代码分析基于android-12.0.0_r28
前期阶段
kernel/init/main.c:
static int __ref kernel_init(void *unused)
{
// ...省略一堆代码
if (execute_command) {
ret = run_init_process(execute_command);
if (!ret)
return 0;
panic("Requested init %s failed (error %d).",
execute_command, ret);
}
if (!try_to_run_init_process("/sbin/init") ||
!try_to_run_init_process("/etc/init") ||
!try_to_run_init_process("/bin/init") ||
!try_to_run_init_process("/bin/sh"))
return 0;
panic("No working init found. Try passing init= option to kernel. "
"See Linux Documentation/admin-guide/init.rst for guidance.");
}
首先对内核启动命令进行判断,如果有路径对应的命令输入,则执行路径下对应的用户空间进程。execute_command 的值是通过uboot传递的,在 bootargs 中使用"init=xxxx"就可以将值传给他,比如"init=/linuxrc"表示根文件系统中的 linuxrc 就是要执行的用户空间 init 程序。
如果没有用户空间进程的路径,则执行linux内核中默认指定的用户空间进程路径:
/sbin/init 、/etc/init 、/bin/init、/bin/sh
如果以上linux内核指定的默认用户空间进程路径下都不存在对应的程序,linux内核将输出panic信息。
正常启动来说,内核层传给system/core/init/main.cpp的参数:argc:1,argv:init。所以,第一阶段调用了FirstStageMain
Linux Kernel在启动完成之后,随后是找到要启动的init程序并启动init进程,在Android中,init进程的入口是在:
android-12.0.0_r28/system/core/init/main.cpp
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
#if __has_feature(address_sanitizer)
__asan_set_error_report_callback(AsanReportCallback);
#endif
// Boost prio which will be restored later
// 设置当前进程的优先级, init的进程ID为0
setpriority(PRIO_PROCESS, 0, -20);
if (!strcmp(basename(argv[0]), "ueventd")) {
// 初始化设备,监听uevent事件
return ueventd_main(argc, argv);
}
if (argc > 1) {
if (!strcmp(argv[1], "subcontext")) {
android::base::InitLogging(argv, &android::base::KernelLogger);
const BuiltinFunctionMap& function_map = GetBuiltinFunctionMap();
return SubcontextMain(argc, argv, &function_map);
}
if (!strcmp(argv[1], "selinux_setup")) {
// 创建Selinux
return SetupSelinux(argv);
}
if (!strcmp(argv[1], "second_stage")) {
return SecondStageMain(argc, argv);
}
}
return FirstStageMain(argc, argv);
}
setpriority:是一个方法,它可以用于设置进程的优先级。进程的优先级决定了系统在有限的资源下如何为进程分配资源。通过设置优先级,您可以指定进程在系统中的重要性级别,以便系统可以为其分配适当的资源。- 头文件为
#include <sys/time.h>,#include <sys/resource.h> - 函数原型:
int setpriority(int which, id_t who, int prio);which:PRIO_PROCESS:表示设置指定进程的优先级;PRIO_PGRP:表示设置指定进程组的所有进程的优先级;PRIO_USER:表示设置指定用户的所有进程的优先级。who:参数指定要设置优先级的进程、进程组或用户的 IDprio:参数指定要设置的优先级值,范围从-20(最高优先级)到19(最低优先级)
- 头文件为
第一阶段调用FirstStageMain
android-12.0.0_r28/system/core/init/first_stage_init.cpp
int FirstStageMain(int argc, char** argv) {
//该宏REBOOT_BOOTLOADER_ON_PANIC由system/core/init/Android.mk中定义,
//只有user,eng版本,REBOOT_BOOTLOADER_ON_PANIC=1
if (REBOOT_BOOTLOADER_ON_PANIC) {
// init信号处理器,当init crash,打印当前进程的回溯信息对象(调用栈信息),
// 并重启到 bootLoader,可以看1.1、InstallRebootSignalHandlers分析
InstallRebootSignalHandlers();
}
//记录当前时间start_time
boot_clock::time_point start_time = boot_clock::now();
// 用来存放执行的命令失败时的error code的std::vector窗口
std::vector<std::pair<std::string, int>> errors;
#define CHECKCALL(x) \
if ((x) != 0) errors.emplace_back(#x " failed", errno);
// umask(0)用于设置当前进程的文件模式创建屏蔽字
// 用户创建文件夹权限值=初始创建文件夹默认值-umask的预设值
// 如:775=777-002
// 用户创建文件权限值=初始创建文件默认值-umask的预设值
// 如:664=666-002
umask(0);
// clearenv是一个 C 标准库函数,它的作用是清除当前进程环境中所有的环境变量
CHECKCALL(clearenv());
// 将默认的 PATH 环境变量设置到进程环境中
CHECKCALL(setenv("PATH", _PATH_DEFPATH, 1));
/*
initramfs(Initial RAM File System)是一个临时的文件系统,
它存在于内存中,在 Linux 内核引导过程中使用。
Android 启动过程中,initramfs中的文件会被挂载为根文件系统,
然后init进程会按照 /init.rc 文件中的配置启动其他服务和进程,最终构建出完整的 Android 系统
*/
// 将文件系统tmpfs挂载到/dev目录下
CHECKCALL(mount("tmpfs", "/dev", "tmpfs", MS_NOSUID, "mode=0755"));
// 创建权限值为0755的目录/dev/pts
CHECKCALL(mkdir("/dev/pts", 0755));
// 创建权限值为0755的目录/dev/socket
CHECKCALL(mkdir("/dev/socket", 0755));
// 创建权限值为0755的目录/dev/dm-user
CHECKCALL(mkdir("/dev/dm-user", 0755));
// 将文件系统devpts挂载/dev/pts目录下
CHECKCALL(mount("devpts", "/dev/pts", "devpts", 0, NULL));
#define MAKE_STR(x) __STRING(x)
// 将文件系统proc挂载proc目录下
CHECKCALL(mount("proc", "/proc", "proc", 0, "hidepid=2,gid=" MAKE_STR(AID_READPROC)));
#undef MAKE_STR
// 禁止非特权进程(即非root进程)读取文件内容
// 设置文件/proc/cmdline的权限为0440
CHECKCALL(chmod("/proc/cmdline", 0440));
std::string cmdline;
// 读取文件/proc/cmdline的信息到cmdline中
android::base::ReadFileToString("/proc/cmdline", &cmdline);
// 禁止非特权进程(即非root进程)读取文件内容
// 设置文件/proc/bootconfig的权限为0440
chmod("/proc/bootconfig", 0440);
std::string bootconfig;
// 读取文件/proc/bootconfig的信息到bootconfig中
android::base::ReadFileToString("/proc/bootconfig", &bootconfig);
gid_t groups[] = {AID_READPROC};
/*
设置进程的附属组为AID_READPROC(3009)
通过将init进程的附属组设置为 AID_READPROC 组,
init进程就具有了读取 /proc 目录下文件的权限
*/
CHECKCALL(setgroups(arraysize(groups), groups));
// 将文件系统sysfs挂载到/sys目录下
CHECKCALL(mount("sysfs", "/sys", "sysfs", 0, NULL));
// 将文件系统selinuxfs挂载到/sys/fs/selinux目录下
CHECKCALL(mount("selinuxfs", "/sys/fs/selinux", "selinuxfs", 0, NULL));
// 创建字符设备节点/dev/kmsg,主设备号为1,次设备号为11,权限cr--------
CHECKCALL(mknod("/dev/kmsg", S_IFCHR | 0600, makedev(1, 11)));
if constexpr (WORLD_WRITABLE_KMSG) {
CHECKCALL(mknod("/dev/kmsg_debug", S_IFCHR | 0622, makedev(1, 11)));
}
// 创建字符设备节点/dev/random,主设备号为1,次设备号为8,权限crw-rw-rw-
CHECKCALL(mknod("/dev/random", S_IFCHR | 0666, makedev(1, 8)));
// 创建字符设备节点/dev/urandom,主设备号为1,次设备号为9,权限crw-rw-rw-
CHECKCALL(mknod("/dev/urandom", S_IFCHR | 0666, makedev(1, 9)));
// 日志包装器(log wrapper)需要在 ueventd 运行之前运行,因此需要进行一些初始化操作
// 创建字符设备节点/dev/ptmx,主设备号为5,次设备号为2,权限crw-rw-rw-
CHECKCALL(mknod("/dev/ptmx", S_IFCHR | 0666, makedev(5, 2)));
// 创建字符设备节点/dev/null,主设备号为1,次设备号为3,权限crw-rw-rw-
CHECKCALL(mknod("/dev/null", S_IFCHR | 0666, makedev(1, 3)));
/*
挂载一个 tmpfs 文件系统到 /mnt 目录,以便第一阶段启动过程中
挂载 /mnt/{vendor,product}/ 目录的子目录。其他的,放在第二阶段通过rc文件解析来加载
*/
CHECKCALL(mount("tmpfs", "/mnt", "tmpfs", MS_NOEXEC | MS_NOSUID | MS_NODEV,
"mode=0755,uid=0,gid=1000"));
// 创建权限值为0755的目录/mnt/vendor
CHECKCALL(mkdir("/mnt/vendor", 0755));
// 创建权限值为0755的目录/mnt/product
CHECKCALL(mkdir("/mnt/product", 0755));
// /debug_ramdisk目录的作用,即用于保存来自debug ramdisk
// 文件系统中的额外文件。这些文件通常用于调试和故障排除目的
// 将文件系统tmpfs挂载到/debug_ramdisk目录下
CHECKCALL(mount("tmpfs", "/debug_ramdisk", "tmpfs", MS_NOEXEC | MS_NOSUID | MS_NODEV,
"mode=0755,uid=0,gid=0"));
// /second_stage_resources is used to preserve files from first to second
// stage init
// 将文件系统tmpfs挂载到/second_stage_resources目录下
CHECKCALL(mount("tmpfs", kSecondStageRes, "tmpfs", MS_NOEXEC | MS_NOSUID | MS_NODEV,
"mode=0755,uid=0,gid=0"))
#undef CHECKCALL
// 标准输入、标准输出和标准错误输出重定向到/dev/null设备文件中
SetStdioToDevNull(argv);
// Now that tmpfs is mounted on /dev and we have /dev/kmsg, we can actually
// talk to the outside world...
// 初始化kernel的日志
InitKernelLogging(argv);
// 打印上述使用CHECKCALL宏定义执行出错的命令与error code
if (!errors.empty()) {
for (const auto& [error_string, error_errno] : errors) {
LOG(ERROR) << error_string << " " << strerror(error_errno);
}
LOG(FATAL) << "Init encountered errors starting first stage, aborting";
}
LOG(INFO) << "init first stage started!";
// 打开根目录"/"
auto old_root_dir = std::unique_ptr<DIR, decltype(&closedir)>{opendir("/"), closedir};
if (!old_root_dir) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Could not opendir(\"/\"), not freeing ramdisk";
}
struct stat old_root_info;
// 用stat函数获取根目录"/"的文件信息
if (stat("/", &old_root_info) != 0) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Could not stat(\"/\"), not freeing ramdisk";
old_root_dir.reset();
}
// 该宏ALLOW_FIRST_STAGE_CONSOLE 由system/core/init/Android.mk中定义,
// 只有user,eng版本,ALLOW_FIRST_STAGE_CONSOLE =1
// FirstStageConsole:从cmdline,boot获取androidboot.first_stage_console=xx的值,
// 如果没有获取到,直接返回FirstStageConsoleParam::DISABLED
auto want_console = ALLOW_FIRST_STAGE_CONSOLE ? FirstStageConsole(cmdline, bootconfig) : 0;
// 记录当前系统时间到module_start_time
boot_clock::time_point module_start_time = boot_clock::now();
int module_count = 0;
// ForceNormalBoot:从cmdline,bootconfig是否有androidboot.force_normal_boot=1,
// LoadKernelModules:从/lib/modules insmod内核模块,并把加载到的内核模块数量保存到module_count
if (!LoadKernelModules(IsRecoveryMode() && !ForceNormalBoot(cmdline, bootconfig), want_console,
module_count)) {
if (want_console != FirstStageConsoleParam::DISABLED) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to load kernel modules, starting console";
} else {
LOG(FATAL) << "Failed to load kernel modules";
}
}
if (module_count > 0) {
auto module_elapse_time = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(
boot_clock::now() - module_start_time);
//设置INIT_MODULE_DURATION_MS=module_elapse_time(启动内核模块花费时间到)到环境变量中
setenv(kEnvInitModuleDurationMs, std::to_string(module_elapse_time.count()).c_str(), 1);
LOG(INFO) << "Loaded " << module_count << " kernel modules took "
<< module_elapse_time.count() << " ms";
}
bool created_devices = false;
if (want_console == FirstStageConsoleParam::CONSOLE_ON_FAILURE) {
if (!IsRecoveryMode()) {
created_devices = DoCreateDevices();
if (!created_devices){
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to create device nodes early";
}
}
StartConsole(cmdline);
}
// 判断/system/etc/ramdisk/build.prop文件是否存在
if (access(kBootImageRamdiskProp, F_OK) == 0) {
// dest = "/second_stage_resources/system/etc/ramdisk/build.prop"
std::string dest = GetRamdiskPropForSecondStage();
// dir = "/second_stage_resources/system/etc/ramdisk/"
std::string dir = android::base::Dirname(dest);
std::error_code ec;
// 创建dir目录
if (!fs::create_directories(dir, ec) && !!ec) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Can't mkdir " << dir << ": " << ec.message();
}
// 复制/system/etc/ramdisk/build.prop文件到/second_stage_resources/system/etc/ramdisk/目录中
if (!fs::copy_file(kBootImageRamdiskProp, dest, ec)) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Can't copy " << kBootImageRamdiskProp << " to " << dest << ": "
<< ec.message();
}
LOG(INFO) << "Copied ramdisk prop to " << dest;
}
/*
如果设备的 /force_debuggable 文件存在,则第二阶段调用SecondStageMain的进程会使用userdebug版本的SELinux Policy,
同时还会解析adb_debug.prop属性文件,以便在设备未锁定的情况下(bootloader解锁)允许使用adb root权限。
*/
// 判断/force_debuggable文件是否存在
if (access("/force_debuggable", F_OK) == 0) {
std::error_code ec; // to invoke the overloaded copy_file() that won't throw.
// 复制文件/adb_debug.prop到/debug_ramdisk/adb_debug.prop文件
// 复制文件/userdebug_plat_sepolicy.cil到/debug_ramdisk/userdebug_plat_sepolicy.cil文件
if (!fs::copy_file("/adb_debug.prop", kDebugRamdiskProp, ec) ||
!fs::copy_file("/userdebug_plat_sepolicy.cil", kDebugRamdiskSEPolicy, ec)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to setup debug ramdisk";
} else {
// setenv for second-stage init to read above kDebugRamdisk* files.
