
//一个类的对象可以作为另外一个类的属性看待
Cat cat;
}
class Cat {
String name;//猫的名字
String color;//猫的毛色
char sex;//猫的性别
}
//写了那么多属性,无外乎就是赋值和取值
public class Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Man man = new Man();
System.out.println(man.name);//null
System.out.println(man.age);//0
System.out.println(man.cat);//null
//对他们进行赋值
man.name = "狗蛋";
man.age = 3;
Cat cat = new Cat();
cat.name = "加菲";
cat.color = "绿色";
cat.sex = '公';
man.cat = cat;
System.out.println(man.name);//狗蛋
System.out.println(man.age);//3
System.out.println(man.cat);//com.qf.a_test.Cat@15db9742
System.out.println(man.cat.name);//加菲
System.out.println(man.cat.color);
System.out.println(man.cat.sex);
}
}
package com.qf.a_test;
class Women {
private String name;
private int age;
private Bag bag;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Bag getBag() {
return bag;
}
public void setBag(Bag bag) {
this.bag = bag;
}
}
class Bag {
private String color;
private double price;
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
public class Demo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bag bag = new Bag();
bag.setColor("黄色");
bag.setPrice(9.9);
Women women = new Women();
women.setName("二佳");
women.setAge(18);
women.setBag(bag);
System.out.println(women.getName());//二佳
System.out.println(women.getAge());//18
System.out.println(women.getBag());//com.qf.a_test.Bag@15db9742
System.out.println(women.getBag().getColor());//黄色
System.out.println(women.getBag().getPrice());//9.9
}
}
案例:
成年人(Adult)
属性
名字,年龄,孩子
孩子:(Child)
年龄 玩具
玩具:(Toy)
价格 种类
package com.qf.a_test;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
class Adult {
private String name;
private int age;
//成年人有孩子
private Child child;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Child getChild() {
return child;
}
public void setChild(Child child) {
this.child = child;
}
}
class Child {
private String name;
private int age;
private Toy toy;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Toy getToy() {
return toy;
}
public void setToy(Toy toy) {
this.toy = toy;
}
}
class Toy {
private String kind;
private double price;
public String getKind() {
return kind;
}
public void setKind(String kind) {
this.kind = kind;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
public class Demo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Adult adult = new Adult();
adult.setName("老邢");
adult.setAge(73);
Child child = new Child();
child.setName("小邢");
child.setAge(4);
Toy toy = new Toy();
toy.setKind("乐高");
toy.setPrice(998.89);
child.setToy(toy);
adult.setChild(child);
System.out.println(adult.getName());
System.out.println(adult.getAge());
System.out.println(adult.getChild());//
System.out.println(adult.getChild().getName());
System.out.println(adult.getChild().getAge());
System.out.println(adult.getChild().getToy());
System.out.println(adult.getChild().getToy().getKind());
}
}
回顾上午的内容
1.this关键字
this代表的是当前对象
1.this 可以调用属性和方法
2.this可以调用构造方法
2.类对象可以作为方法的参数
3.类对象可以作为另外一个类的属性
4.继承【重点】
Java有三大特性: 封装 继承 多态
