目录
1.req.body——接收前端body的参数(下面演示:2)
26、数据交互
(1)原生请求
Xhr请求(下面演示:1-4)
var xmlhttp = getXMLHttpRequest();
// xmlhttp.open("get", "http://localhost:3000/info?name=jack",true);
// xmlhttp.send();
// json
// xmlhttp.open("post", "http://localhost:3000/info4", true);
// xmlhttp.setRequestHeader("Content-Type", "application/json");
// xmlhttp.send(JSON.stringify({ "name": "joho", "age": 20 }));
// formdata 不要配置请求头
// xmlhttp.open("post", "http://localhost:3000/info41", true);
// var formdata = new FormData();
// formdata.append("name", "joho");
// formdata.append("age", 20)
// xmlhttp.send(formdata);
xmlhttp.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xmlhttp.readyState == 4 && xmlhttp.status == 200) {
console.log(xmlhttp.responseText);
}
}
Fetch接收(下面演示:5)
//get
fetch('http://localhost:3000/info?name=jack')
.then(function (response) {
return response.json();
})
.then(function (myJson) {
console.log(myJson);
});
//post
fetch('http://localhost:3000/info4', {
body: JSON.stringify({ "name": "joho", "age": 20 }),
headers: {
'content-type': 'application/json'
},
method: 'POST',
})
.then(function (response) {
return response.json();
})
.then(function (myJson) {
console.log(myJson);
});
//formdata
var formdata = new FormData();
formdata.append("name", "joho");
formdata.append("age", 200)
fetch('http://localhost:3000/info41', {
body: formdata,
method: 'POST',
})
.then(function (response) {
return response.json();
})
.then(function (myJson) {
console.log(myJson);
});
(2)参数解析
获取请求很中的参数是每个web后台处理的必经之路,nodejs的 express框架 提供了3种方法来实现
1.req.body——接收前端body的参数(下面演示:2)
包含了提交数据的键值对在请求体中,默认是underfined,
你可以用body-parser或者multer来解析body
对应前端传入参数及内容类型如下:
application/json
{"name"="jack"}
req.body.name
2.req.query(下面演示:1)
包含在路由中每个查询字符串参数属性的对象。如果没有,默认为{ }
注:此方法多适用于GET请求,解析GET里的参数
application/x-www-form-urlencoded
// GET /search?q=tobi+ferret //下面的案例
req.query.q
3.req.params(下面演示:2、3)
包含映射到指定的路线“参数”属性的对象。
例如,如果你有route/user/:name,那么“name”属性可作为req.params.name。
该对象默认为{}。
// GET /user/tj
req.params.name
// => "tj"
多适用于restful风格url中的参数的解析
4.formdata(下面演示:4)
处理formdata需要下载依赖包multiparty
cnpm i –S multiparty
router.post("/test", function (req, res) {
var form = new multiparty.Form();
form.parse(req, function (err, fields, files) {
//fields:类似post 的一些字符串,
//files 文件
})
})
req.query与req.params区别:
req.params包含路由参数(在URL的路径部分)
req.query包含URL的查询参数(在URL的?后的参数)
5.演示:
(1)get请求
demo.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<button onclick="sendData()">get请求</button>
<button onclick="sendData2()">post/put请求</button>
<button onclick="sendData3()">路径中请求参数</button>
<button onclick="sendData4()">formdata参数</button>
<button onclick="sendData5()">fetch get请求</button>
<div id="content"></div>
<script>
===================================== 添加 =========================================
function sendData() {
var xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xmlhttp.open("get", "http://localhost:3000/data/query?name=jack");
xmlhttp.send(); //发送
xmlhttp.onreadystatechange = function () { //接收数据
if (xmlhttp.readyState == 4 && xmlhttp.status == 200) {
console.log(xmlhttp.responseText)
//把拿到的数据展示
content.innerHTML = xmlhttp.responseText;
}
}
}
===================================================================================
</script>
</body>
</html>
server.js
var express = require("express") //加载依赖包
//var bodyParser = require('body-parser'); //body解析
var app = express();
var path = require("path"); //node自带
var allowCrossDomain = function (req, res, next) {
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');//自定义中间件,设置跨域需要的响应头。
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Methods', 'GET, POST, OPTIONS, PUT, DELETE'); //允许任何方法
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Headers', 'X-Requested-With,content-type,X-Session-Token'); //允许任何类型
next(); //下一步
};
app.use(allowCrossDomain);//运用跨域的中间件
//app.use(bodyParser.json()) 创建 application/json 解析
//app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({extended: true})) // 创建 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 解析
var arr = [1,2,3]
//http://localhost:3000/
//接口实现
//请求方式 get post put delete
//"/data/query" 接口地址
//req==request, res==response
app.get("/", function(req, res){
res.send('index')
})
===================================== 添加 =========================================
app.get("/data/query", function(req, res){
console.log(req.body, req.query)
res.send(JSON.stringify(arr));
})
===================================================================================
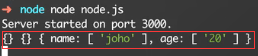
app.listen(3000, function(){console.log("Server started on port 3000.")});