/*
复制成功后设置INIT_FORCE_DEBUGGABLE的环境变量为1,会用于第二阶段调用SecondStageMain的init读取
kDebugRamdiskRrop(/debug_ramdisk/adb_debug.prop)文件:
SecondStageMain->PropertyInit->PropertyLoadBootDefaults。
*/
setenv("INIT_FORCE_DEBUGGABLE", "true", 1);
}
}
// ForceNormalBoot:从cmdline,bootconfig是否有androidboot.force_normal_boot=1,
if (ForceNormalBoot(cmdline, bootconfig)) {
mkdir("/first_stage_ramdisk", 0755);
// SwitchRoot() must be called with a mount point as the target, so we bind mount the
// target directory to itself here.
// 重新挂载/first_stage_ramdisk目录
if (mount("/first_stage_ramdisk", "/first_stage_ramdisk", nullptr, MS_BIND, nullptr) != 0) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Could not bind mount /first_stage_ramdisk to itself";
}
// 将根目录由"/"切换到/first_stage_ramdisk
SwitchRoot("/first_stage_ramdisk");
}
// 挂载 system、vendor 、product等系统分区
if (!DoFirstStageMount(!created_devices)) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Failed to mount required partitions early ...";
}
struct stat new_root_info;
if (stat("/", &new_root_info) != 0) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Could not stat(\"/\"), not freeing ramdisk";
old_root_dir.reset();
}
if (old_root_dir && old_root_info.st_dev != new_root_info.st_dev) {
FreeRamdisk(old_root_dir.get(), old_root_info.st_dev);
}
// 初始化安全框架 Android Verified Boot,用于防止系统文件本身被篡改、防止系统回滚,以免回滚系统利用以前的漏洞。
// 包括Secure Boot, verified boot 和 dm-verity(会校验只读分区大小,若只读分区二进制改变则可能上被串改了,例如 user强制root),
// 原理都是对二进制文件进行签名,在系统启动时进行认证,确保系统运行的是合法的二进制镜像文件。其中认证的范围涵盖:bootloader,boot.img,system.img。
// 此处是在recovery模式下初始化avb的版本,不是recovery模式直接跳过
SetInitAvbVersionInRecovery();
// 设置环境变量FIRST_STAGE_STARTED_AT=start_time,即FirstStageMain方法启动时的时间
setenv(kEnvFirstStageStartedAt, std::to_string(start_time.time_since_epoch().count()).c_str(),
1);
const char* path = "/system/bin/init";
const char* args[] = {path, "selinux_setup", nullptr};
auto fd = open("/dev/kmsg", O_WRONLY | O_CLOEXEC);
// 将标准输出重定向到/dev/kmsg
dup2(fd, STDOUT_FILENO);
// 将标准错误重定向到/dev/kmsg
dup2(fd, STDERR_FILENO);
close(fd);
// execv()函数不会创建新的进程,而是将当前进程替换为新的程序
// path为执行程序的路径:/system/bin/init
// args为传递的参数:selinux_setup
// 执行,即重新回到system/core/init/main.cpp,执行第二阶段
execv(path, const_cast<char**>(args));
// execv() only returns if an error happened, in which case we
// panic and never fall through this conditional.
PLOG(FATAL) << "execv(\"" << path << "\") failed";
return 1;
}
1.1、InstallRebootSignalHandlers
void InstallRebootSignalHandlers() {
// Linux panic 状态:内核会终止所有正在运行的进程,并输出一些有关错误的诊断信息,最终系统会被强制关机或者重启
// 当init崩溃时,我们在开发构建(userdebug,eng版本)中更倾向于重启到bootloader,而不是像linux中进入panic状态,
// 因为这将防止boot循环错误的配置,这同时也允许开发人员和测试场轻松恢复
struct sigaction action;
memset(&action, 0, sizeof(action));
sigfillset(&action.sa_mask);
// 信号处理函数
action.sa_handler = [](int signal) {
// These signal handlers are also caught for processes forked from init, however we do not
// want them to trigger reboot, so we directly call _exit() for children processes here.
if (getpid() != 1) {
_exit(signal);
}
// Calling DoReboot() or LOG(FATAL) is not a good option as this is a signal handler.
// RebootSystem uses syscall() which isn't actually async-signal-safe, but our only option
// and probably good enough given this is already an error case and only enabled for
// development builds.
InitFatalReboot(signal);
};
// SA_RESTART 表示如果系统调用被中断,自动重新启动该系统调用。
action.sa_flags = SA_RESTART;
// SIGABRT:中止信号,通常是由程序调用abort函数发送的
sigaction(SIGABRT, &action, nullptr);
// SIGBUS:总线错误信号,通常由进程对不能执行操作的地址进行访问时产生,例如非对齐访问或虚拟地址在物理内存上没有映射等情况
sigaction(SIGBUS, &action, nullptr);
// SIGFPE:浮点异常信号,通常由浮点运算错误产生
sigaction(SIGFPE, &action, nullptr);
// SIGILL:非法指令信号,通常由进程试图执行未定义的指令或数据错误引起
sigaction(SIGILL, &action, nullptr);
// SIGSEGV:段错误信号,通常由进程对非法的地址空间进行访问时产生
sigaction(SIGSEGV, &action, nullptr);
#if defined(SIGSTKFLT)
// SIGSTKFLT:协处理器栈故障
sigaction(SIGSTKFLT, &action, nullptr);
#endif
// SIGSYS:系统调用错误信号。当一个进程调用一个不存在的系统调用时,内核会发送 SIGSYS 信号给该进程,告知它系统调用发生错误。
sigaction(SIGSYS, &action, nullptr);
// SIGTRAP:调试器或进程自身触发的信号,用于暂停进程并允许调试器执行某些操作。通常,调试器会使用SIGTRAP在进程中设置断点或跟踪执行路径。
sigaction(SIGTRAP, &action, nullptr);
}
android-12.0.0_r28/system/core/init/reboot_utils.cpp
void __attribute__((noreturn)) InitFatalReboot(int signal_number) {
auto pid = fork();
if (pid == -1) {
// fork失败,重启到bootloader(init_fatal_reboot_target = "bootloader")
RebootSystem(ANDROID_RB_RESTART2, init_fatal_reboot_target);
} else if (pid == 0) {
// 尽管父进程负责打印当前进程与当前线程的堆栈信息,也负责关机重启的操作。
// 为了安全起见,fork一个子进程也要为我们关机重启操作,就是确保关机重启操作。
sleep(5);
RebootSystem(ANDROID_RB_RESTART2, init_fatal_reboot_target);
}
// In the parent, let's try to get a backtrace then shutdown.
LOG(ERROR) << __FUNCTION__ << ": signal " << signal_number;
// 创建当前进程与当前线程的堆栈信息类
std::unique_ptr<Backtrace> backtrace(
Backtrace::Create(BACKTRACE_CURRENT_PROCESS, BACKTRACE_CURRENT_THREAD));
// 用于获取堆栈信息,并将结果保存在backtrace对象中
if (!backtrace->Unwind(0)) {
LOG(ERROR) << __FUNCTION__ << ": Failed to unwind callstack.";
}
// backtrace->->NumFrames():backtrace保存的堆栈帧数量
for (size_t i = 0; i < backtrace->->NumFrames(); i++) {
// backtrace->FormatFrameData(i):将指定位置的堆栈帧信息格式化为一段字符串
// 然后通过LOG输出
LOG(ERROR) << backtrace->FormatFrameData(i);
}
// 读取/proc/cmdline或者/proc/bootconifg,是否含有roidboot.init_fatal_panic=true,来判断init_fatal_panic的bool值
if (init_fatal_panic) {
LOG(ERROR) << __FUNCTION__ << ": Trigger crash";
//对/proc/sysrq-trigger写入字符‘c’
android::base::WriteStringToFile("c", PROC_SYSRQ);
LOG(ERROR) << __FUNCTION__ << ": Sys-Rq failed to crash the system; fallback to exit().";
// 退出当前进程
_exit(signal_number);
}
// 重启方法调用
RebootSystem(ANDROID_RB_RESTART2, init_fatal_reboot_target);
}
void __attribute__((noreturn)) RebootSystem(unsigned int cmd, const std::string& rebootTarget) {
LOG(INFO) << "Reboot ending, jumping to kernel";
// 判断init进程是否有重启能力,没有则直接退出
if (!IsRebootCapable()) {
// On systems where init does not have the capability of rebooting the
// device, just exit cleanly.
exit(0);
}
switch (cmd) {
case ANDROID_RB_POWEROFF:
// linux系统中一个标准的用户空间命令reboot,用户空间执行
reboot(RB_POWER_OFF);
break;
case ANDROID_RB_RESTART2:
// syscall函数是一种特殊的函数调用,用于从用户空间向内核空间请求服务
// 下面语句用于在内核中执行reboot操作,内核空间执行
syscall(__NR_reboot, LINUX_REBOOT_MAGIC1, LINUX_REBOOT_MAGIC2,
LINUX_REBOOT_CMD_RESTART2, rebootTarget.c_str());
break;
case ANDROID_RB_THERMOFF:
// 当设备温度过高时,系统会尝试通过降低 CPU 频率等方式来降低温度。
// 但如果这些措施都无法降低温度,那么系统就会执行热重启操作,这是一种比正常重启更快的方式,以防止硬件过热而导致设备损坏。
// "ro.thermal_warmreset" 这个属性控制热重启功能的开启和关闭
if (android::base::GetBoolProperty("ro.thermal_warmreset", false)) {
LOG(INFO) << "Try to trigger a warm reset for thermal shutdown";
static constexpr const char kThermalShutdownTarget[] = "shutdown,thermal";
// 调用内核空间执行reboot
syscall(__NR_reboot, LINUX_REBOOT_MAGIC1, LINUX_REBOOT_MAGIC2,
LINUX_REBOOT_CMD_RESTART2, kThermalShutdownTarget);
} else {
// 调用用户空间的reboot方法
reboot(RB_POWER_OFF);
}
break;
}
// In normal case, reboot should not return.
PLOG(ERROR) << "reboot call returned";
// 向进程发送一个SIGABRT信号,使进程终止
abort();
}
第二阶段调用SetupSelinux
system/core/init/main.cpp
if (!strcmp(argv[1], "selinux_setup")) {
// 创建Selinux
return SetupSelinux(argv);
}
system/core/init/selinux.cpp
// The SELinux setup process is carefully orchestrated around snapuserd. Policy
// must be loaded off dynamic partitions, and during an OTA, those partitions
// cannot be read without snapuserd. But, with kernel-privileged snapuserd
// running, loading the policy will immediately trigger audits.
//
// We use a five-step process to address this:
// (1) Read the policy into a string, with snapuserd running.
// (2) Rewrite the snapshot device-mapper tables, to generate new dm-user
// devices and to flush I/O.
// (3) Kill snapuserd, which no longer has any dm-user devices to attach to.
// (4) Load the sepolicy and issue critical restorecons in /dev, carefully
// avoiding anything that would read from /system.
// (5) Re-launch snapuserd and attach it to the dm-user devices from step (2).
//
// After this sequence, it is safe to enable enforcing mode and continue booting.
int SetupSelinux(char** argv) {
// 将标准输入、标准输出和标准错误输出重定向到/dev/null设备文件,
// 在运行时避免产生不必要的输出或接收用户的输入,从而避免产生垃圾信息和消耗系统资源。
SetStdioToDevNull(argv);
// 初始化kernel的日志
InitKernelLogging(argv);
// 该宏REBOOT_BOOTLOADER_ON_PANIC由system/core/init/Android.mk中定义,
// 只有user,eng版本,REBOOT_BOOTLOADER_ON_PANIC=1
if (REBOOT_BOOTLOADER_ON_PANIC) {
// init信号处理器,当init crash,打印当前进程的回溯信息对象(调用栈信息),并重启到 bootLoader,
InstallRebootSignalHandlers();
}
// 记录当前时间start_time
boot_clock::time_point start_time = boot_clock::now();
// 用于检查并挂载缺失的系统分区。具体来说,
// 该函数会依次检查 /system、/vendor、/odm 这些分区是否挂载成功,
// 如果没有挂载成功,则会尝试挂载它们。
MountMissingSystemPartitions();
// 注册回调,用来设置需要写入kmsg的selinux日志
// 对于安全性和调试都非常重要,可以帮助管理员及时发现和解决 SELinux 相关的安全问题。
SelinuxSetupKernelLogging();
LOG(INFO) << "Opening SELinux policy";
// Read the policy before potentially killing snapuserd.
std::string policy;
// snapuserd 是 Android 操作系统中的一个进程,它负责管理 Snapshots 镜像的创建、合并和恢复等操作。
// Snapshots 是一种存储系统状态的技术,它可以让系统在崩溃或其他异常情况下快速恢复到之前的状态,从而提高系统的可靠性和可用性。
// 在 Android 系统中,snapuserd 进程通常在系统启动时就会自动启动,并一直运行在后台。
// 在杀死snapuserd前,读取 SELinux 策略
ReadPolicy(&policy);
// 1.在 Android 系统中,通常会使用 SELinux 上下文转换来提高系统的安全性。
// 2.具体而言,当进程需要执行某些特权操作时,完成 Snapuserd 进程的 SELinux 上下文转换过程
// 3.可以将其当前的 SELinux 上下文转换为具有更高权限的上下文,以完成相应的操作。
// 4.转换完成后,系统会自动将进程的 SELinux 上下文转换回原始的上下文,以保证系统的安全性。
// 创建 Snapuserd 进程所需的 SELinux 上下文
auto snapuserd_helper = SnapuserdSelinuxHelper::CreateIfNeeded();
if (snapuserd_helper) {
// Kill the old snapused to avoid audit messages. After this we cannot
// read from /system (or other dynamic partitions) until we call
// FinishTransition().
// 启动 Snapuserd 进程的 SELinux 上下文转换过程,以授予其必要的特权权限,
// 并确保其能够正常运行。
snapuserd_helper->StartTransition();
}
// 加载 SELinux 策略
LoadSelinuxPolicy(policy);
if (snapuserd_helper) {
// Before enforcing, finish the pending snapuserd transition.
// 完成 Snapuserd 进程的 SELinux 上下文转换过程,
// 转换回原始的SELinux上下文
snapuserd_helper->FinishTransition();
snapuserd_helper = nullptr;
}
// 设置 SELinux 系统的执行模式
SelinuxSetEnforcement();
// We're in the kernel domain and want to transition to the init domain. File systems that
// store SELabels in their xattrs, such as ext4 do not need an explicit restorecon here,
// but other file systems do. In particular, this is needed for ramdisks such as the
// recovery image for A/B devices.
