目录
一、双链表
1.1定义
单链表结点中只有一个指向其后继的指针,使得单链表只能从头结点依次顺序地向后遍历。要访问某个结点的前驱结点(插入、删除操作时),只能从头开始遍历,访问后继结点的时间复杂度o(1),访问前驱结点的时间复杂度为 o(n)。为了克服单链表的上述缺点,引入了双链表,双链表结点中有两个指针 prior 和 next,分别指向其前驱结点和后继结点,
1.2图解
双链表:
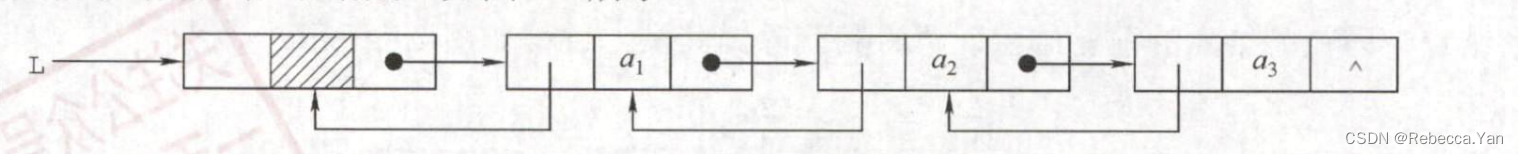
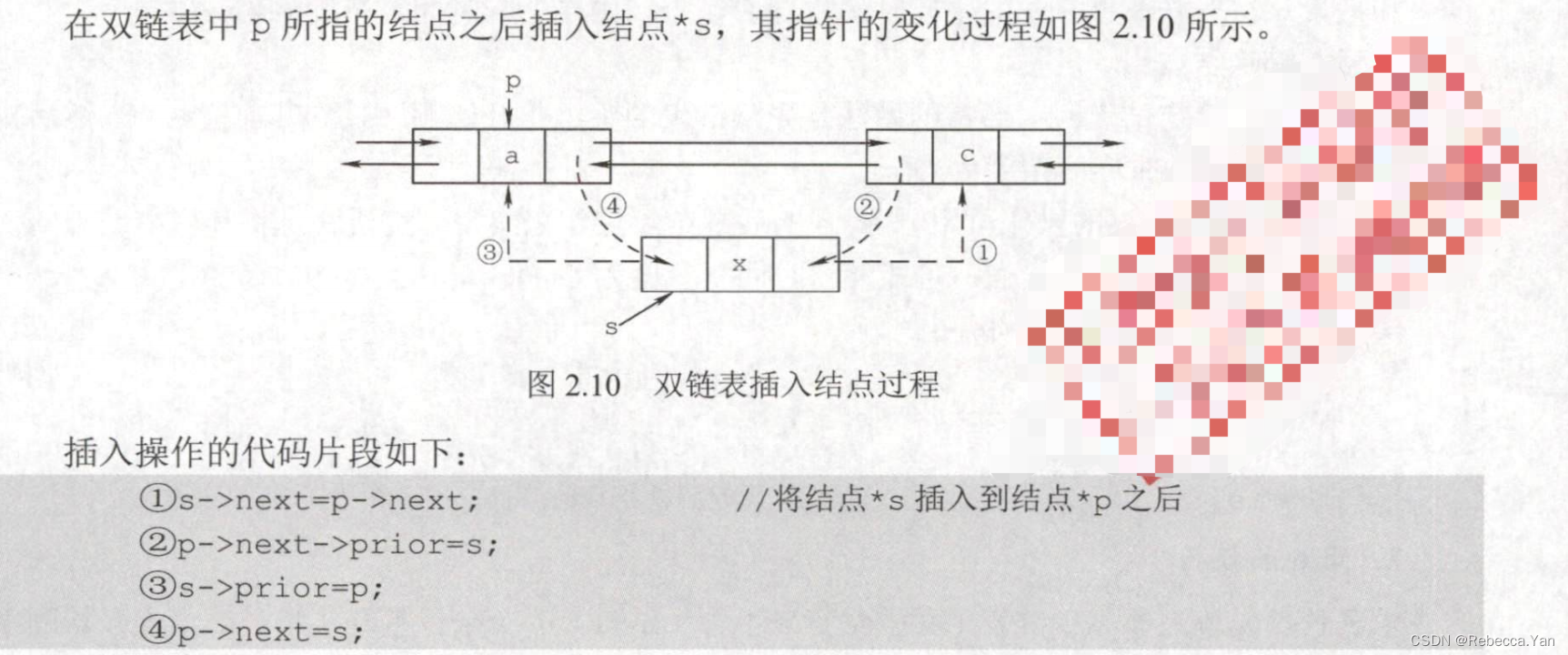
双链表的插入:
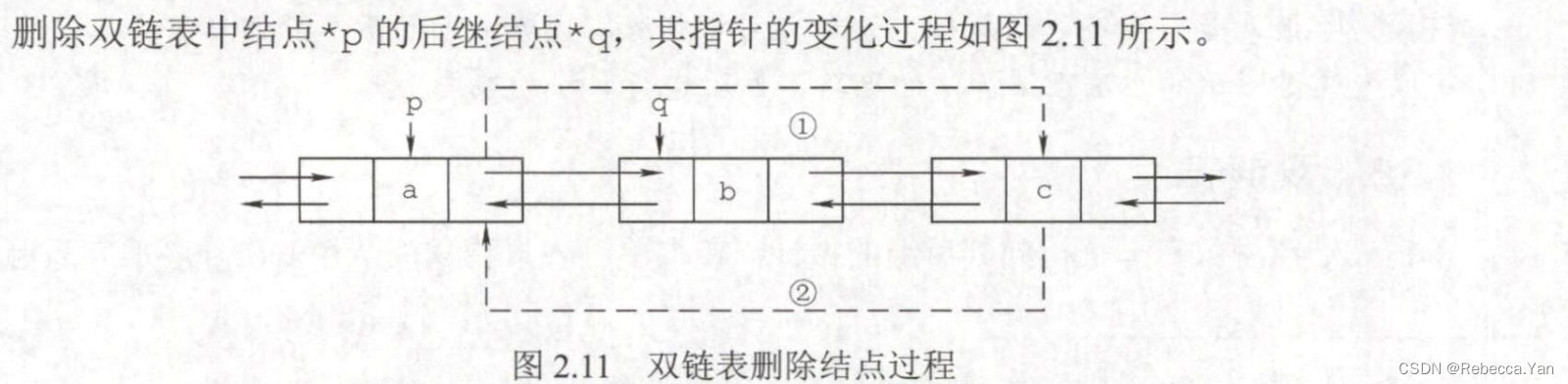
双链表的删除:
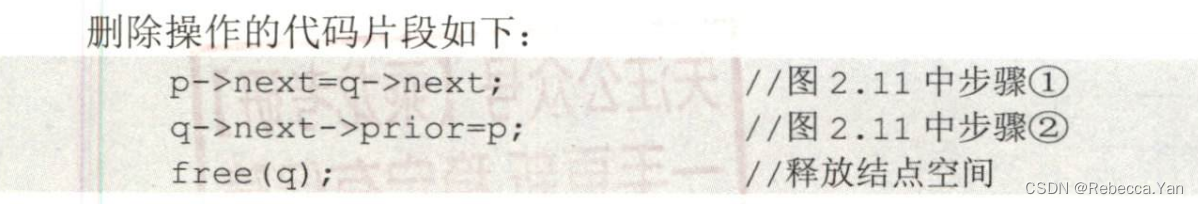
二、代码
1.1双链表的创建
// 创建双链表的函数
struct Node* createLinkedList(int arr[], int size) {
struct Node* head = NULL; // 头指针初始化为 NULL
struct Node* tail = NULL; // 尾指针初始化为 NULL
// 遍历数组并创建节点
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
// 为新节点分配内存空间
struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = arr[i]; // 设置新节点的数据值
newNode->next = NULL; // 新节点的后继节点指针初始化为 NULL
// 处理链表头尾
if (head == NULL) {
// 如果链表为空,将新节点设置为头节点和尾节点
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
} else {
// 如果链表不为空,将新节点链接到尾部,并更新尾节点指针
tail->next = newNode; // 当前尾节点的后继节点指向新节点
newNode->prev = tail; // 新节点的前驱节点指向当前尾节点
tail = newNode; // 更新尾节点指针为新节点
}
}
return head; // 返回链表的头指针
}1.2输出双链表
// 输出节点数值的函数
void printNodeValues(struct Node* head) {
printf("当前链表: ");
while (head != NULL) {
printf("%d ", head->data);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}1.3双链表的删除(进阶)
删除值在 m 到 n 之间的节点
// 删除值在 m 到 n 之间的节点的函数