(2)post/put请求
demo.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<button onclick="sendData()">get请求</button>
<button onclick="sendData2()">post/put请求</button>
<button onclick="sendData3()">路径中请求参数</button>
<button onclick="sendData4()">formdata参数</button>
<button onclick="sendData5()">fetch get请求</button>
<div id="content"></div>
<script>
function sendData() {
var xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xmlhttp.open("get", "http://localhost:3000/data/query?name=jack");
xmlhttp.send(); //发送
xmlhttp.onreadystatechange = function () { //接收数据
if (xmlhttp.readyState == 4 && xmlhttp.status == 200) {
console.log(xmlhttp.responseText)
//把拿到的数据展示
content.innerHTML = xmlhttp.responseText;
}
}
}
===================================== 添加 =========================================
function sendData2() {
var xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
================================ 复制上面,修改 =====================================
xmlhttp.open("post", "http://localhost:3000/data/add", true);
//指定发送的内容格式
xmlhttp.setRequestHeader("Content-Type", "application/json");
xmlhttp.send(JSON.stringify({ "name": "joho", "age": 20 }));
===================================================================================
xmlhttp.onreadystatechange = function () { //接收数据
if (xmlhttp.readyState == 4 && xmlhttp.status == 200) {
console.log(xmlhttp.responseText)
//把拿到的数据展示
content.innerHTML = xmlhttp.responseText;
}
}
}
===================================================================================
</script>
</body>
</html>
server.js
var express = require("express") //加载依赖包
===================================== 添加 =========================================
var bodyParser = require('body-parser'); //body解析
===================================================================================
var app = express();
var path = require("path"); //node自带
var allowCrossDomain = function (req, res, next) {
res.header('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');//自定义中间件,设置跨域需要的响应头。
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Methods', 'GET, POST, OPTIONS, PUT, DELETE'); //允许任何方法
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Headers', 'X-Requested-With,content-type,X-Session-Token'); //允许任何类型
next(); //下一步
};
app.use(allowCrossDomain);//运用跨域的中间件
===================================== 添加 =========================================
app.use(bodyParser.json()) 创建 application/json 解析
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({extended: true})) // 创建 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 解析
===================================================================================
var arr = [1,2,3]
//http://localhost:3000/
//接口实现
//请求方式 get post put delete
//req==request, res==response
app.get("/", function(req, res){
res.send('index')
})
app.get("/data/query", function(req, res){
console.log(req.body, req.query)
res.send(JSON.stringify(arr));
})
===================================== 添加 =========================================
//post put
app.post("/data/add", function(req,res){
console.log(req.body, req.query)
res.send(JSON.stringify(arr));
})
===================================================================================
app.listen(3000, function(){console.log("Server started on port 3000.")});

![]()
![]()
server.js
app.get("/data/query", function(req, res){
console.log(req.body, req.query)
res.send(JSON.stringify(arr));
})
===================================== 添加 =========================================
// 规定了data/后面就是参数
app.get("/data/:name", function(req, res){
console.log(req.body, req.query, req.params)
res.send(JSON.stringify(arr));
})
===================================================================================
//post put
app.post("/data/add", function(req,res){
console.log(req.body, req.query)
res.send(JSON.stringify(arr));
})
app.listen(3000, function(){console.log("Server started on port 3000.")});


(3)路径中的请求参数
demo.html
function sendData3() {
var xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xmlhttp.open("get", "http://localhost:3000/data/abc");
xmlhttp.send(); //发送
xmlhttp.onreadystatechange = function () { //接收数据
if (xmlhttp.readyState == 4 && xmlhttp.status == 200) {
console.log(xmlhttp.responseText)
//把拿到的数据展示
content.innerHTML = xmlhttp.responseText;
}
}
}