// 该方法用于恢复 /system/bin/init 文件的 SELinux 安全上下文。
// 在 SELinux 系统中,每个文件都有一个对应的安全上下文,用于控制文件的访问权限。
// 如果文件的安全上下文被修改或者损坏,
// selinux_android_restorecon() 函数来重新设置安全上下文。
if (selinux_android_restorecon("/system/bin/init", 0) == -1) {
PLOG(FATAL) << "restorecon failed of /system/bin/init failed";
}
// 设置环境变量SELINUX_STARTED_AT=start_time,即SetupSelinux方法启动时的时间
setenv(kEnvSelinuxStartedAt, std::to_string(start_time.time_since_epoch().count()).c_str(), 1);
const char* path = "/system/bin/init";
const char* args[] = {path, "second_stage", nullptr};
// execv()函数不会创建新的进程,而是将当前进程替换为新的程序
// path为执行程序的路径:/system/bin/init
// args为传递的参数:second_stage
// 执行,即重新回到system/core/init/main.cpp,执行第三阶段
execv(path, const_cast<char**>(args));
// execv() only returns if an error happened, in which case we
// panic and never return from this function.
PLOG(FATAL) << "execv(\"" << path << "\") failed";
return 1;
}
2.1、SetStdioToDevNull
android-12.0.0_r28/system/core/init/util.cpp
void SetStdioToDevNull(char** argv) {
int fd = open("/dev/null", O_RDWR); // NOLINT(android-cloexec-open)
if (fd == -1) {
int saved_errno = errno;
android::base::InitLogging(argv, &android::base::KernelLogger, InitAborter);
errno = saved_errno;
PLOG(FATAL) << "Couldn't open /dev/null";
}
// 将标准输入、标准输出和标准错误输出重定向到/dev/null设备文件,
dup2(fd, STDIN_FILENO);
dup2(fd, STDOUT_FILENO);
dup2(fd, STDERR_FILENO);
if (fd > STDERR_FILENO) close(fd);
}
2.2、InitKernelLogging
android-12.0.0_r28/system/core/init/util.cpp
void InitKernelLogging(char** argv) {
SetFatalRebootTarget();
android::base::InitLogging(argv, &android::base::KernelLogger, InitAborter);
}
android-12.0.0_r28/system/core/init/reboot_utils.cpp
void SetFatalRebootTarget(const std::optional<std::string>& reboot_target) {
std::string cmdline;
android::base::ReadFileToString("/proc/cmdline", &cmdline);
cmdline = android::base::Trim(cmdline);
const std::string kInitFatalPanicParamString = "androidboot.init_fatal_panic";
if (cmdline.find(kInitFatalPanicParamString) == std::string::npos) {
init_fatal_panic = false;
ImportBootconfig(
[kInitFatalPanicParamString](const std::string& key, const std::string& value) {
if (key == kInitFatalPanicParamString && value == "true") {
init_fatal_panic = true;
}
});
} else {
const std::string kInitFatalPanicString = kInitFatalPanicParamString + "=true";
init_fatal_panic = cmdline.find(kInitFatalPanicString) != std::string::npos;
}
if (reboot_target) {
init_fatal_reboot_target = *reboot_target;
return;
}
const std::string kRebootTargetString = "androidboot.init_fatal_reboot_target";
auto start_pos = cmdline.find(kRebootTargetString);
if (start_pos == std::string::npos) {
ImportBootconfig([kRebootTargetString](const std::string& key, const std::string& value) {
if (key == kRebootTargetString) {
init_fatal_reboot_target = value;
}
});
// We already default to bootloader if no setting is provided.
} else {
const std::string kRebootTargetStringPattern = kRebootTargetString + "=";
start_pos += sizeof(kRebootTargetStringPattern) - 1;
auto end_pos = cmdline.find(' ', start_pos);
// if end_pos isn't found, then we've run off the end, but this is okay as this is the last
// entry, and -1 is a valid size for string::substr();
auto size = end_pos == std::string::npos ? -1 : end_pos - start_pos;
init_fatal_reboot_target = cmdline.substr(start_pos, size);
}
}
上面的代码其实,就是从"/proc/cmdline","/proc/bootimage"的读取:
- 是否含有”
androidboot.init_fatal_panic=true“来确定init_fatal_panic是true还是false - 读取到"
androidboot.init_fatal_reboot_target",然后赋值到init_fatal_reboot_target变量(初始化值为bootloader) - 总结来说,代码会通过这两个值,用来设置当内核日志记录发生致命错误时的行为(比如是否打印)
第三阶段调用SecondStageMain
system/core/init/main.cpp
if (!strcmp(argv[1], "second_stage")) {
return SecondStageMain(argc, argv);
}
system/core/init/init.cpp
int SecondStageMain(int argc, char** argv) {
// 该宏REBOOT_BOOTLOADER_ON_PANIC由system/core/init/Android.mk中定义,
// 只有user,eng版本,REBOOT_BOOTLOADER_ON_PANIC=1
if (REBOOT_BOOTLOADER_ON_PANIC) {
// init信号处理器,当init crash,打印当前进程的回溯信息对象(调用栈信息),并重启到 bootLoader,
InstallRebootSignalHandlers();
}
// 记录当前系统时间到module_start_time }
boot_clock::time_point start_time = boot_clock::now();
trigger_shutdown = [](const std::string& command) { shutdown_state.TriggerShutdown(command); };
// 将标准输入、标准输出和标准错误输出重定向到/dev/null设备文件,
// 在运行时避免产生不必要的输出或接收用户的输入,从而避免产生垃圾信息和消耗系统资源。
SetStdioToDevNull(argv);
// 初始化kernel的日志
InitKernelLogging(argv);
LOG(INFO) << "init second stage started!";
// 更新环境变量$PATH,第二阶段 init 比第一阶段 init 更新,因为第一阶段 init 是第一次设置的。
if (setenv("PATH", _PATH_DEFPATH, 1) != 0) {
PLOG(FATAL) << "Could not set $PATH to '" << _PATH_DEFPATH << "' in second stage";
}
/*
SA_RESTART :标志表示如果某个系统调用因为接收到信号而被中断,那么该系统调用将会被自动重启。
SIGPIPE 信号:在 Linux 中表示管道或者套接字已经被关闭,但是程序还在试图向其写入数据;
如果不处理这个信号,程序会立即退出,因为默认情况下 Linux 系统会向进程发送 SIGPIPE 信号并终止进程。
由于 Init 进程不能因为与其他进程的依赖关系而崩溃,
因此它会忽略 SIGPIPE 信号,并在调用处直接处理 EPIPE 错误。
需要注意的是,进程如将信号设置为SIG_IGN,在调用 exec后会被继承,但自定义的信号处理程序(action.sa_handler = [](int) {})不会。
由于我们不希望子进程忽略 SIGPIPE 信号,所以在信号处理函数中设置一个空函数。
这样,对于 Init 进程,SIGPIPE 信号被忽略,而对于子进程,SIGPIPE 信号会按照默认方式处理。
*/
{
struct sigaction action = {.sa_flags = SA_RESTART};
action.sa_handler = [](int) {};
// 设置进程在接收到 SIGPIPE 信号时的处理方式。
sigaction(SIGPIPE, &action, nullptr);
}
/*
设置 init 进程及其衍生的子进程中设置 oom_adj 属性
oom_adj 是一个用于控制进程被内核杀死的顺序的属性。
oom_adj 值越小的进程越不容易被杀死,而oom_adj 值较高的进程则更容易被杀死
DEFAULT_OOM_SCORE_ADJUST=-1000,
将/proc/1/oom_score_adj写值-1000,设置oom_adj,其中1是init的PID
*/
if (auto result =
WriteFile("/proc/1/oom_score_adj", StringPrintf("%d", DEFAULT_OOM_SCORE_ADJUST));
!result.ok()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to write " << DEFAULT_OOM_SCORE_ADJUST
<< " to /proc/1/oom_score_adj: " << result.error();
}
/*
是用来获取进程的会话密钥环的标识符:
会话密钥环是 Linux 内核中的一种机制,用于存储进程会话中使用的密钥。
Android 也使用了这种机制,用于存储应用程序的加密密钥等敏感信息。
通过调用 keyctl_get_keyring_ID() 函数获取会话密钥环的标识符,
Android 系统可以在应用程序运行时访问会话密钥环中存储的密钥,
从而保护应用程序中的敏感数据不受未授权的访问。
*/
keyctl_get_keyring_ID(KEY_SPEC_SESSION_KEYRING, 1);
/*
这个文件描述符的创建是为了让其他进程(如后台固件加载程序)
E.g:
system/core/init/firmware_handler.cpp(负责解析里固件配置)
static bool IsBooting() {
return access("/dev/.booting", F_OK) == 0;
}
能够检查 /dev/.booting 文件的存在来确定系统是否正在启动,是第四阶段调用ueventd_main里面使用到
*/
close(open("/dev/.booting", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_CLOEXEC, 0000));
// 当设备的bootloader已解锁时,查看是否需要加载一些调试的系统属性去允许adb root。
// 获取环境变量$INIT_FORCE_DEBUGGABLE的,再赋值到force_debuggable_env
const char* force_debuggable_env = getenv("INIT_FORCE_DEBUGGABLE");
bool load_debug_prop = false;
// AvbHandle::IsDeviceUnlocked():设备的bootloader是否解锁
if (force_debuggable_env && AvbHandle::IsDeviceUnlocked()) {
load_debug_prop = "true"s == force_debuggable_env;
}
// 清除环境变量$INIT_FORCE_DEBUGGABLE的值
unsetenv("INIT_FORCE_DEBUGGABLE");
// 卸载/debug_ramdisk,让下面的PropertyInit中不会加载它里面的xxx.prop文件
// 如果load_debug_prop=false,则卸载/debug_ramdisk
if (!load_debug_prop) {
UmountDebugRamdisk();
}
// 初始化属性服务相关的,包括属性的selinux上下主,属性的key-value通过MMAP映射到全局,供所有进程使用
PropertyInit();
// 在属性服务读取.prop文件后,将卸载/second_stage_resources
UmountSecondStageRes();
// 在属性服务读取.prop文件后,如果load_debug_prop=true,则卸载/debug_ramdisk
if (load_debug_prop) {
UmountDebugRamdisk();
}
// 将一个 tmpfs 文件系统挂载到 /apex 目录和/linkerconfig下。
// 具体来说,为应用程序提供一个可写的目录,用于存储应用程序的数据和配置信息
MountExtraFilesystems();
// 设置内核日志记录的SELinux标签,以确保内核记录的日志中包含SELinux标签信息
// 对于安全性和调试都非常重要,可以帮助管理员及时发现和解决 SELinux 相关的安全问题。
SelinuxSetupKernelLogging();
// 初始化SELinux标签库,以便可以将SELinux标签应用于文件和目录。
SelabelInitialize();
// 根据文件上下文信息,恢复系统中文件和目录的SELinux安全上下文。
SelinuxRestoreContext();
// 这里的Epoll是在system/core/init/epoll.cpp对<sys/epoll>的封装的一个类
Epoll epoll;
// 创建一个epoll的fd
if (auto result = epoll.Open(); !result.ok()) {
PLOG(FATAL) << result.error();
}
// 防止子进程意外终止或被中断,从而导致父进程无法正常工作;监听子进程终止或者中断事件,回收子进程
InstallSignalFdHandler(&epoll);
/*
Init进程轮询各种fd以等待各种输入。
以前它使用一个阻塞套接字来等待属性更改,该套接字包含与更改相关的信息,然而,很容易填充该套接字并使系统死锁。
现在我们使用锁直接在属性线程中处理属性更改,但是我们仍然必须唤醒epoll来通知init有更改要处理,
因此我们使用此FD。它是非阻塞的,不管WakeMainInitThread()被调用了多少次,只关心epoll会被唤醒。
*/
InstallInitNotifier(&epoll);
/*
之前PropertyInit()初始化了属性服务,这里将开始属性服务,
其实它就是创建socketpair(一对一传递信息)与socket(一对8个连接),去处理客户端发来的请求,
决定是更新属性值还是新增属性值
*/
StartPropertyService(&property_fd);
/*
设置:
ro.boottime.init:linux forc出init进程当时的时间,
ro.boottime.init.first_stage:第一阶段调用FirstStageMain所用的时间
ro.boottime.init.selinux:第二阶段调用SetupSelinux所用的时间
ro.boottime.init.modules:第一阶段调用FirstStageMain时,加载内核模块所用的时间
*/
RecordStageBoottimes(start_time);
// Set libavb version for Framework-only OTA match in Treble build.
// 在升级过程中使用的一种“框架级别”(Framework-only)OTA匹配方式需要,
// 使用 libavb 库的版本信息来进行匹配,而某些较旧的设备没有在sysfs中
// 报告AVB 版本,因此 init 进程需要在这些设备上设置 ro.boot.avb_version 属性,以便进行正确的 OTA 匹配。
// 环境变量INIT_AVB_VERSION,是在FistStageMain->DoFirstStageMount(!created_devices) 可能会设置的
if (const char* avb_version = getenv("INIT_AVB_VERSION"); avb_version != nullptr) {
SetProperty("ro.boot.avb_version", avb_version);
}
unsetenv("INIT_AVB_VERSION");
// 挂载/(system|product)/vendor_overlay/<ver>到 /vendor分区上
fs_mgr_vendor_overlay_mount_all();
// 检测设备是否支持 OEM 解锁功能,并根据 Verified Boot 状态来设置 OEM 锁定状态的属性值。
export_oem_lock_status();
MountHandler mount_handler(&epoll);
SetUsbController();
SetKernelVersion();
// 内置函数的映射表,这个映射表是由 /init.rc 文件中的 service 和 on 命令生成的可调用对象的集合。
const BuiltinFunctionMap& function_map = GetBuiltinFunctionMap();
/*
将内置函数映射表存储到 Action 类中的function_map_,以便后续的操作可以使用这些内置函数。
这些内置函数可以在 /init.rc 文件中定义,并且可以在系统启动过程中被 init 进程调用。
这些内置函数包括一些基本操作,比如创建目录mkdir、启动服务start等,它们为系统启动过程提供了基础支持。
eg:system/core/roodir/init.rc中有,如下
on early-init
write /proc/sys/kernel/sysrq 0
意义:当early-init 触发器被触发,会调用内置函数write,Action类就会从 function_map 中查找该函数(映射->>do_write),
并调用它来执行相应的操作。
*/
Action::set_function_map(&function_map);
if (!SetupMountNamespaces()) {
PLOG(FATAL) << "SetupMountNamespaces failed";
}
// 在 Android 中,每个应用程序和系统组件都被分配了一个特定的安全上下文,该上下文指定了它们可以访问的资源和执行的操作。
// Subcontext 类就是用来管理这些安全上下文的,它可以在初始化过程中为子进程创建特定的安全上下文,以确保它们在访问系统资源时具有适当的权限。
// 为/vendor,/odm ,设置u:r:vendor_init:s0的子上下文
InitializeSubcontext();
// ActionManager 类负责管理系统启动时执行的所有操作(Action)。
// 在启动过程中,init 进程会解析 init.rc 脚本,从中读取各个 Service 的定义,
// 然后构建对应的 Action 并加入到 ActionManager 中。
// ActionManager 会按照事先定义好的顺序执行这些 Action,以启动系统中所有的服务。
ActionManager& am = ActionManager::GetInstance();
// ServiceList 类则是用来管理系统中所有的服务(Service)的。
// 在系统启动时,init 进程会读取 init.rc 中定义的 Service,并创建对应的 Service 实例。
// 这些 Service 实例会被 ServiceList 管理起来,以便其他组件可以方便地查询和控制这些服务。
// 例如,init 进程需要知道哪些服务已经启动成功、哪些服务启动失败等等,都需要通过 ServiceList 来查询。
ServiceList& sm = ServiceList::GetInstance();
// 解析/system/etc/init/hw/init.rc,/system/etc/init目录
// 解析/system_ext/etc/init,/vendor/etc/init,/odm/etc/init,/product/etc/init目录所以*.rc的信息到ActionManager与ServiceList中
LoadBootScripts(am, sm);
// Turning this on and letting the INFO logging be discarded adds 0.2s to
// Nexus 9 boot time, so it's disabled by default.
if (false) DumpState();
// Make the GSI status available before scripts start running.
