子集问题
链接: 78.子集
思路
如果把子集问题、组合问题、分割问题都抽象为一棵树的话,那么组合问题和分割问题都是收集树的叶子节点,而子集问题是找树的所有节点
其实子集也是一种组合问题,因为它的集合是无序的,子集{1,2}和子集{2,1}是一样的
那么既然是无序,取过的元素不会重复取,写回溯算法的时候,for就要从startIndex开始,而不是从0开始
PS:求排列问题的时候,就要从0开始,因为集合是有序的,{1,2}和{2,1}是两个集合
以示例中nums=[1,2,3]为例,把子集抽象为树形结构,如下:
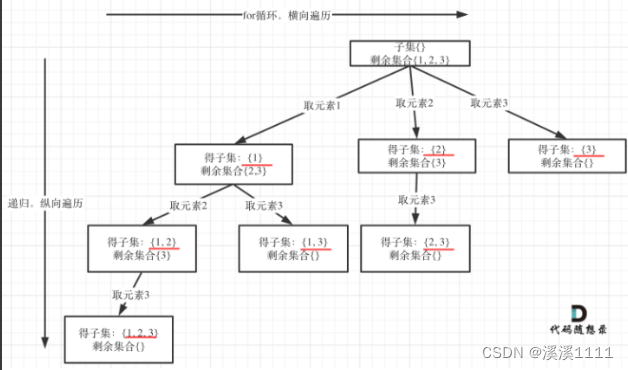
从图中红线部分,可以看出遍历这个树的时候,把所有节点都记录下来,就是要求的子集集合
代码
class Solution {
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
void backTracking(int[] nums,int startIndex){
results.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
if (startIndex >= nums.length){
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex;i < nums.length;i++){
path.adds(nums[i]);
backTracking(nums,i + 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
backTracking(nums,0);
return results;
}
}
子集Il
链接: 90.子集II
思路
问题类型与组合问题类似
都是每次取一个数,不同的是,组合问题收集的是叶子节点(需要在终止函数中判断,加入results),而子集问题收集的是所有节点,需要在回溯函数中收集。
本题因为整数数组包含重复元素,和组合总和II类似,需要一个布尔类型的used数组来保存节点的使用情况,以此区分是树层遍历还是树枝遍历。
代码
class Solution {
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Integer>> results = new ArrayList<>();
void backTracking(int[] nums,int startIndex,boolean[] used){
results.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
if (startIndex >= nums.length){
return;
}
for (int i = startIndex;i < nums.length;i++){
//使用时脑子里面想一想过程
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false){
continue;
}
used[i] = true;
path.add(nums[i]);
backTracking(nums,i + 1,used);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
used[i] = false;
}
}
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
boolean[] used = new boolean[nums.length];
backTracking(nums,0,used);
return results;
}
}
递增子序列
链接: 491.递增子序列
思路
和子集问题很像
- 本题与子集II存在一定的差距,子集II是含重复元素的数组求子集,我们通过排序,再加一个标记数组来达到去重的目的
- 本题求自增子序列,是不能对原数组进行排序的,排完序的数组都是自增子序列了
- 本题的单层逻辑:每一个树层都要设置一个标记数组来记录该元素有没有出现过,每一个树层设置标记数组的话,我们就将它写到for循环中。
- 查看这一层是否出现过同一元素,在给出范围的时候我们可以使用标记数组;或者使用map.本质又到了之前学习数组和哈希表时的思路。
代码
class Solution {
private List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
private List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences(int[] nums) {
backtracking(nums,0);
return res;
}
private void backtracking (int[] nums, int start) {
if (path.size() > 1) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
int[] used = new int[201];
for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (!path.isEmpty() && nums[i] < path.get(path.size() - 1) ||
(used[nums[i] + 100] == 1)) continue;
used[nums[i] + 100] = 1;
path.add(nums[i]);
backtracking(nums, i + 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
//法二:使用map
class Solution {
//结果集合
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
//路径集合
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences(int[] nums) {
getSubsequences(nums,0);
return res;
}
private void getSubsequences( int[] nums, int start ) {
if(path.size()>1 ){
res.add( new ArrayList<>(path) );
// 注意这里不要加return,要取树上的节点
}
HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i=start ;i < nums.length ;i++){
if(!path.isEmpty() && nums[i]< path.getLast()){
continue;
}
// 使用过了当前数字
if ( map.getOrDefault( nums[i],0 ) >=1 ){
continue;
}
map.put(nums[i],map.getOrDefault( nums[i],0 )+1);
path.add( nums[i] );
getSubsequences( nums,i+1 );
path.removeLast();
}
}
}






















 248
248











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