加参数:



server.js
================================== 添加-:age =======================================
// 规定了data/后面就是参数
app.get("/data/:name-:age", function(req, res){
console.log(req.body, req.query, req.params)
res.send(JSON.stringify(arr));
})
===================================================================================

![]()
(4)formdata参数
处理formdata需要下载依赖包multiparty
cnpm i –S multiparty

demo.html
function sendData4() {
var xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
//formdata 不要配置请求头
xmlhttp.open("post", "http://localhost:3000/data/form", true);
var formdata = new FormData();
formdata.append("name", "joho");
formdata.append("age", 20)
xmlhttp.send(formdata);
xmlhttp.onreadystatechange = function () { //接收数据
if (xmlhttp.readyState == 4 && xmlhttp.status == 200) {
console.log(xmlhttp.responseText)
//把拿到的数据展示
content.innerHTML = xmlhttp.responseText;
}
}
}
server.js
var express = require("express") //加载依赖包
var bodyParser = require('body-parser'); //body解析
var app = express();
var path = require("path"); //node自带
//===================================== 添加 =========================================
var multiparty = require('multiparty'); //从node_modules
//===================================================================================
.
.
.
//===================================== 添加 =========================================
//formdata数据格式
app.post("/data/form", function(req, res) {
var form = new multiparty.Form();
form.parse(req, function(err, fields, files) {
console.log(req.body, req.query, fields)
res.send(JSON.stringify(fields));
})
})
//===================================================================================

(5)fetch get请求
demo.html 绿色是一样的
function sendData5() {
// fetch---promise xhr---callback
fetch('http://localhost:3000/data/query?name=jack&age=10')
.then(function (response) {
return response.json(); //数据解析
})
.then(function (myJson) {
console.log(myJson);
});
//post
fetch('http://localhost:3000/data/add', {
body: JSON.stringify({ "name": "joho", "age": 20 }),
headers: {
'content-type': 'application/json'
},
method: 'POST',
})
.then(function (response) {
return response.json();
})
.then(function (myJson) {
console.log(myJson);
});
//formdata
var formdata = new FormData(); //FormData原生对象(浏览器自带)
formdata.append("name", "joho");
formdata.append("age", 200)
fetch('http://localhost:3000/data/form', {
body: formdata,
method: 'POST',
})
.then(function (response) {
return response.json();
})
.then(function (myJson) {
console.log(myJson);
});
}

![]()
//三种请求
27、跨域
跨域:协议、域名、端口号 有一个不同
同源策略:协议、域名、端口号 都相同
(1)什么是跨域

跨域:协议、域名、端口号 有一个不同
同源策略:协议、域名、端口号 都相同
![]()
//协议、 域名、 端口号
(2)为什么浏览器要限制跨域访问呢?
原因就是安全问题:如果一个网页可以随意地访问另外一个网站的资源,那么就有可能在客户完全不知 情的情况下出现安全问题。
(3)为什么要跨域(从一个页面引用其它页面的资源)
既然有安全问题,那为什么又要跨域呢?有时公司内部有多个不同的子域,比如一个是 location.company.com ,而应用是放在app.company.com , 这时想从 app.company.com去访问 location.company.com 的资源就属于跨域
(4)跨域解决方式
1.cors
 //打包之后就没了(一次性?)
//打包之后就没了(一次性?)
server {
listen 8089;
server_name localhost;
root html; #根目录
# cors
add_header Access - Control - Allow - Origin $http_origin always; # '*'
add_header Access - Control - Allow - Credentials true always;
add_header Access - Control - Allow - Methods 'GET, POST, OPTIONS' always;
add_header Access - Control - Allow - Headers 'DNT,X-Mx-ReqToken,KeepAlive,User-Agent,X-Requested-With,If-Modified-Since,Cache-Control,ContentType,Authorization' always;
#请求http://localhost:8080/api,将该请求转发到http://localhost:3000/api
location / api {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3000/api;
}
}
2.nginx
 //中间nginx代理
//中间nginx代理
Windows: 在nginx目录查找nginx.conf文件并添加以下内容
Mac: open -t /usr/local/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
mac默认ng端口8080
server {
listen 8089; #服务监听端口
server_name localhost; #主机ip
root html; #根目录
# cors
add_header Access - Control - Allow - Origin $http_origin always; # '*'
add_header Access - Control - Allow - Credentials true always;
add_header Access - Control - Allow - Methods 'GET, POST, OPTIONS' always;
add_header Access - Control - Allow - Headers 'DNT,X-Mx-ReqToken,KeepAlive,User-Agent,X-Requested-With,If-Modified-Since,Cache-Control,ContentType,Authorization' always;
#请求http://localhost:8080/api,将该请求转发到http://localhost:3000/api
location / api {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3000/api;
}
}
关于Mac下操作:
brew services start nginx
brew services stop nginx
3.jsonp
app.get("/api/jsonp", function (req, res) {
var data = { name: "jsonp数据" }
data = JSON.stringify(data); //转字符串
var callback = `${req.query.callback}(${data})`; //函数名+数据
console.log(callback)
res.send(callback);
})
function getJsonp() {
$.ajax({
url: "http://localhost:3000/api/jsonp",
data: { name: "xxxx" },
dataType: "jsonp",
jsonpCallback: "handleResponse"
})
};
function handleResponse(data) {
console.log(data);
}
(5)解决跨域
代理服务器用XXX方式,让前端请求,然后在代理到后段地址上去
跨域解决办法
1. 前端和后端的解决方案 jsonp
前端解决 后端解决
需要前端和后端都处理
jsonp===本质上用的是<script>
还不如一起交给后端处理
2. cors 纯后端配置跨域处理
最简单 后端配置 前端无需处理
3. 代理方式proxy----nginx
比如存在一些老旧的系统,后端的实在不愿意改的情况下简单后端接口服务:
![]()
![]()
![]()

