文章目录
1,max和min
1,max函数
#include <algorithm>
int a=2;
int b=3;
max(a,b);
2,min函数
#include <algorithm>
int a=2;
int b=3;
min(a,b);
2,sort函数
void sort (RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last, Compare comp);
(1)第一个参数first:是要排序的数组的起始地址。
(2)第二个参数last:是结束的地址(最后一个数据的后一个数据的地址)
(3)第三个参数comp是排序的方法:可以是从升序也可是降序。如果第三个参数不写,则默认的排序方法是从小到大排序。
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
main()
{
//sort函数第三个参数采用默认从小到大
int a[]={45,12,34,77,90,11,2,4,5,55};
sort(a,a+10);
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool cmp(int a,int b);
int main()
{
//sort函数第三个参数自己定义,实现从大到小
int a[]={45,12,34,77,90,11,2,4,5,55};
sort(a,a+10,cmp);
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
//自定义函数
bool cmp(int a,int b){
return a>b;
}
sort()函数和lambda表达式
#include<algorithm>
int main()
{
vector<int> ar = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
sort(ar.begin(), ar.end(), [](int a, int b)->bool {return a > b; });
for (auto x : ar)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}

3,reverse()函数
用来翻转 [a,b) 之间的内容
template <class BidirectionalIterator> void reverse (BidirectionalIterator first, BidirectionalIterator last)
{
while ((first!=last)&&(first!=--last))
{
std::iter_swap (first,last);
++first;
}
}
1.reverse函数可以反转一个字符串
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string str;
str = "Hello,world!";
reverse(str.begin(),str.end());
cout<<str;
return 0;
}
2.反转字符数组
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
char a[10];
for(int i = 0; i<10; i++){