void deleteNodesInRange(struct Node** headRef, int m, int n) {
// 从双链表的头部开始遍历
struct Node* current = *headRef;
while (current != NULL) {
// 如果当前节点的值在 m 和 n 之间
if (current->data >= m && current->data <= n) {
// 如果当前节点有前驱节点,将其指向当前节点的下一个节点
if (current->prev != NULL) {
current->prev->next = current->next;
}
// 如果当前节点有后继节点,将其指向当前节点的前驱节点
if (current->next != NULL) {
current->next->prev = current->prev;
}
// 释放当前节点的内存空间
struct Node* temp = current;
// 将当前节点指针移动到下一个节点
current = current->next;
// 释放当前节点的内存空间
free(temp);
} else {
// 如果当前节点的值不在 m 和 n 之间,继续遍历下一个节点
current = current->next;
}
}
}1.4全部代码(本地直接运行这个)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 双链表节点结构
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* prev;
struct Node* next;
};
// 创建双链表的函数
struct Node* createLinkedList(int arr[], int size) {
struct Node* head = NULL; // 头指针初始化为 NULL
struct Node* tail = NULL; // 尾指针初始化为 NULL
// 遍历数组并创建节点
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
// 为新节点分配内存空间
struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = arr[i]; // 设置新节点的数据值
newNode->next = NULL; // 新节点的后继节点指针初始化为 NULL
// 处理链表头尾
if (head == NULL) {
// 如果链表为空,将新节点设置为头节点和尾节点
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
} else {
// 如果链表不为空,将新节点链接到尾部,并更新尾节点指针
tail->next = newNode; // 当前尾节点的后继节点指向新节点