后端3000服务:
 //源头是5000
//源头是5000

前端5000服务:
index.html
<button onclick="getReq()">发起get请求</button>
<script>
function getReq() {
var xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest()
xmlhttp.open('get', 'http://localhost:3000/api/data')
xmlhttp.send()
xmlhttp.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xmlhttp.readyState == 4 & xmlhttp.status == 200) {
console.log("结果:" + xmlhttp.readyState);
}
}
}
</script>

npm i -g serve
serve
 //vs code软件内输入
//vs code软件内输入

//跨域
//端口不同(前端是5000,而后端是3000)
1.jsonp方式
1. 前端和后端的解决方案 jsonp
前端解决 后端解决
需要前端和后端都处理
jsonp===本质上用的是<script>
(1)方式一:ajax框架
index.html

// 处理jsonp的全局函数
function handleResponse(data) {
console.log(data)
}
function jsonp () {
$.ajax({
url: 'http://localhost:3000/api/data2',
data: {name: 'jack'},
dataType: 'jsonp',
jsonpCallback: "handleResponse"
})
}

server.js
// Access-Control-Allow-Origin
// 访问 控制 允许 源头
var express = require('express')
var app = express();
==================================== 添加 ==========================================
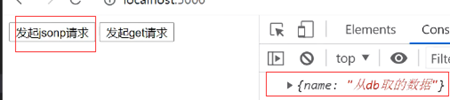
app.get('/api/data2', function(req, res){
var data = {name: '从db取的数据'} //模拟数据库数据
data = JSON.stringify(data); //转字符串
// req.query.callback===handleResponse
var callback = `${req.query.callback}(${data})` //拼接成前端回调参数
res.send(callback)
})
===================================================================================
jsonp方式前后端都要处理,还不如直接交给后端处理


//左边等于前端传过来的函数
(2)方式二:通过script前端标签

index.html
// 处理jsonp的全局函数
function handleResponse(data) {
console.log(data)
}
function jsonp () {
===================================== 添加 =========================================
// 参数是明文
const script = document.createElement("script");
script.setAttribute('src', 'http://localhost:3000/api/data2?callback=handleResponse&name=jack&_=1623158312657')
document.body.appendChild(script)
===================================== 关掉 =========================================
// $.ajax({
// url: 'http://localhost:3000/api/data2',
// data: {name: 'jack'},
// dataType: 'jsonp',
// jsonpCallback: "handleResponse"
// })
===================================================================================
}
 //JQ
//JQ
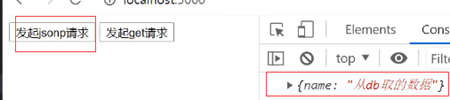
 //也不受同源策略影响,所以能实现
//也不受同源策略影响,所以能实现
1. 前端和后端的解决方案 jsonp
前端解决 后端解决
需要前端和后端都处理
jsonp===本质上用的是<script>
2.cors方式
2. cors 纯后端配置跨域处理
最简单 后端配置 前端无需处理server.js

