注册事件
给元素添加事件,称为注册事件或绑定事件
有两种注册事件的方式:传统方式和方法监听注册方式
传统方式
利用on开头的事件onclick,同一个元素同一个事件只能设置一个处理函数,最后注册的处理函数会吧前面的覆盖
<button onclick="alert('点击了')"></button>
<button onclick="alert('点击了')"></button>
<script>
var btn = document.querySelector('button');
btn.onclick = function() {
}
</script>
方法监听注册方式
W3C推荐的方式
用addEventListener()方法 给事件注册监听
eventTarget.addEventListener(type,listener,useCapture)
type是事件触发了类型,click等等
listener事件处理函数,事件发生时会调用此监听函数
useCapture可选参数,是布尔值,默认是false
<button>dianji</button>
<script>
var btn = document.querySelector('button');
btn.addEventListener('click', function() {
alert('dianji');
})
</script>
attachEvent(IE8版本之前支持)
eventTarget.attachEvent(eventNameWithOn,callback)
此方法会将指定的监听器注册到eventTarget(目标对象)上,当此对象触发指定事件时,指定的回调函数就会被执行
eventNameWithOn事件类型字符串,onclick等等(要带on)
callback事件处理函数,目标触发事件时函数被调用
<button>dianji</button>
<script>
var btn = document.querySelector('button');
btn.attachEvent('onclick', function() {
console.log('dianji');
})
</script>
解绑
传统解绑1
<div>1111</div>
<script>
var div = document.querySelector('div');
div.onclick = function() {
alert('1111');
div.onclick = null;
}
</script>
解绑方式2
<div>1111</div>
<script>
var div = document.querySelector('div');
// 括号里是事件和函数名,所以需要把函数提出来
div.addEventListener('click', fn); //fn不需要加小括号
function fn() {
alert('1111');
div.removeEventListener('click', fn);
}
</script>
事件流
DOM事件流分为三个阶段
捕获阶段
当前目标阶段
冒泡阶段
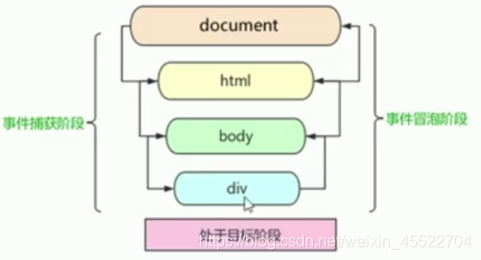
捕获阶段
点son盒子,father盒子会先弹出提示
<div class="father" style="width: 500px; height: 300px; background-color: aqua;">
<div class="son" style="width: 300px; height: 300px; background-color: pink;"></div>
</div>
<script>
var son = document.querySelector('.son');
son.addEventListener('click', function() {
alert('son');
}, true) //true代表在捕获阶段调用函数
var father = document.querySelector('.father');
father.addEventListener('click', function() {
alert('father');
}, true) //true代表在捕获阶段调用函数
</script>
冒泡阶段
点son盒子father盒子会后弹出提示
<div class="father" style="width: 500px; height: 300px; background-color: aqua;">
<div class="son" style="width: 300px; height: 300px; background-color: pink;"></div>
</div>
<script>
var son = document.querySelector('.son');
son.addEventListener('click', function() {
alert('son');
}, false) //false代表在冒泡阶段调用函数
var father = document.querySelector('.father');
father.addEventListener('click', function() {
alert('father');
}, false) //false代表在冒泡阶段调用函数
</script>
注意
js代码只能执行捕获或者冒泡其中的一个阶段
onclick和attachEvent只能得到冒泡阶段
eventTarget.addEventListener(type,listener,useCapture)如果第三参数是true表示在捕获阶段调用函数
实际中很少用事件捕获,更关注事件冒泡
有些事件没有冒泡比如onblur、onfocus、onmouseenter、onmouseleave
事件对象
<div style="width: 500px; height: 300px; background-color: aqua;"></div>
<script>
var div = document.querySelector('div');
div.onclick = function(e) {
console.log(e);
// e.target绑定的是触发事件的对象
console.log(e.target);
// this返回的是绑定事件的对象
console.log(this);
}
// 事件对象只有有了事件才会存在,不需要传参
// 事件对象是事件一系列相关数据的集合,比如鼠标点击位置
// 事件对象可以自己命名
// 兼容ie678通过window.event
// 兼容写法e = e || window.event;
</script>
e和this
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
<li>5</li>
</ul>
<script>
var ul = document.querySelector('ul');
ul.addEventListener('click', function(e) {
console.log(this);
console.log(e.target);
})
</script>
常见的属性和方法
e.target 返回触发事件的对象
e.srcElement 返回触发事件的对象 非标准ie6 - 8 使用
e.type 返回事件的类型 click等
e.cancelBubble 阻止冒泡
e.returnValue 阻止默认事件非标准ie6 - 8 使用
e.preventDefault() 阻止默认事件 标准