newNode->prev = tail; // 新节点的前驱节点指向当前尾节点
tail = newNode; // 更新尾节点指针为新节点
}
}
return head; // 返回链表的头指针
}
// 删除值在 m 到 n 之间的节点的函数
void deleteNodesInRange(struct Node** headRef, int m, int n) {
// 从双链表的头部开始遍历
struct Node* current = *headRef;
while (current != NULL) {
// 如果当前节点的值在 m 和 n 之间
if (current->data >= m && current->data <= n) {
// 如果当前节点有前驱节点,将其指向当前节点的下一个节点
if (current->prev != NULL) {
current->prev->next = current->next;
}
// 如果当前节点有后继节点,将其指向当前节点的前驱节点
if (current->next != NULL) {
current->next->prev = current->prev;
}
// 释放当前节点的内存空间
struct Node* temp = current;
// 将当前节点指针移动到下一个节点
current = current->next;
// 释放当前节点的内存空间
free(temp);
} else {
// 如果当前节点的值不在 m 和 n 之间,继续遍历下一个节点
current = current->next;
}
}
}
// 输出节点数值的函数
void printNodeValues(struct Node* head) {
printf("当前链表: ");
while (head != NULL) {
printf("%d ", head->data);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("正在创建双链表...\n");
struct Node* head = createLinkedList(arr, size);
printNodeValues(head); // 调用新的输出函数
int m = 2; // 设定要删除的范围
int n = 4;
printf("正在删除数值在 %d 到 %d 之间的节点...\n", m, n);
deleteNodesInRange(&head, m, n);
printNodeValues(head); // 调用新的输出函数
printf("\n");
return 0;
}























 1420
1420











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