// 根据/metadata/gsi/dsu/booted文件是否存在,设置系统属性ro.gsid.image_running的值
auto is_running = android::gsi::IsGsiRunning() ? "1" : "0";
SetProperty(gsi::kGsiBootedProp, is_running);
// 根据/metadata/gsi/dsu/install_status文件是否存在,设置系统属性gsid.image_installed的值
auto is_installed = android::gsi::IsGsiInstalled() ? "1" : "0";
SetProperty(gsi::kGsiInstalledProp, is_installed);
// 用于设置 cgroup 的相关属性,这是 Android 系统中进行资源隔离和限制的一种手段。
am.QueueBuiltinAction(SetupCgroupsAction, "SetupCgroups");
// 用于设置内核指针泄漏保护机制,它可以限制用户空间程序访问内核空间的信息,从而增强系统的安全性。
am.QueueBuiltinAction(SetKptrRestrictAction, "SetKptrRestrict");
// 用于测试 PerfEvent 与 SELinux 之间的交互是否正常。
am.QueueBuiltinAction(TestPerfEventSelinuxAction, "TestPerfEventSelinux");
// 执行.rc文件中触发器为 on early-init 的语句
am.QueueEventTrigger("early-init");
// 等冷插拔设备初始化完成
am.QueueBuiltinAction(wait_for_coldboot_done_action, "wait_for_coldboot_done");
// ... so that we can start queuing up actions that require stuff from /dev.
am.QueueBuiltinAction(SetMmapRndBitsAction, "SetMmapRndBits");
Keychords keychords;
am.QueueBuiltinAction(
[&epoll, &keychords](const BuiltinArguments& args) -> Result<void> {
for (const auto& svc : ServiceList::GetInstance()) {
keychords.Register(svc->keycodes());
}
keychords.Start(&epoll, HandleKeychord);
return {};
},
"KeychordInit");
// Trigger all the boot actions to get us started.
// 执行.rc文件中触发器为on init的语句
am.QueueEventTrigger("init");
// 当设备处于充电模式时,不需要mount文件系统或者启动系统服务
// 充电模式下,将charger解发执行队列,否则把late-init触发执行队列
std::string bootmode = GetProperty("ro.bootmode", "");
if (bootmode == "charger") {
am.QueueEventTrigger("charger");
} else {
am.QueueEventTrigger("late-init");
}
// 基于属性当前状态 运行所有的属性触发器.
// 运行所有属性触发器(action),例如 on property
am.QueueBuiltinAction(queue_property_triggers_action, "queue_property_triggers");
// Restore prio before main loop
setpriority(PRIO_PROCESS, 0, 0);
while (true) {
// By default, sleep until something happens.
// 定义 epoll 超时变量,默认为无限等待
auto epoll_timeout = std::optional<std::chrono::milliseconds>{};
// 检查系统是否有关机的命令
auto shutdown_command = shutdown_state.CheckShutdown();
if (shutdown_command) {
// 如果系统有关机命令,则打印日志,并处理关机操作
LOG(INFO) << "Got shutdown_command '" << *shutdown_command
<< "' Calling HandlePowerctlMessage()";
HandlePowerctlMessage(*shutdown_command);
shutdown_state.set_do_shutdown(false);
}
// 依次执行每个action中携带command对应的执行函数
// 如果没有属性等待或执行服务运行,则执行一条命令action命令
if (!(prop_waiter_state.MightBeWaiting() || Service::is_exec_service_running())) {
am.ExecuteOneCommand();
}
// 如果系统没有在关机状态,那么检查是否有需要重新启动的进程,
// 如果有,则计算下一次执行该进程的时间并设置 epoll 等待时间为该时间。
if (!IsShuttingDown()) {
auto next_process_action_time = HandleProcessActions();
// If there's a process that needs restarting, wake up in time for that.
if (next_process_action_time) {
epoll_timeout = std::chrono::ceil<std::chrono::milliseconds>(
*next_process_action_time - boot_clock::now());
if (*epoll_timeout < 0ms) epoll_timeout = 0ms;
}
}
// 如果没有属性等待或执行服务运行,并且还有更多的命令需要执行,则立即唤醒 epoll。
if (!(prop_waiter_state.MightBeWaiting() || Service::is_exec_service_running())) {
if (am.HasMoreCommands()) epoll_timeout = 0ms;
}
// 循环等待事件发生,等待 epoll 唤醒,执行在 epoll 中注册的回调函数
auto pending_functions = epoll.Wait(epoll_timeout);
if (!pending_functions.ok()) {
LOG(ERROR) << pending_functions.error();
} else if (!pending_functions->empty()) {
// We always reap children before responding to the other pending functions. This is to
// prevent a race where other daemons see that a service has exited and ask init to
// start it again via ctl.start before init has reaped it.
ReapAnyOutstandingChildren();
for (const auto& function : *pending_functions) {
(*function)();
}
}
if (!IsShuttingDown()) {
HandleControlMessages();
SetUsbController();
}
}
return 0;
}
PropertyInit
android-12.0.0_r28/system/core/init/property_service.cpp
void PropertyInit() {
// 设置 SELinux 回调函数(PropertyAuditCallback),以便在属性服务修改属性值时进行安全审计audit。
selinux_callback cb;
cb.func_audit = PropertyAuditCallback;
selinux_set_callback(SELINUX_CB_AUDIT, cb);
// 创建属性服务的文件夹/dev/__properties__
mkdir("/dev/__properties__", S_IRWXU | S_IXGRP | S_IXOTH);
// 读plat_property_contexts文件,初始化到propertyInfo数据结构中,
// 然后创建trie数据结构,最后将trie数据结构写入到/dev/__properties__/property_info文件
CreateSerializedPropertyInfo();
if (__system_property_area_init()) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Failed to initialize property area";
}
if (!property_info_area.LoadDefaultPath()) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Failed to load serialized property info file";
}
// If arguments are passed both on the command line and in DT,
// properties set in DT always have priority over the command-line ones.
/*设置属性值:
ro.boot.hardware=xxx
ro.boot.mode=xxx
ro.boot.serialno=xxx
*/
ProcessKernelDt();
// 从/proc/cmdline读取是否含有androidboot=xxx,如有,刚设置ro.boot.androidboot=xxx
ProcessKernelCmdline();
// 从/proc/bootconfig读取是否含有androidboot=xxx,如有,刚设置ro.boot.androidboot=xxx
ProcessBootconfig();
/*
将下面ro.boot.xx的属性值复制给ro.xxx,即初始化ro.xxx的值
{ "ro.boot.serialno", "ro.serialno", UNSET, },
{ "ro.boot.mode", "ro.bootmode", "unknown", },
{ "ro.boot.baseband", "ro.baseband", "unknown", },
{ "ro.boot.bootloader", "ro.bootloader", "unknown", },
{ "ro.boot.hardware", "ro.hardware", "unknown", },
{ "ro.boot.revision", "ro.revision", "0", },
*/
ExportKernelBootProps();
/*
读取
1、/system/build.prop
2、/system_ext/etc/build.prop
如上失败,android R(30)设备及以下,则会解析如下两:
2.1、/system_ext/default.prop
2.2、/system_ext/build.prop
3、/vendor/default.prop
4、/vendor/build.prop
5、/vendor_dlkm/etc/build.prop
6、/odm_dlkm/etc/build.prop
7、/odm/etc/build.prop
如上失败,android P(28)设备及以下,则会解析如下两
7.1、/odm/default.prop
7.2、/odm/build.prop
8、/product/etc/build.prop
如上失败,android R(30)设备及以下,则会解析如下两
8.1、/product/default.prop
8.2、/product/build.prop
越是靠后读取的key-value,优先级越高,因为读取后会覆盖原来的值,优先级:
product > odm > odm_dlkm > vendor > system_ext > system,
最后将上面读取的数据通过MMAP映射到全局内存中,供所有进程访问
*/
PropertyLoadBootDefaults();
}
//...
CreateSerializedPropertyInfo
android-12.0.0_r28/system/core/init/property_service.cpp
void CreateSerializedPropertyInfo() {
// PropertyInfoEntry 是一个结构体,用于存储属性信息,解析下面的xxx_property_contexts文件用的
auto property_infos = std::vector<PropertyInfoEntry>();
// 判断/system/etc/selinux/plat_property_contexts文件是否可读
if (access("/system/etc/selinux/plat_property_contexts", R_OK) != -1) {
// 解析/system/etc/selinux/plat_property_contexts,该文件内容配置的是属性值的selinux上下文,selinux权限相关
if (!LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/system/etc/selinux/plat_property_contexts",
&property_infos)) {
return;
}
// 解析/system_ext/etc/selinux/system_ext_property_contexts
if (access("/system_ext/etc/selinux/system_ext_property_contexts", R_OK) != -1) {
LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/system_ext/etc/selinux/system_ext_property_contexts",
&property_infos);
}
// 解析/vendor/etc/selinux/vendor_property_contexts
if (!LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/vendor/etc/selinux/vendor_property_contexts",
&property_infos)) {
// Fallback to nonplat_* if vendor_* doesn't exist.
LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/vendor/etc/selinux/nonplat_property_contexts",
&property_infos);
}
// 解析/product/etc/selinux/product_property_contexts
if (access("/product/etc/selinux/product_property_contexts", R_OK) != -1) {
LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/product/etc/selinux/product_property_contexts",
&property_infos);
}
// 解析/odm/etc/selinux/odm_property_contexts
if (access("/odm/etc/selinux/odm_property_contexts", R_OK) != -1) {
LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/odm/etc/selinux/odm_property_contexts", &property_infos);
}
} else {
// 解析/plat_property_contexts,
if (!LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/plat_property_contexts", &property_infos)) {
return;
}
// 解析/system_ext_property_contexts,
LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/system_ext_property_contexts", &property_infos);
// 解析/vendor_property_contexts,
if (!LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/vendor_property_contexts", &property_infos)) {
// Fallback to nonplat_* if vendor_* doesn't exist.
// 解析/nonplat_property_contexts,
LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/nonplat_property_contexts", &property_infos);
}
// 解析/product_property_contexts,
LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/product_property_contexts", &property_infos);
// 解析/odm_property_contexts,
LoadPropertyInfoFromFile("/odm_property_contexts", &property_infos);
}
auto serialized_contexts = std::string();
auto error = std::string();
// 1、将property_infos转化成Trie树(字典树,方便高效查询)
// 2、Trie树序列化成字符串serialized_contexts
if (!BuildTrie(property_infos, "u:object_r:default_prop:s0", "string", &serialized_contexts,
&error)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to serialize property contexts: " << error;
return;
}
// 3、将字符串serialized_contexts写进/dev/__properties__/property_info中
constexpr static const char kPropertyInfosPath[] = "/dev/__properties__/property_info";
if (!WriteStringToFile(serialized_contexts, kPropertyInfosPath, 0444, 0, 0, false)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Unable to write serialized property infos to file";
}
// 将dev/__properties__/property_info文件的`selinux上下文设置为`u:object_r:property_info:s0`
selinux_android_restorecon(kPropertyInfosPath, 0);
}
// ... `std::set<std::string> contexts_`;
-
读取以下文件,这些文件描述了属性和
selinux上下文的对应关系:
/system/etc/selinux/plat_property_contexts,/system_ext/etc/selinux/system_ext_property_contexts,/vendor/etc/selinux/vendor_property_contexts,/product/etc/selinux/product_property_contexts,/odm/etc/selinux/odm_property_contexts读取到的内容解析成PropertyInfoEntry数组,每个PropertyInfoEntry对象对应着属性的名称,selinux上下文,属性的类型以及是否为exact_match属性。
-
调用
BuildTrie函数将PropertyInfoEntry数组解析Trie树(字典树),树由TrieBuilder类表示,树的结点由TrieBuilderNode类表示,树的根结点对象为TrieBuilder类的成员变量TrieBuilderNode builder_root_
TrieBuilder类另有两个成员变量:std::set<std::string> contexts_和std::set<std::string> types_分别表示解析到的所有selinux上下文列表以及所有属性的类型列表。
接下来将通过类TrieSerializer的SerializeTrie()函数来实现序列化,将TrieBuilder对象序列化为一个字符串,并且将字符串写入文件:/dev/__properties__/property_info,此文件本身的selinux上下文为:u:object_r:property_info:s0。 -
调用
selinux_android_restorecon将/dev/__properties__/property_info文件的selinux上下文设置为u:object_r:property_info:s0。
LoadPropertyInfoFromFile
android-12.0.0_r28/system/core/init/property_service.cpp
bool LoadPropertyInfoFromFile(const std::string& filename,
std::vector<PropertyInfoEntry>* property_infos) {
auto file_contents = std::string();
// 读取filename的文件到file_contents中
if (!ReadFileToString(filename, &file_contents)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Could not read properties from '" << filename << "'";
return false;
}
auto errors = std::vector<std::string>{};
// SelinuxGetVendorAndroidVersion:读取/vendor/etc/selinux/plat_sepolicy_vers.txt,获取SELinux厂商映射的Android版本号
// require_prefix_or_exact:决定是否要求系统属性名必须以特定的前缀开头,或者完全匹配才能被访问;
// Android R(30) 以上的设备,require_prefix_or_exact一般为true
bool require_prefix_or_exact = SelinuxGetVendorAndroidVersion() >= __ANDROID_API_R__;
// 解析xxx_property_contexts文件的每一行数据,
// 然后将每一行的数据读取后转化成存储属性信息的结构体PropertyInfoEntry,最后每一行的PropertyInfoEntry添加到列表property_infos中
ParsePropertyInfoFile(file_contents, require_prefix_or_exact, property_infos, &errors);
// Individual parsing errors are reported but do not cause a failed boot, which is what
// returning false would do here.