e.stopPropagation() 阻止冒泡 标准
<div style="width: 500px; height: 300px; background-color: aqua;"></div>
<script>
var div = document.querySelector('div');
div.onclick = function(e) {
console.log(e.type);
}
</script>
<a href="#">1111</a>
<script>
var a = document.querySelector('a');
a.addEventListener('click', function(e) {
e.preventDefault(); //阻止跳转的DOM标准写法
})
a.onclick = function(e) {
// 此种阻止行为只局限于传统的注册方式
return false;
}
</script>
<div class="father" style="width: 500px; height: 300px; background-color: aqua;">
<div class="son" style="width: 300px; height: 300px; background-color: pink;"></div>
</div>
<script>
var son = document.querySelector('.son');
son.addEventListener('click', function(e) {
alert('son');
e.stopPropagation(); //停止冒泡
e.cancelBubble = true; //非标准取消冒泡
}, false)
var father = document.querySelector('.father');
father.addEventListener('click', function() {
alert('father');
}, false)
</script>
事件委托
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
</ul>
<script>
// 给父节点添加侦听器,利用事件冒泡影响每一个子节点
var ul = document.querySelector('ul');
ul.addEventListener('click', function(e) {
e.target.style.backgroundColor = 'pink';
})
</script>
常用鼠标事件
contextmenu主要控制应该何时显示上下文菜单,主要用于取消默认的上下文菜单
selectstart禁止鼠标选中
<script>
document.addEventListener('contextmenu', function(e) {
// 禁止使用菜单
e.preventDefault();
})
document.addEventListener('selectstart', function(e) {
// 禁止选中
e.preventDefault();
})
</script>
鼠标事件对象
e.clientX 返回鼠标相对于浏览器窗口的可视区的X坐标
e.clientY 返回鼠标相对于浏览器窗口的可视区的Y坐标
e.pageX 返回鼠标相对于页面文档的可视区的X坐标
e.pageY 返回鼠标相对于页面文档的可视区的Y坐标
e.screenX 返回鼠标相对于电脑屏幕的X坐标
e.screenY 返回鼠标相对于电脑屏幕的Y坐标
键盘事件
如果不使用addEventListener需要加on
onkeydown金额onkeyup不区分大小写,onpress区分大小写
<script>
document.addEventListener('keyup', function() {
// 按键弹起时触发
console.log('tanqi');
})
document.addEventListener('keydown', function() {
// 按下的时候触发,能识别功能键ctrl shift 箭头等等
console.log('anxia');
})
document.addEventListener('keypress', function() {
// 按下的时候触发,不能识别功能键
console.log('press');
})
</script>
键盘事件对象
keyCode 返回该键的ASCII码值
<script>
document.addEventListener('keyup', function(e) {
console.log(e.keyCode);
})
</script>
offset偏移量
获得元素距离,带有定位元素的位置
获得元素自身大小
返回的数值都不带单位
<div class="father">
<div class="children"></div>
</div>
<script>
var children = document.querySelector('.children');
var father = document.querySelector('.father');
// 返回带有定位父元素的上方偏移
console.log(children.offsetTop);
// 返回带有定位父元素的左方偏移
console.log(children.offsetLeft);
// 如果父元素没有定位,则以body为准
console.log(father.offsetLeft);
// 可以得到元素的大小宽度和高度, 包含padding border width
console.log(father.offsetWidth);
console.log(father.offsetHeight);
// 返回的是带有定位的父元素,否则返回body
console.log(children.offsetParent);
</script>
offset与style区别
offset可以得到任意表中的样式值
style只能得到行内样式表中的样式值
offset获得的值没有单位
style.width获得的是带有单位的字符串
offsetWidth包含padding border width
style.width不包含padding和border
offsetWidth是只读属性
style.width是可读写属性
scoll滚动
scrollTop: 返回被卷去的上侧距离
scrollLeft: 返回被卷去的左侧距离
scrollWidth:返回自身实际宽度,不含边框,不带单位
scrollHeight:返回自身实际高度,不含边框,不带单位
offset常用于获得元素位置
client常用于获得元素大小
scroll常用于获取滚动距离
页面的滚动距离通过window.pageXoffset获得
定时器
setInterval(函数,定时时间);
clearInterval(需要清除的函数);
<div></div>
<script>
var div = document.querySelector('div');
var timer = setInterval(function() {
if (div.offsetLeft >= 400) {
clearInterval(timer);
}
div.style.left = div.offsetLeft + 5 + 'px';
}, 30);
</script>






















 370
370











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