a[i] = 'a' + i;
}
reverse(a,a+10);
puts(a);
return 0;
}
3.反转整型数组
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a[10];
for(int i = 0; i<10; i++){
a[i] = i;
}
reverse(a,a+10);
for(int i = 0; i<10; i++){
cout<<a[i]<<' ';
}
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
4,swap函数
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
int a = 10;
int b = 5;
std::swap( a, b );
cout << "a = " << a << ", b = " << b << endl;
}
5,memset()函数
C 库函数 **void memset(void str, int c, size_t n) 复制字符 c(一个无符号字符)到参数 str 所指向的字符串的前 n 个字符。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main ()
{
char str[50];
strcpy(str,"This is string.h library function");
puts(str);
memset(str,'$',7);
puts(str);
return(0);
}
输出结果:
This is string.h library function
$$$$$$$ string.h library function
6,memcpy()
#include<string.h>
将seq.data数据复制到data里面
memcpy(data, seq.data, sizeof(data));
7,strcpy()
#include<string.h>
char *strcpy(char *dest, const char *src)
将src的内容复制到dest,并返一个指向dest的指针
8,substr()string的切割赋值
string s="";
s=s1.substr(pos, len);
//pos的默认值是0,len的默认值是s.size() - pos,即不加参数会默认拷贝整个s)
//若pos的值超过了string的大小,则substr函数会抛出一个out_of_range异常;若pos+n的值超过了string的大小,则substr会调整n的值,只拷贝到string的末尾
//从第pos位开始复制n位给s
9,abs()求绝对值函数
int num=abs(a-b);求a-b的绝对值
10,从屏幕中输入一行数字到数组里面
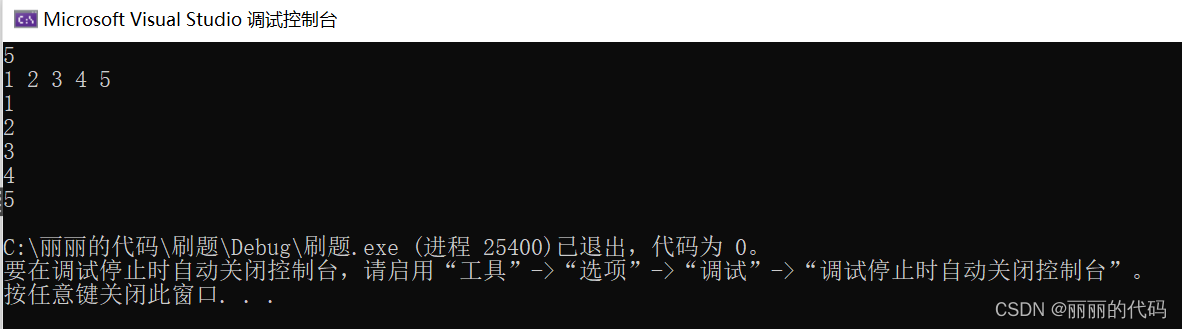
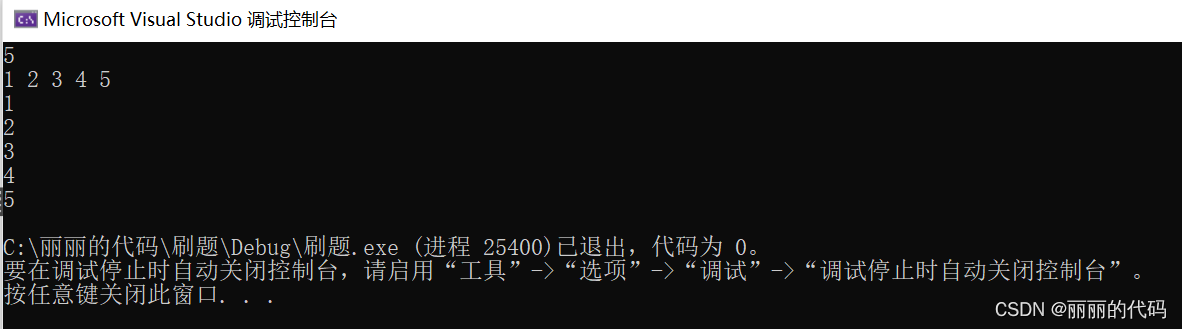
已知数组个数
int main() {
vector<int>ar;
int n, m;
cin >> n;
while (n--&& cin >> m) {
ar.push_back(m);
}
for (auto x : ar) {
cout << x << endl;
}