for (const auto& error : errors) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Could not read line from '" << filename << "': " << error;
}
return true;
}
ParsePropertyInfoFile
android-12.0.0_r28/system/core/property_service/libpropertyinfoserializer/property_info_file.cpp
void ParsePropertyInfoFile(const std::string& file_contents, bool require_prefix_or_exact,
std::vector<PropertyInfoEntry>* property_infos,
std::vector<std::string>* errors) {
errors->clear();
// 每行进行解析
for (const auto& line : Split(file_contents, "\n")) {
auto trimmed_line = Trim(line);
// 空行和以#开头注释不解析
if (trimmed_line.empty() || StartsWith(trimmed_line, "#")) {
continue;
}
// 创建存储属性信息的结构体PropertyInfoEntry
auto property_info_entry = PropertyInfoEntry{};
auto parse_error = std::string{};
// 真正解析xxx_property_contexts文件每一行数据的方法ParsePropertyInfoLine
if (!ParsePropertyInfoLine(trimmed_line, require_prefix_or_exact, &property_info_entry,
&parse_error)) {
errors->emplace_back(parse_error);
continue;
}
property_infos->emplace_back(property_info_entry);
}
}
// 真正解析xxx_property_contexts文件每一行数据的方法ParsePropertyInfoLine
bool ParsePropertyInfoLine(const std::string& line, bool require_prefix_or_exact,
PropertyInfoEntry* out, std::string* error) {
// SpaceTokenizer是解析字符串的类
auto tokenizer = SpaceTokenizer(line);
// GetNext():从第0个字符开始,存取遍历的字符串line的每个字符,
// 如遇到空白字符则停止获取,并保存当前的迭代器,并下次调用GetNext()时,从当前的当前的迭代器遍历字符串Line
/* E.g: /system/etc/selinux/plat_property_contexts中有
fastbootd.protocol u:object_r:fastbootd_protocol_prop:s0 exact enum usb tcp
*/
// 第一次,GetNext(),则返回:fastbootd.protocol,
// 第二次,GetNext(),则返回:u:object_r:fastbootd_protocol_prop:s0
// 第三次,GetNext(),则返回:exact
// 第四次,GetNext(),则返回:enum
// 第五次,GetNext(),则返回:usb
// 第六次,GetNext(),则返回:tcp
// 用上面的例子,property就是fastbootd.protocol,匹配属性名的字符串(用正则表达式写的字符串)
auto property = tokenizer.GetNext();
if (property.empty()) {
*error = "Did not find a property entry in '" + line + "'";
return false;
}
// 用上面的例子,context就是u:object_r:fastbootd_protocol_prop:s0,表示该属性property(fastbootd.protocol)的安全上下文
auto context = tokenizer.GetNext();
if (context.empty()) {
*error = "Did not find a context entry in '" + line + "'";
return false;
}
// 用上面的例子,match_operation就是exact,完全匹配
auto match_operation = tokenizer.GetNext();
auto type_strings = std::vector<std::string>{};
// 用上面的例子,std::vector类型的type_strings包括了[enum,usb,tcp]
auto type = tokenizer.GetNext();
while (!type.empty()) {
//
type_strings.emplace_back(type);
type = tokenizer.GetNext();
}
// match_operation只能是"exact"或者是"prefix"或者是空字符
bool exact_match = false;
if (match_operation == "exact") {
exact_match = true;
} else if (match_operation != "prefix" && match_operation != "" && require_prefix_or_exact) {
*error = "Match operation '" + match_operation +
"' is not valid: must be either 'prefix' or 'exact'";
return false;
}
// 判断type_strings的内容是否合法
if (!type_strings.empty() && !IsTypeValid(type_strings)) {
*error = "Type '" + Join(type_strings, " ") + "' is not valid";
return false;
}
// 对PropertyInfoEntry的name(property),context(context),
// type(Join(type_strings, " ")),exact_match(exact_match)进行赋值
/* 用上面的例子,out其实就是:
注:enum 后面会接它的至少一个枚举成员,这个比较特殊,除了"enum",还有
"string", "bool", "int", "uint", "double", "size"。
out = {.name = "fastbootd.protocol",
.context = "u:object_r:fastbootd_protocol_prop:s0",
.type = "enum usb tcp",
.exact_match = true,
}
*/
*out = {property, context, Join(type_strings, " "), exact_match};
return true;
}
BuildTrie
先了解一些知识点:
trie树是一种数据结构,用于高效地存储和查找字符串。
Android中定义了一个名为TrieBuilder的类,用于构建trie树的结构
android-12.0.0_r28/system/core/property_service/libpropertyinfoserializer/trie_builder.h
class TrieBuilder {
//...省略
TrieBuilderNode builder_root_;
std::set<std::string> contexts_;
std::set<std::string> types_;
};
-
TrieBuilderNode builder_root_:Trie树的根节点,是一个TrieBuilderNode类型的对象 -
std::set<std::string> contexts_:存放安全上下文的字符串容器,比如u:object_r:default_prop:s0等 -
std::set<std::string> types_:存放类型的字符串容器,比如string,int等
android-12.0.0_r28/system/core/property_service/libpropertyinfoserializer/trie_builder.h
class TrieBuilderNode {
//...省略
PropertyEntryBuilder property_entry_;
std::vector<TrieBuilderNode> children_;
std::vector<PropertyEntryBuilder> prefixes_;
std::vector<PropertyEntryBuilder> exact_matches_;
};
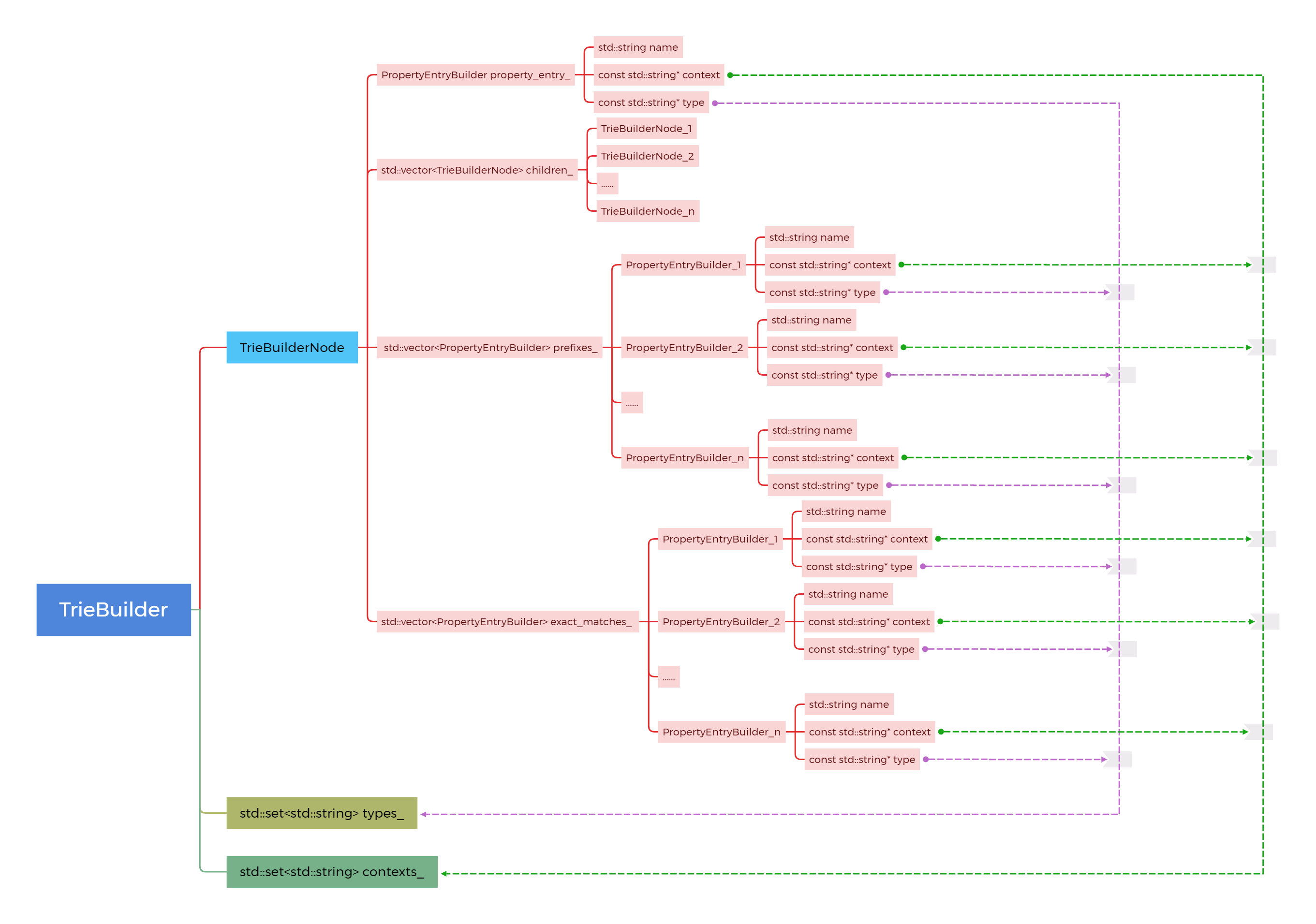
TrieBuilderNode结构体表示Trie树中的一个节点,它包含了以下成员:
-
PropertyEntryBuilder property_entry_:表示该节点对应的属性信息,是一个PropertyEntryBuilder类型的对象。 -
std::vector<TrieBuilderNode> children_:存储该节点的子节点。 -
std::vector<PropertyEntryBuilder> prefixes_:用于存储与该节点的字符串前缀匹配的属性信息 -
std::vector<PropertyEntryBuilder> exact_matches_:用于存储与该节点的字符串完全匹配的属性信息。
android-12.0.0_r28/system/core/property_service/libpropertyinfoserializer/trie_builder.h
struct PropertyEntryBuilder {
PropertyEntryBuilder() : context(nullptr), type(nullptr) {}
PropertyEntryBuilder(const std::string& name, const std::string* context, const std::string* type)
: name(name), context(context), type(type) {}
std::string name;
const std::string* context;
const std::string* type;
};
描述属性信息的结构体:
name:用于存储属性的名字,比如:fastbootd_protocol等context:用于存储属性的上下文,比如:u:object_r:fastbootd_protocol_prop:s0等type:用于存储属性的类型,比如:string,boot,int等
它们的关系如下图:
bool BuildTrie(const std::vector<PropertyInfoEntry>& property_info,
const std::string& default_context, const std::string& default_type,
std::string* serialized_trie, std::string* error) {
// 创建TrieBuilder,初始化转化上下文context:u:object_r:default_prop:s0,default_type:string,树
auto trie_builder = TrieBuilder(default_context, default_type);
for (const auto& [name, context, type, is_exact] : property_info) {
// 把 property_info 的每一项添加trie_builder中
if (!trie_builder.AddToTrie(name, context, type, is_exact, error)) {
return false;
}
}
// 使用TrieSerializer
auto trie_serializer = TrieSerializer();
*serialized_trie = trie_serializer.SerializeTrie(trie_builder);
return true;
}
system/core/property_service/libpropertyinfoserializer/trie_builder.cpp
TrieBuilder::TrieBuilder(const std::string& default_context, const std::string& default_type)
: builder_root_("root") {
// 构建树的根节点root的数据
auto* context_pointer = StringPointerFromContainer(default_context, &contexts_);
builder_root_.set_context(context_pointer);
auto* type_pointer = StringPointerFromContainer(default_type, &types_);
builder_root_.set_type(type_pointer);
}
bool TrieBuilder::AddToTrie(const std::string& name, const std::string& context,
const std::string& type, bool exact, std::string* error) {
auto* context_pointer = StringPointerFromContainer(context, &contexts_);
auto* type_pointer = StringPointerFromContainer(type, &types_);
return AddToTrie(name, context_pointer, type_pointer, exact, error);
}
// 添加树的节点
bool TrieBuilder::AddToTrie(const std::string& name, const std::string* context,
const std::string* type, bool exact, std::string* error) {
// 设置当前节点为树的根节点。
TrieBuilderNode* current_node = &builder_root_;
// 以"."作为分隔,
auto name_pieces = Split(name, ".");
bool ends_with_dot = false;
if (name_pieces.back().empty()) {
ends_with_dot = true;
// 如果以点为结尾,则将分隔得到的std::vector窗口的最后一个元素去掉(空字符)
name_pieces.pop_back();
}
// 如果name_pieces的vector容器数据个数大于1,比如,name_pieces = {"log","tag"}
while (name_pieces.size() > 1) {
// 从当前节点找去子节点,
auto child = current_node->FindChild(name_pieces.front());
if (child == nullptr) {
// 找不着,则创建一个叶节点TrieBuilderNode(name:log,context:null,tpye:null)
child = current_node->AddChild(name_pieces.front());
}
if (child == nullptr) {
*error = "Unable to allocate Trie node";
return false;
}
// 将当前节点设置为上面创建的叶节点
current_node = child;
// 清除 name_pieces = {"log","tag"}的"log",则变成{"tag"}
name_pieces.erase(name_pieces.begin());
}
// 根据匹配的类型来存储上下文context
if (exact) {
// 存储与当前节点的字符串完全匹配的属性信息。
if (!current_node->AddExactMatchContext(name_pieces.front(), context, type)) {
*error = "Duplicate exact match detected for '" + name + "'";
return false;
}
} else if (!ends_with_dot) {
// 存储与当前节点的字符串前缀匹配的属性信息。
if (!current_node->AddPrefixContext(name_pieces.front(), context, type)) {
*error = "Duplicate prefix match detected for '" + name + "'";
return false;
}
} else {
auto child = current_node->FindChild(name_pieces.front());
if (child == nullptr) {
child = current_node->AddChild(name_pieces.front());
}
if (child == nullptr) {
*error = "Unable to allocate Trie node";
return false;
}
if (child->context() != nullptr || child->type() != nullptr) {
*error = "Duplicate prefix match detected for '" + name + "'";
return false;
}
// 存储当前节点属性描述的上下文
child->set_context(context);
// 存储当前节点属性描述的类型
child->set_type(type);
}
return true;
}
const std::string* TrieBuilder::StringPointerFromContainer(const std::string& string,
std::set<std::string>* container) {
// 从容器std::set<std::string> contexts_中插入string,并返回该string在容器的指针,
auto [iterator, _] = container->emplace(string);
return &(*iterator);
}
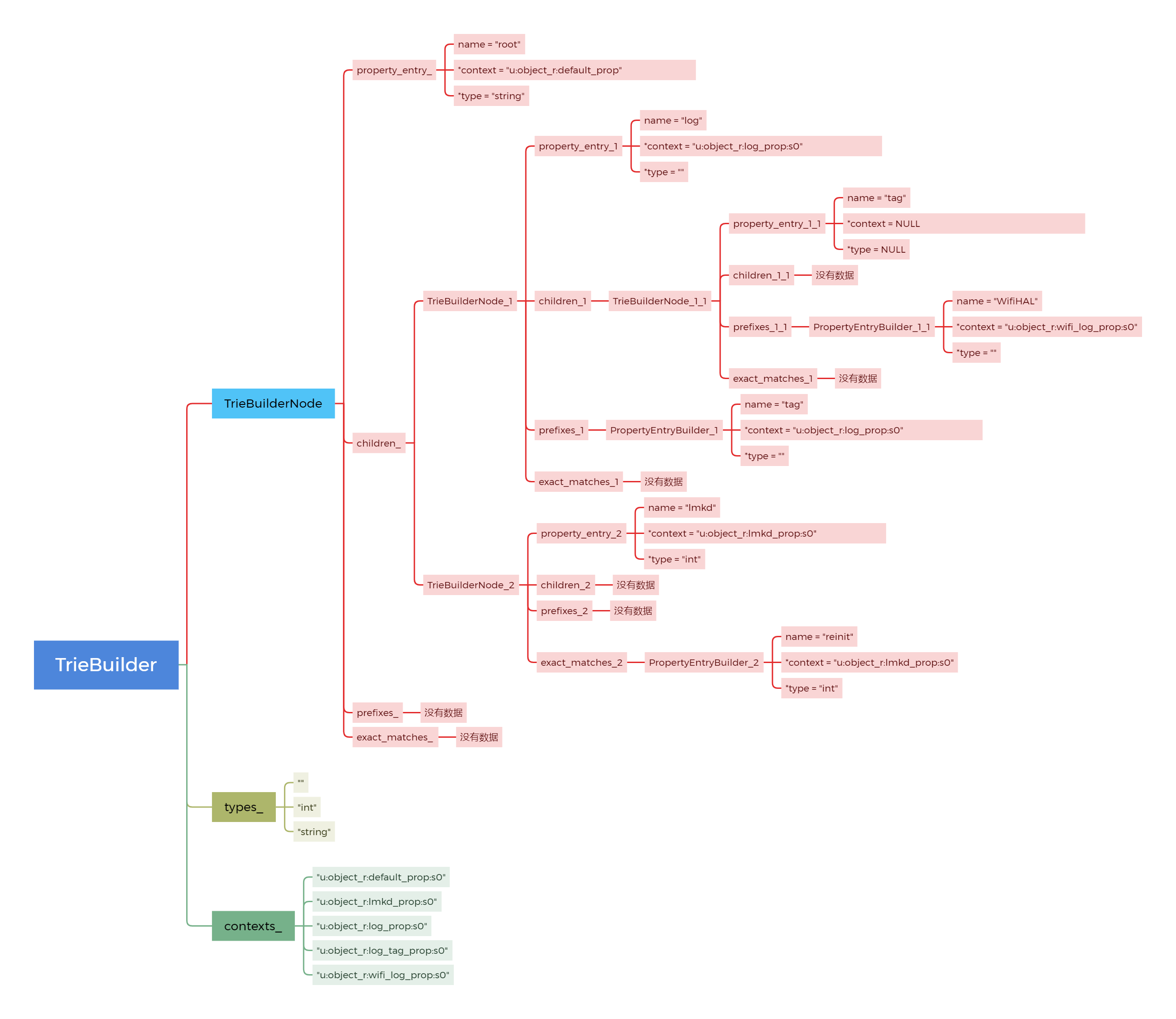
用例子说明:
比如,std::vector<PropertyInfoEntry>& property_info的数据为:
("log.", "u:object_r:log_prop:s0", "", false),
("log.tag", "u:object_r:log_tag_prop:s0", "", false),
("log.tag.WifiHAL", "u:object_r:wifi_log_prop:s0", "", false),
("lmkd.reinit", "u:object_r:lmkd_prop:s0", "int", true)
则它的树结构图:
ProcessKernelDt
android-12.0.0_r28/system/core/init/property_service.cpp
static void ProcessKernelDt() {
// 读取/proc/device-tree/firmware/android/compatible的值是不是和"android,firmware"相等
if (!is_android_dt_value_expected("compatible", "android,firmware")) {
return;
}
std::unique_ptr<DIR, int (*)(DIR*)> dir(opendir(get_android_dt_dir().c_str()), closedir);
if (!dir) return;
std::string dt_file;
struct dirent* dp;
while ((dp = readdir(dir.get())) != NULL) {
if (dp->d_type != DT_REG || !strcmp(dp->d_name, "compatible") ||
