java.lang.Comparable
我们知道基本数据类型的数据(除boolean类型外)需要比较大小的话,之间使用比较运算符即可,但是引用数据类型是不能直接使用比较运算符来比较大小的。那么,如何解决这个问题呢?
Java给所有引用数据类型的大小比较,指定了一个标准接口,就是java.lang.Comparable接口:
那么我们想要使得我们某个类的对象可以比较大小,怎么做呢?
第一步:哪个类的对象要比较大小,哪个类就实现java.lang.Comparable接口,并重写方法
-
方法体就是你要如何比较当前对象和指定的另一个对象的大小
第二步:对象比较大小时,通过对象调用compareTo方法,根据方法的返回值决定谁大谁小。
-
this对象(调用compareTo方法的对象)大于指定对象(传入compareTo()的参数对象)返回正整数
-
this对象(调用compareTo方法的对象)小于指定对象(传入compareTo()的参数对象)返回负整数
-
this对象(调用compareTo方法的对象)等于指定对象(传入compareTo()的参数对象)返回零
public class Student implements Comparable {
private String name;
private int age;
private int score;
public Student(String name, int age, int score) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(int score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", score=" + score +
'}';
}
//年龄相同,按照成绩排,成绩相同按照名字排序
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
Student s = (Student) o;
int i = this.age - s.age;//比较年龄
i = i == 0 ? this.score - s.score : i;//年龄相同,再比较分数
i = i == 0 ? this.name.compareTo(s.name) : i;//分数也相同,比较姓名
return i;
}
}测试类:
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student("tom", 19, 96);
Student s2 = new Student("jack", 18, 88);
Student s3 = new Student("rose", 20, 90);
Student s4 = new Student("jerry", 18, 96);
Student s5 = new Student("james", 19, 96);
Student s6 = new Student("tom", 19, 96);
//创建数组,存储5个学生对象
Student[] stus = new Student[6];
stus[0] = s1;
stus[1] = s2;
stus[2] = s3;
stus[3] = s4;
stus[4] = s5;
stus[5] = s6;
//冒泡排序
for (int i = 0; i < stus.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < stus.length - 1 - i; j++) {
//比较元素大小,并交换位置
if (stus[j].compareTo(stus[j + 1]) > 0) {
Student temp = stus[j];
stus[j] = stus[j + 1];
stus[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
//遍历数组
for (int i = 0; i < stus.length; i++) {
System.out.println(stus[i]);
}
}
}
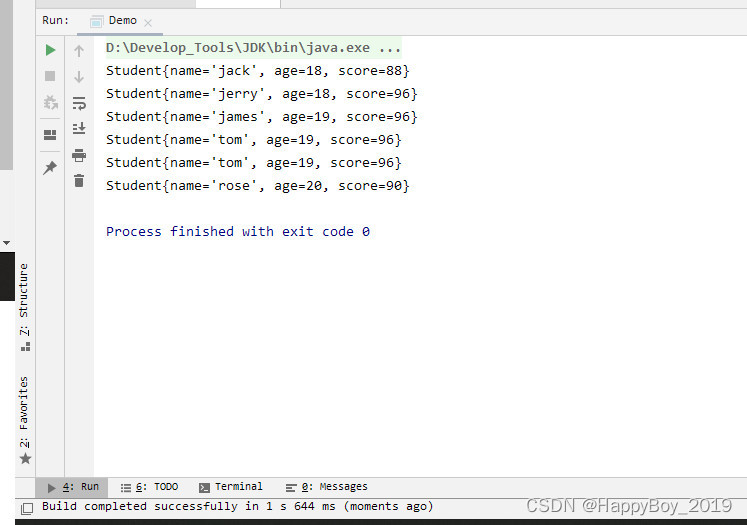
运行结果






















 7348
7348











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








