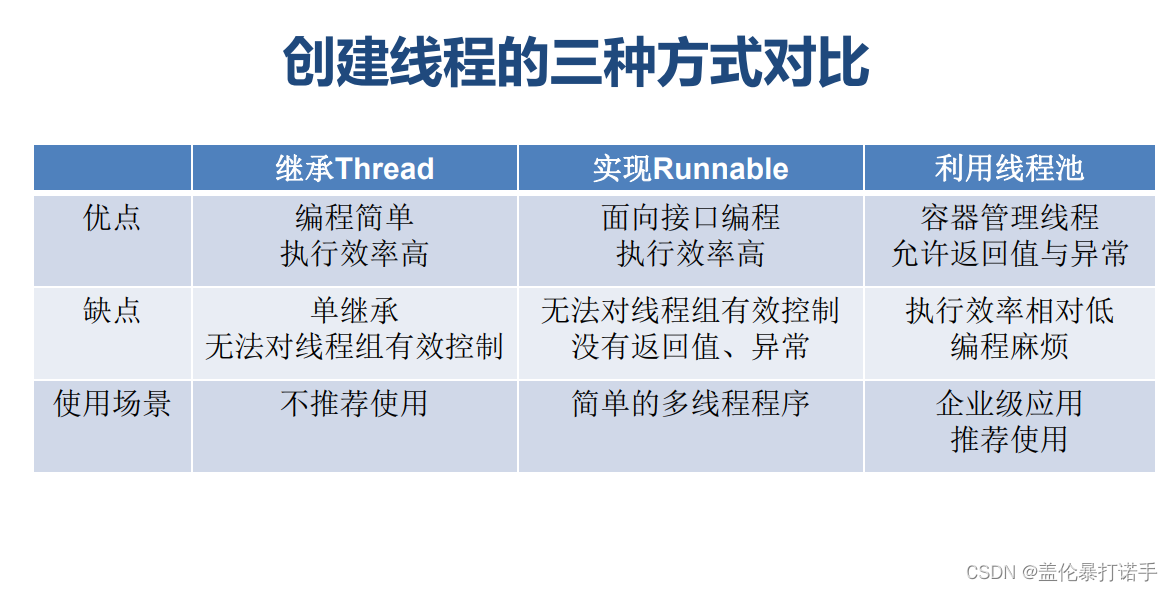
- 继承Thread类创建线程
- 实现Runnable接口创建线程
- 使用Callable和Future创建线程
继承Thread类
/**
* 使用集成Thread的方式实现多线程
*/
public class Match1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runner liuxiang = new Runner();//创建一个新的线程
liuxiang.setName("刘翔");//设置线程名称
Runner laoqi = new Runner();
laoqi.setName("老齐");
Runner op = new Runner();
op.setName("路飞");
liuxiang.start();//启动线程
laoqi.start();
op.start();
}
}
class Runner extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
Integer speed = new Random().nextInt(100);
for(int i = 1 ; i <= 100 ; i++){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000); //当前线程休眠1秒
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//this.getName()打印当前线程的名字
System.out.println(this.getName() + "已前进" + (i * speed) + "米(" + speed + "米/秒)");
}
}
}
实现Runnable接口创建线程
public class Match2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runner2 liuxiang = new Runner2();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(liuxiang);
thread1.setName("刘翔");
Thread laoqi = new Thread(new Runner2());
laoqi.setName("老齐");
Thread op = new Thread(new Runner2());
op.setName("路飞");
thread1.start();
laoqi.start();
op.start();
}
}
class Runner2 implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
Integer speed = new Random().nextInt(100);
for(int i = 1 ; i <= 100 ; i++){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000); //当前线程休眠1秒
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//Thread.currentThread()用于获取当前执行的线程对象
//在Runnable中是无法使用this获取到当前线程对象的
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "已前进" + (i * speed) + "米(" + speed + "米/秒)");
}
}
}
使用Callable和Future创建线程
public class Match3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
//创建一个线程池。里面天生有3个“空”线程。Executors是调度器,对线程池进行管理
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
Runner3 liuxiang = new Runner3();//实例化Callable对象
liuxiang.setName("刘翔");
Runner3 laoqi = new Runner3();
laoqi.setName("老齐");
Runner3 op = new Runner3();
op.setName("路飞");
//将这个对象扔到线程池中,线程池自动分配一个线程来运行liuxiang这个对象的call方法
//Future用于接受线程内部call方法的返回值
Future<Integer> result1 = executorService.submit(liuxiang);
Future<Integer> result2 = executorService.submit(laoqi);
Future<Integer> result3 = executorService.submit(op);
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
executorService.shutdown();//关闭线程池释放所有资源
System.out.println("刘翔累计跑了" + result1.get() + "米" );
System.out.println("老齐累计跑了" + result2.get() + "米" );
System.out.println("路飞累计跑了" + result3.get() + "米" );
}
}
class Runner3 implements Callable<Integer>{
private String name ;
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
//实现Callable接口可以允许我们的线程返回值或抛出异常
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
Integer speed = new Random().nextInt(100);
Integer distince = 0; //总共奔跑的距离
for(int i = 1 ; i <= 100 ; i++){
Thread.sleep(10);
distince = i * speed;
System.out.println(this.name + "已前进" + distince + "米(" + speed + "米/秒)");
}
return distince;
}
}
案例3中Java共创建的几个线程?
。。。























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