!strcmp(dp->d_name, "name")) {
continue;
}
// 读取/proc/device-tree/firmware/android/文件下的xxxx文件的值(除了compatible与name文件)
/* 一般有:
/proc/device-tree/firmware/android/hardware
/proc/device-tree/firmware/android/mode
/proc/device-tree/firmware/android/serialno
*/
std::string file_name = get_android_dt_dir() + dp->d_name;
// 读取hardware,mode,serailno文件的值
android::base::ReadFileToString(file_name, &dt_file);
std::replace(dt_file.begin(), dt_file.end(), ',', '.');
/* 设置属性值:
ro.boot.hardware=xxx
ro.boot.mode=xxx
ro.boot.serialno=xxx
*/
InitPropertySet("ro.boot."s + dp->d_name, dt_file);
}
}
PropertyLoadBootDefaults
void PropertyLoadBootDefaults() {
std::map<std::string, std::string> properties;
// 如果是恢复模式则解析/prop.default文件
if (IsRecoveryMode()) {
load_properties_from_file("/prop.default", nullptr, &properties);
}
// 对新的android 版本与旧的android 版本的xxx.prop的路径支持问题,从而判断是否加载
const auto load_properties_from_partition = [&properties](const std::string& partition,
int support_legacy_path_until) {
auto path = "/" + partition + "/etc/build.prop";
// 先解析/${partition}/etc/build.prop文件,如果失败,就走下面代码旧的路径
if (load_properties_from_file(path.c_str(), nullptr, &properties)) {
return;
}
// 下面通过读取 ro.<partition>.build.version.sdk 的值,并且判断该值是否需要使用旧的路径来读取
std::map<std::string, std::string> temp;
auto legacy_path1 = "/" + partition + "/default.prop";
auto legacy_path2 = "/" + partition + "/build.prop";
// 解析/${partition}/default.prop与/${partition}/build.prop,
// 并所有key-value存到std::map<std::string, std::string> temp
load_properties_from_file(legacy_path1.c_str(), nullptr, &temp);
load_properties_from_file(legacy_path2.c_str(), nullptr, &temp);
bool support_legacy_path = false;
auto version_prop_name = "ro." + partition + ".build.version.sdk";
auto it = temp.find(version_prop_name);
// 在我的android 12的手机上,获取:getprop | grep -E ro.*.build.version.sdk
/*
[ro.bootimage.build.version.sdk]: [31]
[ro.build.version.sdk]: [31]
[ro.odm.build.version.sdk]: [31]
[ro.product.build.version.sdk]: [31]
[ro.system.build.version.sdk]: [31]
[ro.system_ext.build.version.sdk]: [31]
[ro.vendor.build.version.sdk]: [31]
[ro.vendor_dlkm.build.version.sdk]: [31]
*/
if (it == temp.end()) {
// 没有找到ro.<partition>.build.version.sdk,则支持旧的路径
support_legacy_path = true;
}
// 如果找到,并且获取到的值小于等于传进来的support_legacy_path_until版本号,
else if (int value;
ParseInt(it->second.c_str(), &value) && value <= support_legacy_path_until) {
support_legacy_path = true;
}
if (support_legacy_path) {
// 如果支持,则解析/${partition}/default.prop与/${partition}/build.prop,
// 并所有key-value存到std::map<std::string, std::string> properties
load_properties_from_file(legacy_path1.c_str(), nullptr, &properties);
load_properties_from_file(legacy_path2.c_str(), nullptr, &properties);
} else {
LOG(FATAL) << legacy_path1 << " and " << legacy_path2 << " were not loaded "
<< "because " << version_prop_name << "(" << it->second << ") is newer "
<< "than " << support_legacy_path_until;
}
};
// 如/second_stage_resources/system/etc/ramdisk/build.prop存在,则解析这个文件,
// 并所有key-value存到std::map<std::string, std::string> properties中
LoadPropertiesFromSecondStageRes(&properties);
// 解析/system/build.prop文件,并所有key-value存到std::map<std::string, std::string> properties中
load_properties_from_file("/system/build.prop", nullptr, &properties);
/*
解析/system_ext/(|ect)/(build.prop|default.prop)文件,
如/system_ext/ect/build.prop有,则解析,
否则就判断ro.system_ext.build.version.sdk的值是否小于等于30或者没有读取到值,则
解析/system_ext/default.prop与/system_ext/build.prop
*/
load_properties_from_partition("system_ext", /* support_legacy_path_until */ 30);
// 解析/vendor/default.prop文件,并所有key-value存到std::map<std::string, std::string> properties中
load_properties_from_file("/vendor/default.prop", nullptr, &properties);
// 解析/vendor/build.prop文件,并所有key-value存到std::map<std::string, std::string> properties中
load_properties_from_file("/vendor/build.prop", nullptr, &properties);
// 解析/vendor_dlkm/etc/build.prop文件,并所有key-value存到std::map<std::string, std::string> properties中
load_properties_from_file("/vendor_dlkm/etc/build.prop", nullptr, &properties);
// 解析/odm_dlkm/etc/build.prop文件,并所有key-value存到std::map<std::string, std::string> properties中
load_properties_from_file("/odm_dlkm/etc/build.prop", nullptr, &properties);
/*
解析/odm/(|ect)/(build.prop|default.prop)文件,
如/odm/ect/build.prop有,则解析,
否则就判断ro.odm.build.version.sdk的值是否小于等于28或者没有读取到值,则
解析/odm/default.prop与/odm/build.prop
*/
load_properties_from_partition("odm", /* support_legacy_path_until */ 28);
/*
解析/product/(|ect)/(build.prop|default.prop)文件,
如/product/ect/build.prop有,则解析,
否则就判断ro.product.build.version.sdk的值是否小于等于30或者没有读取到值,则
解析/product/default.prop与/product/build.prop
*/
load_properties_from_partition("product", /* support_legacy_path_until */ 30);
// 判断/debug_ramdisk/adb_debug.prop是否可以读,可读则解析这个文件
if (access(kDebugRamdiskProp, R_OK) == 0) {
LOG(INFO) << "Loading " << kDebugRamdiskProp;
load_properties_from_file(kDebugRamdiskProp, nullptr, &properties);
}
// 遍历std::map<std::string, std::string> properties,
// 设置系统属性值key-value通过MMAP映射到全局内存中,供所有进程访问
for (const auto& [name, value] : properties) {
std::string error;
if (PropertySet(name, value, &error) != PROP_SUCCESS) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Could not set '" << name << "' to '" << value
<< "' while loading .prop files" << error;
}
}
/*
功能:设置ro.product.{brand | device | manufacturer | model | name }的值。
是通过读取ro.product.<partition>.{brand | device | manufacturer | model | name },
来设置它们的值(如果有值,就不会再赋值),所以,默认读取的优先级是product,odm,vendor,system_ext,system,
可以通过ro.product.property_source_order来设置这5个字符串的摆放的数组位置来设置这个优先级。
*/
property_initialize_ro_product_props();
/*
功能:设置ro.build.id的值
如果读取ro.build.id的值为空,则通过读取ro.build.legacy.id和ro.boot.vbmeta.digest的值设置,
如果ro.boot.vbmeta.digest读取的字符串大小小于8,则设置ro.build.id为读取ro.build.legacy.id的值,
否则,设置ro.build.id = getprop(ro.build.legacy.id) + [getprop(ro.boot.vbmeta.digest)的前8个字符]
*/
property_initialize_build_id();
/*
功能:设置ro.build.fingerprint
如果读取ro.build.fingerprint的值为空,
则ro.build.fingerprint =
getprop(ro.product.brand) + "/" + getprop(ro.product.name) + "/" +
getprop(ro.product.device) + "/" + getprop(ro.build.version.release_or_codename) + "/" +
getprop(ro.build.id) + "/" + getprop(ro.build.version.incremental) + "/" +
getprop(ro.build.type) + "/" + getprop(ro.build.tags) + "/" +
*/
property_derive_build_fingerprint();
/*
功能:设置ro.build.legacy.fingerprint
如果读取ro.build.legacy.fingerprint的值为空,
则ro.build.fingerprint =
getprop(ro.product.brand) + "/" + getprop(ro.product.name) + "/" +
getprop(ro.product.device) + "/" + getprop(ro.build.version.release_or_codename) + "/" +
getprop(ro.build.legacy.id) + "/" + getprop(ro.build.version.incremental) + "/" +
getprop(ro.build.type) + "/" + getprop(ro.build.tags) + "/" +
*/
property_derive_legacy_build_fingerprint();
/*
功能:设置ro.product.cpu.abilist,ro.product.cpu.abilist32,ro.product.cpu.abilist64的值
如果读取ro.product.cpu.abilis的值为空,则通过读取ro.{product|odm|vendor|system}.product.cpu.abilist32与
ro.{product|dom|vendor|system}.product.cpu.abilist64的值,分别来设置ro.product.cpu.abilist32与
product.cpu.abilist64的值,其中{product|dom|vendor|system},优先级最高是product>odm>vendor>system,
然后再将两者的值ro.xxx.product.cpu.abilist32与ro.xxx.product.cpu.abilist64拼接起来,再设置ro.product.cpu.abilist的值
*/
property_initialize_ro_cpu_abilist();
/*
功能:设置persist.sys.usb.config的值
通过读取ro.debuggable的值来设置
*/
update_sys_usb_config();
}
// ...
static Result<void> load_properties_from_file(const char* filename, const char* filter,
std::map<std::string, std::string>* properties) {
Timer t;
//读取xxx.prop文件内容到file_contents
auto file_contents = ReadFile(filename);
if (!file_contents.ok()) {
return Error() << "Couldn't load property file '" << filename
<< "': " << file_contents.error();
}
file_contents->push_back('\n');
// 解析从xxx.prop的内容file_contents
LoadProperties(file_contents->data(), filter, filename, properties);
LOG(VERBOSE) << "(Loading properties from " << filename << " took " << t << ".)";
return {};
}
LoadProperties
static void LoadProperties(char* data, const char* filter, const char* filename,
std::map<std::string, std::string>* properties) {
char *key, *value, *eol, *sol, *tmp, *fn;
size_t flen = 0;
static constexpr const char* const kVendorPathPrefixes[4] = {
"/vendor",
"/odm",
"/vendor_dlkm",
"/odm_dlkm",
};
// kInitContext = "u:r:init:s0";
const char* context = kInitContext;
// __ANDROID_API_P__ = 28
if (SelinuxGetVendorAndroidVersion() >= __ANDROID_API_P__) {
for (const auto& vendor_path_prefix : kVendorPathPrefixes) {
// filename如果是以上面/vendor,/odm,/vendor_dlkm,/odm_dlkm开头的
if (StartsWith(filename, vendor_path_prefix)) {
// kVendorContext[] = "u:r:vendor_init:s0";
// context 就更换成""
context = kVendorContext;
}
}
}
// 如果有过滤器,则获取其长度
if (filter) {
flen = strlen(filter);
}
//sol:当前行头
sol = data;
// strchr读取字符指针sol第一个出现'\n'换行符
// eol指向字符串中第一个出现字符'\n'的地址
while ((eol = strchr(sol, '\n'))) {
// 将当前行头的sol赋值给key
key = sol;
// 此时eol指向的是换行符'\n',然后把换行符'\n'改成0,即字符串结束标志,
// 然后eol++,为下面sol行头赋值
*eol++ = 0;
// 上面行尾eol++,即是行头了sol
sol = eol;
// 获取到key,遇到非空格字符停止,即行头有可能以空格符开始的,则除去空格符,再获取key
while (isspace(*key)) key++;
// 以#的注释行跳过
if (*key == '#') continue;
// eol目前,指向的是下一行的行头,此时eol-1,即是指向当前行的字符串结束标志'\0',
// eol-2,tmp即是当前的行尾
tmp = eol - 2;
// 如果当前的行尾tmp还有多余的空格的,将全部转化成字符串结束标志'\0'
while ((tmp > key) && isspace(*tmp)) *tmp-- = 0;
// 如果当前key是import,且没有过滤器
if (!strncmp(key, "import ", 7) && flen == 0) {
fn = key + 7;
// 找到不是以空格符的fn文件名(包含路径),即import /system/etc/aaa.prop,
// import与/system/etc/aaa.prop之前存在多个空格符
while (isspace(*fn)) fn++;
// 查看文件名后面是否有空格符号,如有,将全部转化成字符串结束标志'\0',则此时key为nullptr
/*E.g.