// Access-Control-Allow-Origin
// 访问 控制 允许 源头
var express = require('express')
var app = express();
===================================== 添加 =========================================
// cors处理跨域
var cors = function(req, res, next) {
// 允许访问的请求源头
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
// 允许访问的请求方法 get post
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Methods', 'GET, POST, OPTIONS, PUT, DELETE');
// 允许访问的请求头 content-type token
// 后端规定需要哪些请求头 前端就必须要传
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Headers', 'content-type, x-token');
next();
}
app.use(cors)
===================================================================================
app.get('/api/data2', function(req, res){
var data = {name: '从db取的数据'} //模拟数据库数据
data = JSON.stringify(data); //转字符串
// req.query.callback===handleResponse
var callback = `${req.query.callback}(${data})` //拼接成前端回调参数
res.send(callback);
})


3.nginx方式
3. 代理方式proxy----nginx
比如,存在一些老旧的系统,后端的实在不愿意改的情况下



 //停掉(因为两个80端口冲突)
//停掉(因为两个80端口冲突)
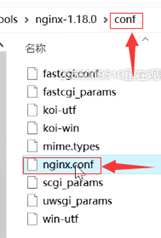


 //从这里返回页面
//从这里返回页面
//复制
# 另一个服务
server {
listen 8089;
server_name localhost;
# 没有/api开头就走这里
location / {
root html; # 根目录===html目录
index index.html index.htm;
}
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin $http_origin always;
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Credentials true always;
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Methods 'GET, POST, OPTIONS' always;
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Headers 'DNT,X-Mx-ReqToken,Keep- Alive,User-Agent,X-Requested-With,If-Modified-Since,Cache-Control,Content- Type,Authorization' always;
# 有/api开头就走这里
location /api { proxy_pass http://localhost:3000/api; }
}
//粘贴

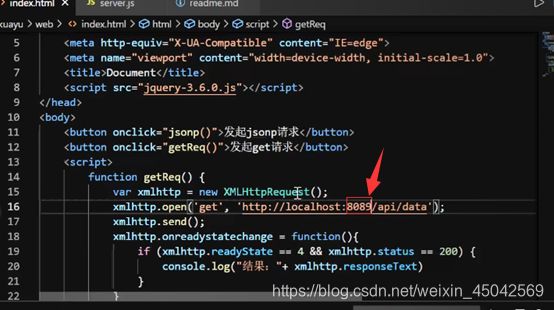
 //复制
//复制

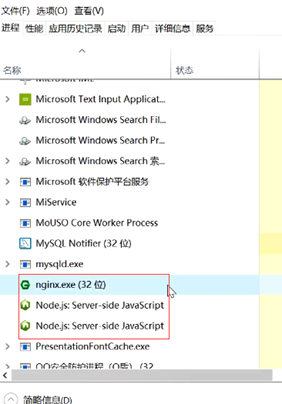

//再关掉,重启
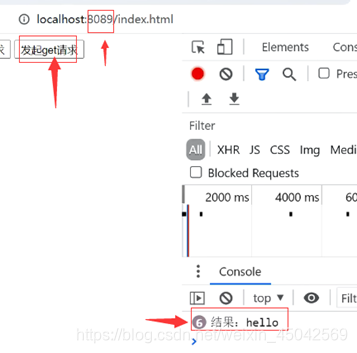
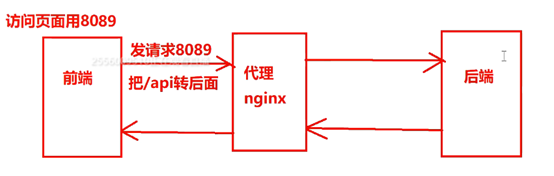








 本文详细讲解了Node.js中数据交互的各种方法,包括原生请求、参数解析,如req.body、req.query、req.params和formData的使用。同时深入探讨了跨域的概念、原因、解决方案,如CORS、JSONP和Nginx配置。
本文详细讲解了Node.js中数据交互的各种方法,包括原生请求、参数解析,如req.body、req.query、req.params和formData的使用。同时深入探讨了跨域的概念、原因、解决方案,如CORS、JSONP和Nginx配置。
















 353
353

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