return 0;
}
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int>ar(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cin >> ar[i];
}
for (auto x : ar) {
cout << x << endl;
}
return 0;
int main() {
int n,m;
cin >> n;
vector<int>ar;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cin >>m;
ar.push_back(m);
}
for (auto x : ar) {
cout << x << endl;
}
return 0;
}
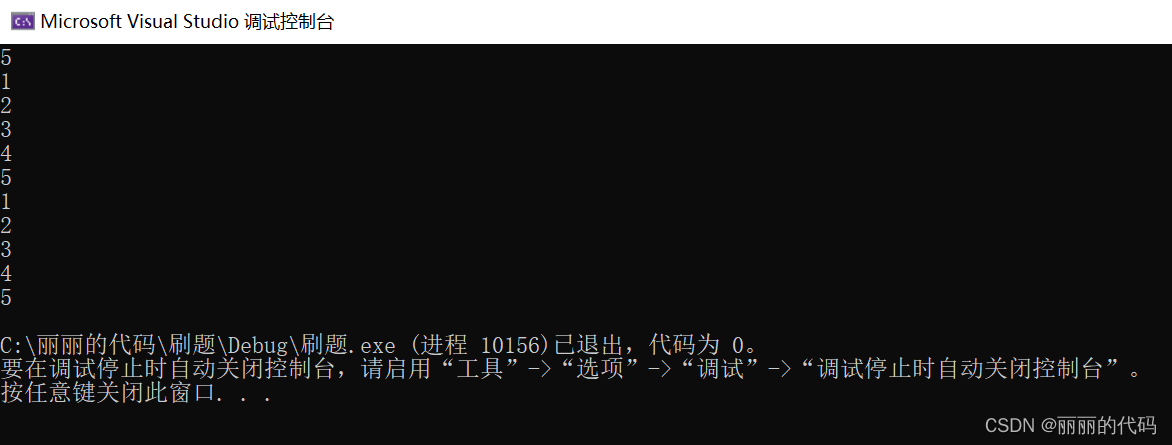
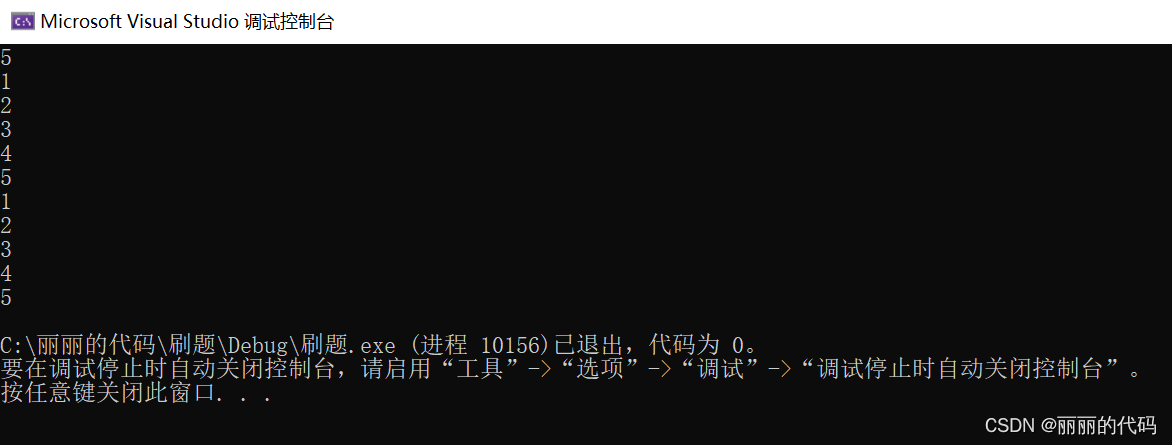
未知数组个数
int main() {
int m;
vector<int>ar;
while(cin>>m) {
ar.push_back(m);
if (cin.get() == '\n') break;
}
for (auto x : ar) {
cout << x << endl;
}
return 0;
}

11,map set
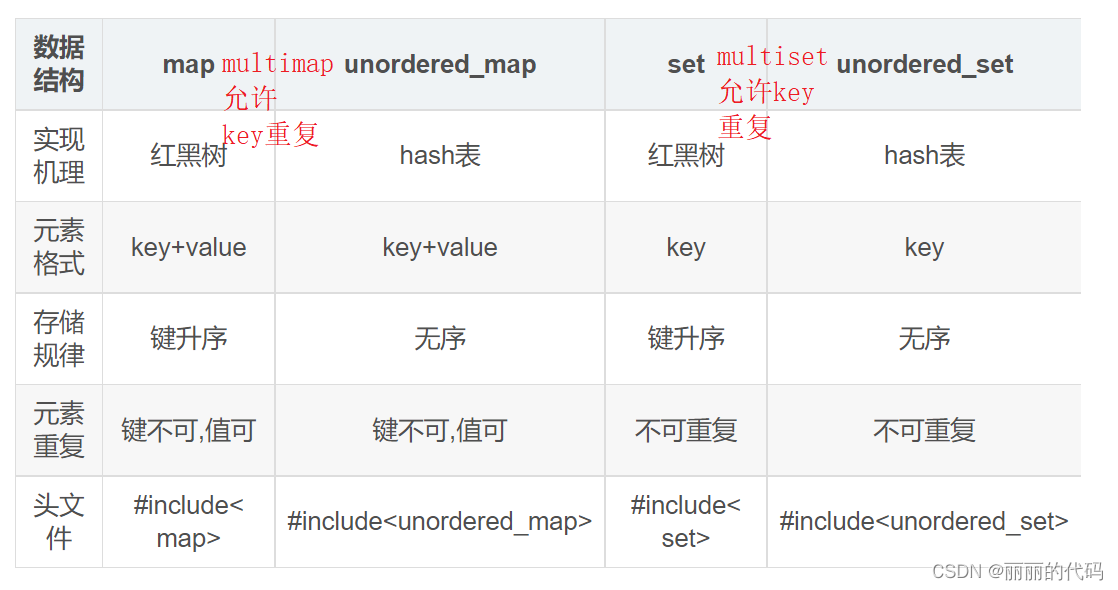
map插入
ret = mymap.insert(make_pair("C语言教程", "http://c.biancheng.net/c/"));
map查询
1,第1种:用count函数来判断关键字是否出现,其缺点是无法定位数据出现的位置,由于map的一对一的映射特性,就决定了count函数的返回值只有两个,要么是0,要么是1,当要判断关键字出现时返回1.
2,用find函数来定位数据出现的位置,它返回一个迭代器,当数据出现时,它返回数据所在位置的迭代器;如果没有要查找的数据,返回end()
map<int, string>::iterator iter=mapStudent.find(1);
map删除
void erase (iterator position);//删除迭代器指向的位置的元素
size_type erase (const key_type& x);//删除key的对
void erase (iterator first, iterator last);//删除从first到last的迭代器指向的元素
c++提供的大小写转换库函数
int main()
{
string str = "THIS IS A STRING";
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
str[i] = tolower(str[i]);
cout << str << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); ++i) {
str[i] = toupper(str[i]);
}
cout << str << endl;
return 0;
}























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