"import /system/etc/aaa.prop ",这一行数据中,
要把"/system/etc/aaa.prop"后面的空格符全部转化成字符串结束标志'\0',直接key没有指向任何数据nullptr
*/
key = strchr(fn, ' ');
if (key) {
*key++ = 0;
while (isspace(*key)) key++;
}
std::string raw_filename(fn);
// ExpandProp主要是拓展了文件的灵活性
/*
1、变量的格式可以是 $x.y 或者 ${x.y},前者适用于变量名是字符串的一部分的情况。
2、双美元符号 ($$) 会被解释为一个普通的美元符号 ($)
3、不支持嵌套的属性扩展,例如 ${foo.${bar}} 不受支持。
4、如果变量为空,则 ${x.y:-default} 将返回默认值 default。
*/
auto expanded_filename = ExpandProps(raw_filename);
if (!expanded_filename.ok()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Could not expand filename ': " << expanded_filename.error();
continue;
}
// 递归执行load_properties_from_file
load_properties_from_file(expanded_filename->c_str(), key, properties);
} else {
value = strchr(key, '=');
if (!value) continue;
// 此时value指向'=',然后把符号'='改成0,即字符串结束标志,value++,即是'='的下一个符号的位置,即真正的value值
/* E.g:
ro.build.type=user,value此时向的是"user",
*/
*value++ = 0;
// value - 1:'\0'的位置,value - 2:'\0'的前一个位置,即是tmp:指向的是key字符串的尾部,
tmp = value - 2;
// 将key后面的空格符,全部转化成字符串结束标志'\0'
while ((tmp > key) && isspace(*tmp)) *tmp-- = 0;
// 获取value不是以空格符开头的值
while (isspace(*value)) value++;
if (flen > 0) {
if (filter[flen - 1] == '*') {
if (strncmp(key, filter, flen - 1) != 0) continue;
} else {
if (strcmp(key, filter) != 0) continue;
}
}
// kRestoreconProperty = "selinux.restorecon_recursive"
// 如果key是以ctlg开头,或者key=sys.powerctl,key=selinux.restorecon_recursive,不做处理
if (StartsWith(key, "ctl.") || key == "sys.powerctl"s ||
std::string{key} == kRestoreconProperty) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Ignoring disallowed property '" << key
<< "' with special meaning in prop file '" << filename << "'";
continue;
}
ucred cr = {.pid = 1, .uid = 0, .gid = 0};
std::string error;
// 检查当前进程是否有权限修改指定的属性值
if (CheckPermissions(key, value, context, cr, &error) == PROP_SUCCESS) {
auto it = properties->find(key);
if (it == properties->end()) {
// std::map<std::string, std::string> properties中不存在key,则添加
(*properties)[key] = value;
} else if (it->second != value) {
LOG(WARNING) << "Overriding previous property '" << key << "':'" << it->second
<< "' with new value '" << value << "'";
// std::map<std::string, std::string> properties中存在key,且值不相同,就重新赋值覆盖掉原来的值
it->second = value;
}
} else {
LOG(ERROR) << "Do not have permissions to set '" << key << "' to '" << value
<< "' in property file '" << filename << "': " << error;
}
}
}
}
InstallSignalFdHandler
static void InstallSignalFdHandler(Epoll* epoll) {
// 步骤1 start
// .sa_handler = SIG_DFL:表示使用默认的信号处理函数
// .sa_flags = SA_NOCLDSTOP:表示不将停止子进程的信号发送给当前进程
const struct sigaction act { .sa_handler = SIG_DFL, .sa_flags = SA_NOCLDSTOP };
// SIGCHLD 是一个信号名,它表示子进程状态改变信号(Child status changed);
// 当一个子进程终止或停止时,会向其父进程发送该信号,以通知父进程子进程的状态发生了变化。
// 将 act 对象与 SIGCHLD 信号关联,这样当进程收到 SIGCHLD 信号时,就会使用默认的信号处理函数。
sigaction(SIGCHLD, &act, nullptr);
sigset_t mask;
sigemptyset(&mask);
sigaddset(&mask, SIGCHLD);
// 判断init进程是否有重启设备能力,IsRebootCapable()一般为true
if (!IsRebootCapable()) {
// If init does not have the CAP_SYS_BOOT capability, it is running in a container.
// In that case, receiving SIGTERM will cause the system to shut down.
sigaddset(&mask, SIGTERM);
}
// 设置屏蔽信号集合(SIGCHLD,SIGTERM)
if (sigprocmask(SIG_BLOCK, &mask, nullptr) == -1) {
PLOG(FATAL) << "failed to block signals";
}
// 设置子进程可以正确地接收 SIGCHLD 和 SIGTERM 信号,并且不会继承父进程对这些信号的阻塞
const int result = pthread_atfork(nullptr, nullptr, &UnblockSignals);
if (result != 0) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Failed to register a fork handler: " << strerror(result);
}
// 步骤1 end
// 步骤2 start
// 创建信号集(SIGINT,SIGTERM信号)的文件描述符signal_fd,通过Epoll监听signal_fd可将异步接收SIGCHLD,SIGTERM信号。
signal_fd = signalfd(-1, &mask, SFD_CLOEXEC);
if (signal_fd == -1) {
PLOG(FATAL) << "failed to create signalfd";
}
// 使用Epoll监听信号集为SIGINT,SIGTERM的文件描述符signal_fd,处理函数为HandleSignalFd
// 这里的Epoll是在system/core/init/epoll.cpp对<sys/epoll>的封装的一个类,
// 通过RegisterHandler监听这个signal_fd
if (auto result = epoll->RegisterHandler(signal_fd, HandleSignalFd); !result.ok()) {
LOG(FATAL) << result.error();
}
// 步骤2 end
}
static void UnblockSignals() {
const struct sigaction act { .sa_handler = SIG_DFL };
sigaction(SIGCHLD, &act, nullptr);
sigset_t mask;
sigemptyset(&mask);
sigaddset(&mask, SIGCHLD);
sigaddset(&mask, SIGTERM);
// 设置解除屏蔽信号集合(SIGCHLD,SIGTERM)
if (sigprocmask(SIG_UNBLOCK, &mask, nullptr) == -1) {
PLOG(FATAL) << "failed to unblock signals for PID " << getpid();
}
}
// 监听信号集(SIGINT,SIGTERM信号)的文件描述符signal_fd的处理函数
static void HandleSignalFd() {
signalfd_siginfo siginfo;
ssize_t bytes_read = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(read(signal_fd, &siginfo, sizeof(siginfo)));
if (bytes_read != sizeof(siginfo)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "Failed to read siginfo from signal_fd";
return;
}
switch (siginfo.ssi_signo) {
// 子进程停止信号
case SIGCHLD:
/*
终止出现问题的子进程,
里面使用ReapOneProcess调用waitpid找出挂掉进程的pid,然后根据pid找到对应Service,
最后调用Service的Reap方法清除资源,根据进程对应的类型,决定
是否重启机器或重启进程
*/
ReapAnyOutstandingChildren();
break;
case SIGTERM:
// 会发送一个广播通知系统组件和应用程序进行清理工作,最终执行关机操作。
HandleSigtermSignal(siginfo);
break;
default:
PLOG(ERROR) << "signal_fd: received unexpected signal " << siginfo.ssi_signo;
break;
}
}
步骤1:设置信号处理函数,并将 SIGCHLD 和 SIGTERM 信号加入到信号屏蔽集中,从而防止这两个信号在信号处理函数运行期间中断程序的执行。这种设置通常用于多进程编程中,以防止子进程意外终止或被中断,从而导致父进程无法正常工作。然后通过pthread_atfork设置子进程可以正确地接收 SIGCHLD 和 SIGTERM 信号,即设置不继承父进程对这些信号的阻塞
步骤2:创建signal_fd文件描述符,通过Epoll监听该文件描述符来达到异步接收 SIGCHLD,SIGTERM信号
InstallInitNotifier
static int wake_main_thread_fd = -1;
static void InstallInitNotifier(Epoll* epoll) {
/*
创建事件通知的文件描述符
当进程需要等待某个事件发生时,可以通过 eventfd 创建一个eventfd 对象,
并使用 read 系统调用阻塞等待该事件的发生。
当事件发生时,通过 write 系统调用向 eventfd 对象写入一个计数值,唤醒正在等待该事件的进程。
*/
wake_main_thread_fd = eventfd(0, EFD_CLOEXEC);
if (wake_main_thread_fd == -1) {
PLOG(FATAL) << "Failed to create eventfd for waking init";
}
auto clear_eventfd = [] {
uint64_t counter;
// 事件通知eventfd的读事件,与WakeMainInitThread配合使用,写完才能读,读完才能写。
TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(read(wake_main_thread_fd, &counter, sizeof(counter)));
};
// 使用Epoll监听事件通知的文件描述符wake_main_thread_fd,
// 处理函数为:read(wake_main_thread_fd, &counter, sizeof(counter))
// 通过RegisterHandler监听这个wake_main_thread_fd
if (auto result = epoll->RegisterHandler(wake_main_thread_fd, clear_eventfd); !result.ok()) {
LOG(FATAL) << result.error();
}
}
static void WakeMainInitThread() {
uint64_t counter = 1;
// 事件通知eventfd的写事件,与上面clear_eventfd方法配合使用,写完才能读,读完才能写。
TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(write(wake_main_thread_fd, &counter, sizeof(counter)));
}
StartPropertyService
void StartPropertyService(int* epoll_socket) {
InitPropertySet("ro.property_service.version", "2");
int sockets[2];
// 创建Linux的socketpair通讯
if (socketpair(AF_UNIX, SOCK_SEQPACKET | SOCK_CLOEXEC, 0, sockets) != 0) {
PLOG(FATAL) << "Failed to socketpair() between property_service and init";
}
*epoll_socket = from_init_socket = sockets[0];
init_socket = sockets[1];
StartSendingMessages();
// PROP_SERVICE_NAME = "property_service"
// 创建一个指向/dev/socket/property_service的PF_UNIX的socket
if (auto result = CreateSocket(PROP_SERVICE_NAME, SOCK_STREAM | SOCK_CLOEXEC | SOCK_NONBLOCK,
false, 0666, 0, 0, {});
result.ok()) {
property_set_fd = *result;
} else {
LOG(FATAL) << "start_property_service socket creation failed: " << result.error();
}
// 监听该fd,最大8个连接
listen(property_set_fd, 8);
// 通过epoll监听from_init_socket与property_fd
auto new_thread = std::thread{PropertyServiceThread};
property_service_thread.swap(new_thread);
}
CreateSocket
android-12.0.0_r28/system/core/init/util.cpp
Result<int> CreateSocket(const std::string& name, int type, bool passcred, mode_t perm, uid_t uid,
gid_t gid, const std::string& socketcon) {
if (!socketcon.empty()) {
if (setsockcreatecon(socketcon.c_str()) == -1) {
return ErrnoError() << "setsockcreatecon(\"" << socketcon << "\") failed";
}
}
// 创建socket,协议域:PF_UNIX,与AF_UNIX两者等价,可以互换
android::base::unique_fd fd(socket(PF_UNIX, type, 0));
if (fd < 0) {
return ErrnoError() << "Failed to open socket '" << name << "'";
}
if (!socketcon.empty()) setsockcreatecon(nullptr);
struct sockaddr_un addr;
memset(&addr, 0 , sizeof(addr));
addr.sun_family = AF_UNIX;
// 指定AF_UNIX协议的本地套接字的地址
// ANDROID_SOCKET_DIR = "/dev/socket"
// addr.sun_path = /dev/socket/property_service
snprintf(addr.sun_path, sizeof(addr.sun_path), ANDROID_SOCKET_DIR "/%s", name.c_str());
if ((unlink(addr.sun_path) != 0) && (errno != ENOENT)) {
return ErrnoError() << "Failed to unlink old socket '" << name << "'";
}
std::string secontext;
// 查找/dev/socket/property_service的selinux上下文,存放到secontext
if (SelabelLookupFileContext(addr.sun_path, S_IFSOCK, &secontext) && !secontext.empty()) {
// 设置文件系统创建的默认安全上下文为secontext
setfscreatecon(secontext.c_str());
}
if (passcred) {
int on = 1;
if (setsockopt(fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_PASSCRED, &on, sizeof(on))) {
return ErrnoError() << "Failed to set SO_PASSCRED '" << name << "'";
}
}
// 绑定该fd
int ret = bind(fd, (struct sockaddr *) &addr, sizeof (addr));
int savederrno = errno;
// /dev/socket/property_service的selinux上下文,不为空,刚
if (!secontext.empty()) {
// 恢复文件系统创建的默认安全上下文
setfscreatecon(nullptr);
}
auto guard = android::base::make_scope_guard([&addr] { unlink(addr.sun_path); });
if (ret) {
errno = savederrno;
return ErrnoError() << "Failed to bind socket '" << name << "'";
}
// 设置/dev/socket/property_service文件的属主
if (lchown(addr.sun_path, uid, gid)) {
return ErrnoError() << "Failed to lchown socket '" << addr.sun_path << "'";
}
// 设置/dev/socket/property_service的文件权限
if (fchmodat(AT_FDCWD, addr.sun_path, perm, AT_SYMLINK_NOFOLLOW)) {
return ErrnoError() << "Failed to fchmodat socket '" << addr.sun_path << "'";
}
LOG(INFO) << "Created socket '" << addr.sun_path << "'"
<< ", mode " << std::oct << perm << std::dec
<< ", user " << uid
<< ", group " << gid;
guard.Disable();
return fd.release();
}
PropertyServiceThread
system/core/init/property_service.cpp
static void PropertyServiceThread() {
Epoll epoll;
if (auto result = epoll.Open(); !result.ok()) {
LOG(FATAL) << result.error();
}
// 监听/dev/socket/property_service的sokcet fd,
if (auto result = epoll.RegisterHandler(property_set_fd, handle_property_set_fd);
!result.ok()) {
LOG(FATAL) << result.error();
}
// 监听socketpair的read fd
if (auto result = epoll.RegisterHandler(init_socket, HandleInitSocket); !result.ok()) {
LOG(FATAL) << result.error();
}
while (true) {
// 等待消息
auto pending_functions = epoll.Wait(std::nullopt);
if (!pending_functions.ok()) {
LOG(ERROR) << pending_functions.error();
} else {
for (const auto& function : *pending_functions) {
// 回调上面的epoll.RegisterHandler的中设置的函数
(*function)();
}
}
}
}
fs_mgr_vendor_overlay_mount_all
system/core/fs_mgr/fs_mgr_vendor_overlay.cpp
bool fs_mgr_vendor_overlay_mount_all() {
// kVndkVersionPropertyName = "ro.vndk.version"
static const auto vndk_version = android::base::GetProperty(kVndkVersionPropertyName, "");
if (vndk_version.empty()) {
LINFO << "vendor overlay: vndk version not defined";
return false;
}
// 获取 "/system/vendor_overlay/<ver>",
// "/product/vendor_overlay/<ver>"下的所有子目录
const auto vendor_overlay_dirs = fs_mgr_get_vendor_overlay_dirs(vndk_version);
if (vendor_overlay_dirs.empty()) return true;
if (fs_mgr_overlayfs_valid() == OverlayfsValidResult::kNotSupported) {
LINFO << "vendor overlay: kernel does not support overlayfs";
return false;
}
// Mount each directory in /(system|product)/vendor_overlay/<ver> on /vendor
// 挂载/(system|product)/vendor_overlay/<ver>到 /vendor分区上
auto ret = true;
for (const auto& vendor_overlay_dir : vendor_overlay_dirs) {
if (!fs_mgr_vendor_overlay_mount(vendor_overlay_dir)) {
ret = false;
}
}
return ret;
}
export_oem_lock_status
static void export_oem_lock_status() {
if (!android::base::GetBoolProperty("ro.oem_unlock_supported", false)) {
return;
}
SetProperty(
"ro.boot.flash.locked",
android::base::GetProperty("ro.boot.verifiedbootstate", "") == "orange" ? "0" : "1");
}
system/core/init/mount_handler.cpp
MountHandler
// 监听/proc/mounts 文件fd,有变化就执行MountHandlerFunction方法去解析这个文件内容
MountHandler::MountHandler(Epoll* epoll) : epoll_(epoll), fp_(fopen("/proc/mounts", "re"), fclose) {
if (!fp_) PLOG(FATAL) << "Could not open /proc/mounts";
auto result = epoll->RegisterHandler(
fileno(fp_.get()), [this]() { this->MountHandlerFunction(); }, EPOLLERR | EPOLLPRI);
if (!result.ok()) LOG(FATAL) << result.error();
}
// ...
