题意解析:
题中matching指的就是一个逆元为本身的置换,并且要求不能有不变元。这样可知p中的数必定是两两配对的(互相映射),如果p的长度为奇数必定会剩余一个数与自己配对,则无法构成matching,故长度必为偶数。
cost中由于i与pi是对称的(如1映射到5时,|a1-a5|与|a5-a1|计算了两次)。所以除2后,cost的含义为每次从a中取两个数,求其差的绝对值。
题解:
下面的提到的数组都是排好序后的
最小的取法:
其实我们需要找的就是一个使得cost最小的p和次小的q,显然最小就是排序后相邻的数两两相减(图1)。

次小的取法:
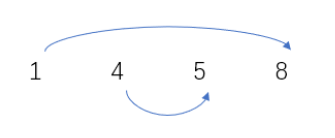
- 首先考虑n最小,n=4时
如图2取法为仅有的一种:
- 再看n=6时:
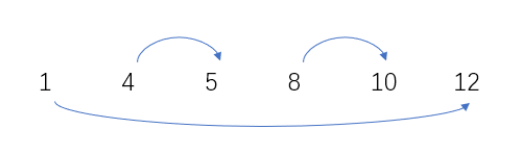
这种取法是最小的,具体证明参考https://blog.csdn.net/m0_43448982/article/details/107431309
上面两种取法都是与最小取法互补的,故result=2 *(尾-头) - 而n>6时,可以拆分为4与6的组合(由拓展欧几里得可推出4x+6y=n,n>=8且为偶数,x,y必有整数解),如果不拆分采用类似n=6的最优取法的话,必然没有拆分后的小(拆分后少了拆分的段与段的间隔的值)。所以能拆分就必拆分。
现在问题就变成了如何拆分数组了。总共就两种拆法,长度为4或6,但是明显无法贪心,所以可以想到采用动态规划。dp[i]定义为排序后前i个数取得的最小值,每次当前可选的状态为拆分成4或6
状态转移方程:
dp[i]=min(dp[i-4]+2*(arr[i]-arr[i-3]),dp[i-6]+2*(arr[i]-arr[i-5]));
不过需要注意先处理出来 i 等于4,6,8的情况(i=8时取不了6)
AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_N=2e5+5;
typedef long long ll;
ll dp[MAX_N];
ll arr[MAX_N];
inline int read()
{
int sum=0,f=1;
char c=getchar();
while(c<'0'||c>'9'){if(c=='-')f=-1;c=getchar();}
while(c>='0'&&c<='9'){sum=(sum<<1)+(sum<<3)+c-'0';c=getchar();}
return sum*f;
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)arr[i]=read();
sort(arr+1,arr+n+1);
dp[4]=2*(arr[4]-arr[1]);
dp[6]=2*(arr[6]-arr[1]);
dp[8]=2*(arr[8]-arr[5]+arr[4]-arr[1]);
for(int i=10;i<=n;i+=2)
{
dp[i]=min(dp[i-4]+2*(arr[i]-arr[i-3]),dp[i-6]+2*(arr[i]-arr[i-5]));
}
cout<<dp[n]<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}






















 392
392











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