4.1生活中的继承
子承父业
龙生龙
你长得真像你父亲
4.2Java中继承
Java中继承至少两个类:
语法格式:
class B extends A {//B继承了A A叫B儿子 B叫A 父类 ,超类或者 基类 }
入门级别案例
package com.qf.b_extends;
class Father {//
String name;
int age;
public void eat () {
System.out.println("吃窝窝头");
}
}
class Son extends Father{
}
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Son son = new Son();
//son中本身看着没有name和age 这两个属性,但是可以直接用!!!为啥? 因为继承关系
//子类可以使用父类的一些属性和方法
son.name = "狗蛋";
son.age = 23;
son.eat();
}
}
Java中的 继承,就是父类的属性和方法拿到子类中使用
1.成员变量(属性)
1.公开的和默认的成员变量,子类是可以通过继承使用的
2.私有的成员变量,子类是无法使用的
2.成员方法(行为)
1.公开的和默认的成员方法,子类是可以通过继承使用的
2.私有的成员方法,子类是无法使用的
3.构造方法
1.先执行父类的构造方法,然后再执行子类的额构造方法
2.子类有无参的构造方法,那么父类也必须有无参构造方法,不然编译不通过
package com.qf.c_extends;
class Father {
//公开的成员变量
public String name;
int age;//默认的成员的变量
private int id;//私有的成员变量
public Father () {
}
//构造方法
public Father (String name) {
System.out.println("我是父类的有参的构造方法");
}
//成员方法
//公开的方法
public void eat () {
System.out.println("吃窝窝头...");
}
//默认的方法
void work () {
System.out.println("种地");
}
private void smoking () {
System.out.println("抽旱烟");
}
}
class Son extends Father {
//儿子有无参的构造方法,那么父类也必须有无参构造方法
}
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//尽管实例化的是子类,但是父类也会执行的
Son son = new Son();
son.name = "狗蛋";
son.age = 12;
//son.id = 12;私有的成员变量,子类是无法使用的
son.eat();
son.work();
//son.smoking();私有的成员方法,子类是无法使用的
}
}
1.继承可以代码复用
2.Java中只能是单继承,只能有一个亲爹
3.Java中可以多重继承
package com.qf.c_extends;
class Animal {
String name;
int age;
}
class Pet extends Animal{//宠物
double weight;
}
class Dog extends Pet {
}
class Cat extends Animal {
}
class Pog extends Animal {
}
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog= new Dog();
dog.name = "旺财";
dog.age = 21;
dog.weight = 89.9;
}
}
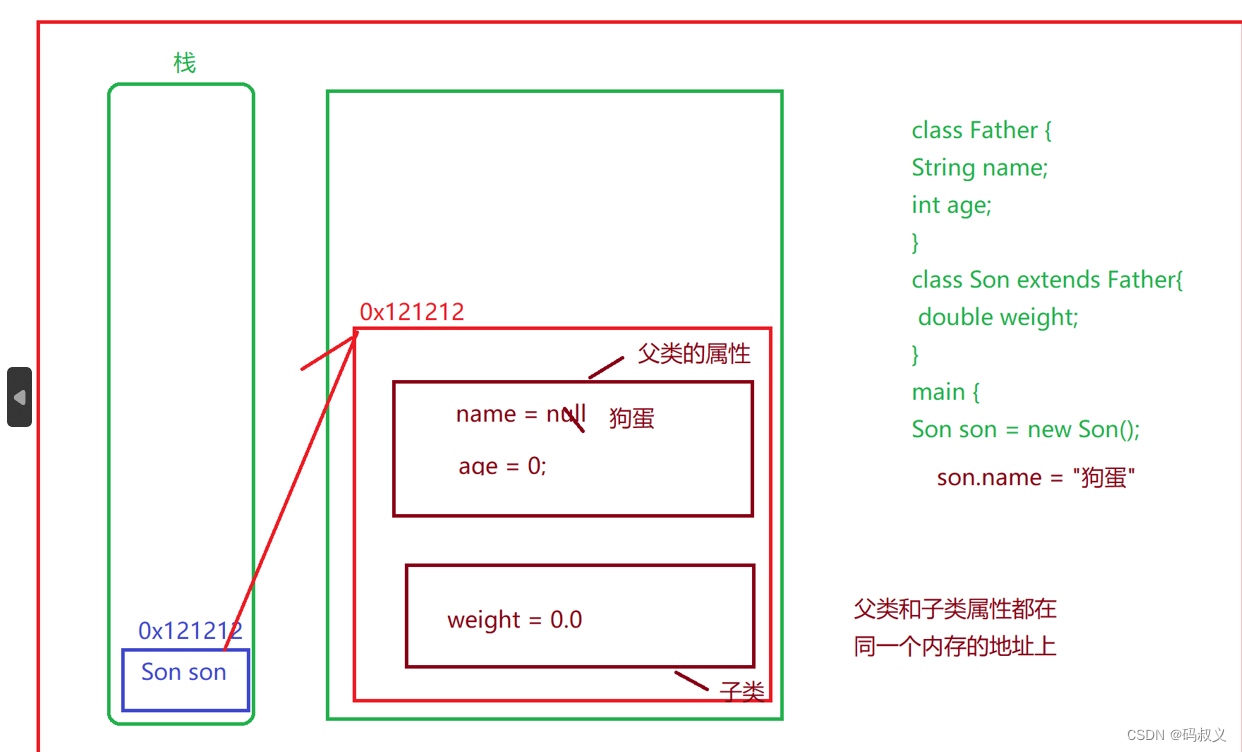
4.3Java内存分析
4.4重写【Override】
重写的目的: 子类是可以继承父类的非私有化的方法,但是有的时候,父类的方法满足不了子类的需求
这个时候可以重写父类的方法。再不改变原来父类的方法架构基础上,只改方法体。
package com.qf.d_override;
class Father {
public void eat () {
System.out.println("吃树皮!!!");
}
}
class Son extends Father{
//当父类的需求满足不了子类,可以重写方法
@Override//@Override重写的严格的限制,告知程序员,此时下面方法是重写的方法
//不是自己独有的方法,是重写的方法
public void eat() {
System.out.println("吃白面");
}
public void sleep () {
}
}
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Son son = new Son();
son.eat();
}
}
重写要求:
1.必须得有继承关系
2.父类方法必须是公开或者默认的
3.在子类中重写的方法和父类一样(方法的名字, 方法的参数列表, 方法的返回类型)
4.必须在子类中重写父类的方法
4重写【Override】
重写的目的: 子类是可以继承父类的非私有化的方法,但是有的时候,父类的方法满足不了子类的需求
这个时候可以重写父类的方法。再不改变原来父类的方法架构基础上,只改方法体。
package com.qf.d_override;
class Father {
public void eat () {
System.out.println("吃树皮!!!");
}
}
class Son extends Father{
//当父类的需求满足不了子类,可以重写方法
@Override//@Override重写的严格的限制,告知程序员,此时下面方法是重写的方法
//不是自己独有的方法,是重写的方法
public void eat() {
System.out.println("吃白面");
}
public void sleep () {
}
}
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Son son = new Son();
son.eat();
}
}
重写要求:
1.必须得有继承关系
2.父类方法必须是公开或者默认的
3.在子类中重写的方法和父类一样(方法的名字, 方法的参数列表, 方法的返回类型)
4.必须在子类中重写父类的方法





















 4068
4068











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