void MountHandler::MountHandlerFunction() {
rewind(fp_.get());
std::vector<MountHandlerEntry> touched;
auto untouched = mounts_;
char* buf = nullptr;
size_t len = 0;
// 读取文件内容中的每一行
while (getline(&buf, &len, fp_.get()) != -1) {
auto buf_string = std::string(buf);
// 若读取的有"/emulated则跳过"
if (buf_string.find("/emulated") != std::string::npos) {
continue;
}
/* 取每行的前三个字段挂载的块设备,(以空格" "分隔,再取,不足则用""空字符补全)
blk_device: 挂载的块设备
mount_point:挂载的路径或者点
fs_type: 挂载的文件系统类型
*/
auto entry = ParseMount(buf_string);
auto match = untouched.find(entry);
if (match == untouched.end()) {
touched.emplace_back(std::move(entry));
} else {
untouched.erase(match);
}
}
free(buf);
// 将匹配到的entry进行移除,并记录Mount属性值
for (auto& entry : untouched) {
// 设置一些dev.mnt.xxx属性
SetMountProperty(entry, false);
mounts_.erase(entry);
}
// 将未匹配到的entry追加到mounts_,并记录Mount属性值
for (auto& entry : touched) {
// 设置一些dev.mnt.xxx属性
SetMountProperty(entry, true);
mounts_.emplace(std::move(entry));
}
}
第四阶段调用init.rc
当属性服务建立完成后,init的自身功能基本就告一段落,接下来
需要来启动其他的进程。但是init进程如何其他其他进程呢?其他
进程都是一个二进制文件,我们可以直接通过exec的命令方式来
启动,例如 ./system/bin/init second_stage,来启动init进程的第
二阶段。但是Android系统有那么多的Native进程,如果都通过传
exec在代码中一个个的来执行进程,那无疑是一个灾难性的设
计。
在这个基础上Android推出了一个init.rc的机制,即类似通过读取
配置文件的方式,来启动不同的进程。
init.rc是一个配置文件,内部由Android初始化语言编写
(Android Init Language)编写的脚本。
init.rc主要包含五种类型语句:
-
Action
-
Command
-
Service
-
Option
-
Import
Action
动作表示了一组命令(commands)组成.动作包括一个触发器,决
定了何时运行这个动作
Action: 通过触发器trigger,即以on开头的语句来决定执行相应
的service的时机,具体有如下时机:
on early-init:在初始化早期阶段触发;
on init:在初始化阶段触发;
on late-init:在初始化晚期阶段触发;
on boot/charger: 当系统启动/充电时触发;
on property: 当属性值满足条件时触发;
Command
command是action的命令列表中的命令,或者是service中的选项
onrestart 的参数命令,命令将在所属事件发生时被一个个地执行.
下面列举常用的命令
class_start <service_class_name>: 启动属于同一个class的所有
服务;
class_stop <service_class_name> : 停止指定类的服务
start <service_name>: 启动指定的服务,若已启动则跳过;
stop <service_name>: 停止正在运行的服务
setprop :设置属性值
mkdir :创建指定目录
symlink <sym_link>: 创建连接到的<sym_link>符号链接;
write : 向文件path中写入字符串;
exec: fork并执行,会阻塞init进程直到程序完毕;
exprot :设定环境变量;
loglevel :设置log级别
hostname : 设置主机名
import :导入一个额外的init配置文件
####Service
服务Service,以 service开头,由init进程启动,一般运行在init的
一个子进程,所以启动service前需要判断对应的可执行文件是否
存在。
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| 表示此服务的名称 | |
| 此服务所在路径因为是可执行文件,所以一定有存储路径。 | |
| 启动服务所带的参数 | |
| 对此服务的约束选项 |
init生成的子进程,定义在rc文件,其中每一个service在启动时会
通过fork方式生成子进程。
例如: service servicemanager /system/bin/servicemanager代
表的是服务名为servicemanager,服务执行的路径
为/system/bin/servicemanager。
Options
Options是Service的可选项,与service配合使用
disabled: 不随class自动启动,只有根据service名才启动;
oneshot: service退出后不再重启;
user/group: 设置执行服务的用户/用户组,默认都是root;
class:设置所属的类名,当所属类启动/退出时,服务也启动/停
止,默认为default;
onrestart:当服务重启时执行相应命令;
socket: 创建名为/dev/socket/的socket
critical: 在规定时间内该service不断重启,则系统会重启并进入恢
复模式
default: 意味着disabled=false,oneshot=false,critical=false。
#####import
用来导入其他的rc文件
命令:import
调用uevent_main启动
cc_binary {
name: "init_second_stage",
recovery_available: true,
// 编译成init模块名字
stem: "init",
defaults: ["init_defaults"],
static_libs: ["libinit"],
required: [
"e2fsdroid",
"init.rc",
"mke2fs",
"sload_f2fs",
"make_f2fs",
"ueventd.rc",
],
srcs: ["main.cpp"],
// 创建一个/system/bin/ueventd 链接到/system/bin/init
symlinks: ["ueventd"],
....
创建一个/system/bin/ueventdl 软链接到/system/bin/init
SeondStateMain->LoadBootScripts(am, sm)>am.QueueEventTrigger("early-init"):
on early-init
# ...
start ueventd
# ...
service ueventd /system/bin/ueventd
class core
critical
seclabel u:r:ueventd:s0
shutdown critical
service ueventd /system/bin/ueventd,执行/system/bin/ueventd,其实就是执行system/bin/init,所以传递给system/core/init/main.cpp,只不过[argv]=“/system/bin/ueventd”
android-12.0.0_r28/system/core/init/main.cpp
...
if (!strcmp(basename(argv[0]), "ueventd")) {
// 初始化设备,监听uevent事件
return ueventd_main(argc, argv);
}
...
int ueventd_main(int argc, char** argv) {
// umask(0)用于设置当前进程的文件模式创建屏蔽字
// 用户创建文件夹权限值=初始创建文件夹默认值-umask的预设值
// 如:775=777-002
// 用户创建文件权限值=初始创建文件默认值-umask的预设值
// 如:664=666-002
umask(000);
// 初始化内核日志,位于节点/dev/kmsg, 此时logd、logcat进程还没有起来,
// 采用kernel的log系统,打开的设备节点/dev/kmsg, 那么可cat /dev/kmsg来获取内核log。
android::base::InitLogging(argv, &android::base::KernelLogger);
LOG(INFO) << "ueventd started!";
// 注册selinux相关的用于打印log的回调函数
SelinuxSetupKernelLogging();
// SelabelInitialize() 函数的作用是初始化 libselinux 库,
// 加载 SELinux 的策略文件和文件上下文文件,以确保在 Android 系统运行过程中,能够正确地运行 SELinux 策略。
SelabelInitialize();
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<UeventHandler>> uevent_handlers;
// 解析"/system/etc/ueventd.rc", /vendor/ueventd.rc", "/odm/ueventd.rc",
" /ueventd.${getprop(ro.hardware)}.rc"
auto ueventd_configuration = GetConfiguration();
uevent_handlers.emplace_back(std::make_unique<DeviceHandler>(
std::move(ueventd_configuration.dev_permissions),
std::move(ueventd_configuration.sysfs_permissions),
std::move(ueventd_configuration.subsystems), android::fs_mgr::GetBootDevices(), true));
uevent_handlers.emplace_back(std::make_unique<FirmwareHandler>(
std::move(ueventd_configuration.firmware_directories),
std::move(ueventd_configuration.external_firmware_handlers)));
if (ueventd_configuration.enable_modalias_handling) {
std::vector<std::string> base_paths = {"/odm/lib/modules", "/vendor/lib/modules"};
uevent_handlers.emplace_back(std::make_unique<ModaliasHandler>(base_paths));
}
UeventListener uevent_listener(ueventd_configuration.uevent_socket_rcvbuf_size);
// 冷启动
if (!android::base::GetBoolProperty(kColdBootDoneProp, false)) {
ColdBoot cold_boot(uevent_listener, uevent_handlers,
ueventd_configuration.enable_parallel_restorecon);
cold_boot.Run();
}
for (auto& uevent_handler : uevent_handlers) {
uevent_handler->ColdbootDone();
}
// 忽略子进程终止信号
signal(SIGCHLD, SIG_IGN);
// 在上一次调用 waitpid() 和设置 SIGCHLD 信号的 SIG_IGN 之间退出的子进程需要被回收
while (waitpid(-1, nullptr, WNOHANG) > 0) {
}
// Restore prio before main loop
setpriority(PRIO_PROCESS, 0, 0);
// 监听来自驱动的uevent,进行“热插拔”处理
uevent_listener.Poll([&uevent_handlers](const Uevent& uevent) {
for (auto& uevent_handler : uevent_handlers) {
uevent_handler->HandleUevent(uevent);
}
return ListenerAction::kContinue;
});
return 0;
}
Zygote启动
#...
import /system/etc/init/hw/init.${ro.zygote}.rc
#....
init.rc位于/system/core/rootdir下。在这个路径下还包括四个关
于zygote的rc文件。
分别是init.zygote32.rc,init.zygote32_64.rc,init.zygote64.rc,
init.zygote64_32.rc,由硬件决定调用哪个文件。
这里拿64位处理器为例,init.zygote64.rc的代码如下所示:
system/core/rootdir/init.zygote64.rc
service zygote /system/bin/app_process64 -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server
# class是一个option,指定zygote服务的类型为main
class main
priority -20
user root
group root readproc reserved_disk
# socket关键字表示一个option,创建一个名为dev/socket/zygote,
# 类型为stream,权限为660的socket
socket zygote stream 660 root system
socket usap_pool_primary stream 660 root system
onrestart是一个option,说明在zygote重启时需要执行的command
onrestart exec_background - system system -- /system/bin/vdc volume abort_fuse
onrestart write /sys/power/state on
onrestart restart audioserver
onrestart restart cameraserver
onrestart restart media
onrestart restart netd
onrestart restart wificond
writepid /dev/cpuset/foreground/tasks
critical window=${zygote.critical_window.minute:-off} target=zygote-fatal
service zygote /system/bin/app_process64 -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --start-system-server解析:
service zygote :init.zygote64.rc 中定义了一个zygote服务。 init进程就是通过这个service名称来创建zygote进程
/system/bin/app_process64 -Xzygote /system/bin --zygote --
start-system-server解析:
zygote这个服务,通过执行进行/system/bin/app_process64 并
传入4个参数进行运行:
-
参数1:
-Xzygote该参数将作为虚拟机启动时所需的参数 -
参数2:
/system/bin代表虚拟机程序所在目录 -
参数3:
--zygote指明以ZygoteInit.java类中的main函数作为虚拟机执行入口 -
参数4:-
-start-system-server告诉Zygote进程启动systemServer进程
总结
-
init进程第一阶段做的主要工作是挂载分区,创建设备节点和一些关键目录,初始化日志输出系统,启用SELinux安全策略。 -
init进程第二阶段主要工作是初始化属性系统,解析SELinux的匹配规则,处理子进程终止信号,启动系统属性服务,可以说每一项都很关键,如果说第一阶段是为属性系统,SELinux做准备,那么第二阶段就是真正去把这些功能落实。 -
init进行第三阶段主要是解析init.rc来启动其他进程,进入无限循环,进行子进程实时监控。





















 4310
4310











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








