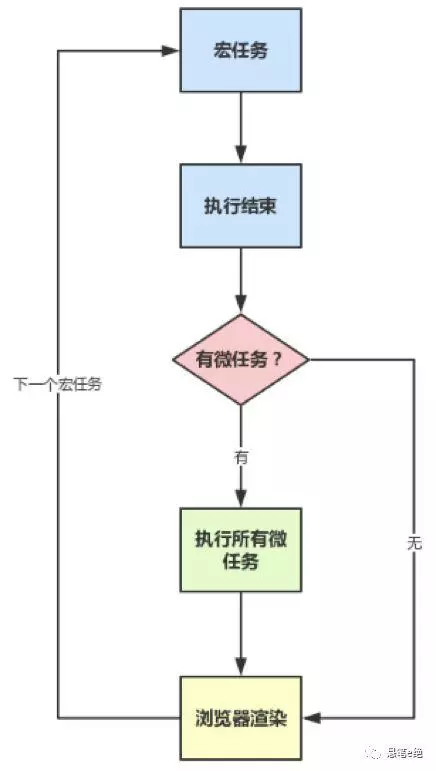
1.宏任务:
分类:setTimeout setInterval requrestAnimationFrame
1>这些都是浏览器或者Node环境实现的。
2>第一个宏任务列中只有一个任务,执行主线程的js代码
3>宏任务队列可以有多个
2.微任务:
分类:new promise().then(回调) process.nextTick
1.微任务所处的队列 就是微任务队列
2.只有一个微任务队列
3.在上一个宏任务队列执行完毕后如果有微任务队列就会执行微任务队列中所有的任务,如果在执行微任务的过程中,产生了新的微任务,同样会将该微任务添加到微任务队列中,V8 引擎一直循环执行微任务队列中的任务,直到队列为空才算执行结束。也就是说在执行微任务过程中产生的新的微任务并不会推迟到下个宏任务中执行,而是在当前的宏任务中继续执行。
宏任务包含script(整体代码),所以一开始就是一个宏任务执行栈
setTimeout(function(){
console.log('定时器开始啦')
});
new Promise(function(resolve){
console.log('马上执行for循环啦');
for(var i = 0; i < 10000; i++){
i == 99 && resolve();
}
}).then(function(){
console.log('执行then函数啦')
});
console.log('代码执行结束');
//执行结果
//马上执行for循环
//代码执行结束
//执行then函数
//定时器开始
setTimeout(() => console.log('setTimeout1'), 0); //1宏任务
setTimeout(() => { //2宏任务
console.log('setTimeout2');
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log('promise3');
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log('promise4');
})
console.log(5)
})
setTimeout(() => console.log('setTimeout4'), 0); //4宏任务
}, 0);
setTimeout(() => console.log('setTimeout3'), 0); //3宏任务
Promise.resolve().then(() => {//1微任务
console.log('promise1');
})
//输出结果为
// promise1
// setTimeout1
// setTimeout2
// promise3
// 5
// promise4
// setTimeout3
// setTimeout4

async function async1() {
console.log( 'async1 start' )
await async2()
console.log( 'async1 end' )
}
async function async2() {
console.log( 'async2' )
}
async1()
console.log( 'script start' )
执行结果
async1 start
async2
script start
async1 end
一旦遇到await 就立刻让出线程,阻塞后面的代码
等候之后,对于await来说分两种情况
不是promise 对象
是promise对象
如果不是promise,await会阻塞后面的代码,先执行async外面的同步代码,同步代码执行完毕后,在回到async内部,把promise的东西,作为await表达式的结果
如果它等到的是一个 promise 对象,await 也会暂停async后面的代码,先执行async外面的同步代码,等着 Promise 对象 fulfilled,然后把 resolve 的参数作为 await 表达式的运算结果。
如果一个 Promise 被传递给一个 await 操作符,await 将等待 Promise 正常处理完成并返回其处理结果。
async function async1() {
console.log( 'async1 start' ) //2
await async2()
console.log( 'async1 end' )//7
}
async function async2() {
console.log( 'async2' )//3
}
console.log( 'script start' ) //1
setTimeout( function () {
console.log( 'setTimeout' )//8
}, 0 )
async1();
new Promise( function ( resolve ) {
console.log( 'promise1' )//4
resolve();
} ).then( function () {
console.log( 'promise2' ) //6
} )
console.log( 'script end' )//5
new Promise( ( resolve, reject ) => {
console.log( "promise1" )
resolve()
} )
.then( () => {
console.log( 1 )
} )
.then( () => {
console.log( 2 )
} )
.then( () => {
console.log( 3 )
} )
new Promise( ( resolve, reject ) => {
console.log( "promise2" )
resolve()
} )
.then( () => {
console.log( 4 )
} )
.then( () => {
console.log( 5 )
} )
.then( () => {
console.log( 6 )
} )
// 输出结果
//promise1
//promise2
//1
//4
//2
//5
//3
//6
先执行同步代码 promise1, promise2,此时微任务有两个任务 log(1)和log(4)
执行完log(1)和log(4)此时任务中有log(2)和log(5)两个微任务
执行log(2)和log(5)此时任务中有log(3)和log(6)两个微任务
连续的几个then()回调,并不是连续的创建了一系列的微任务并推入微任务队列,因为then()的返回值必然是一个Promise,而后续的then()是上一步then()返回的Promise的回调
async function t1 () {
console.log(1)
console.log(2)
await Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log('t1p'))
console.log(3)
console.log(4)
}
async function t2() {
console.log(5)
console.log(6)
await Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log('t2p'))
console.log(7)
console.log(8)
}
t1()
t2()
console.log('end')
// 输出:
// 1
// 2
// 5
// 6
// end
// t1p
// t2p
// 3
// 4
// 7
// 8
async function t1 () {
console.log(1)
console.log(2)
await new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('t1p')
resolve()
}, 1000)
})
await console.log(3)
console.log(4)
}
async function t2() {
console.log(5)
console.log(6)
await Promise.resolve().then(() => console.log('t2p'))
console.log(7)
console.log(8)
}
t1()
t2()
console.log('end')
// 输出:
// 1
// 2
// 5
// 6
// end
// t2p
// 7
// 8
// t1p
// 3
// 4




















 1066
1066











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








