——比较——
返回两值中的较小值:min()
返回两值中的较大值:max()
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
cout << "MAX: " << max(a, b) << endl;
cout << "MIN: " << min(a, b) << endl;
运行结果:
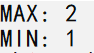
返回序列中最小值的位置:min_element()
返回序列中最大值的位置:max_element()
注意函数的参数与返回值都为指针变量;且注意第二个参数要比判断序列中的最后一个数后一位。
int Arr[] = { 1, 2, 3 };
int *min_postion,*max_postion;
min_postion = min_element(Arr, Arr + 3);
max_postion = max_element(Arr, Arr + 3);
cout << "max_postion: " << *max_postion << endl;
cout << "min_postion: " << *min_postion << endl;
运行结果:

——交换——
交换两个数值:swap()
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
cout << a << " " << b << endl;
swap(a, b);
cout << a << " " << b << endl;
运行结果:

——排序——
排序一段范围的数值:sort()
*参数为指针变量,第一个参数指向范围开端,第二个参数指向范围末端后一位。
vector<int> arr{ 3, 2, 5, 1, 6, 9 };
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end());
for (int i = 0; i<arr.size(); ++i){
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
运行结果:

全排列一段数:next_permutation()
按字典序逐个排列
int main(){
vector<int> arr{ 1, 2, 3 };
do{
cout << arr[0] << " " << arr[1] << " " << arr[2] << endl;
} while (next_permutation(arr.begin(), arr.end()));
}

反转指定范围中的元素:reverse()
参数参考排序函数
具体实现略
——计数——
统计某序列中某数值的出现次数:count()
参数为(起始位置,结束位置,待查找的数值)
vector<int> arr{ 3, 2, 5, 1, 6, 9, 6, 6 };
cout << count(arr.begin(), arr.end(), 6) << endl;
运行结果

——查找——
找出某数值在序列中出现的第一个位置:find()
*参数意义类比count()。
vector<int> arr{ 3, 2, 5, 1, 6, 9, 6, 6 };
cout << *find(arr.begin(), arr.end(), 6) << endl;
参数返回值为指针类型

找出某子序列在父序列中出现的第一个位置:search()
vector<int> arr{ 3, 2, 5, 1, 6, 9, 6, 6 };
vector<int> test{ 2, 5, 1 };
cout << *search(arr.begin(), arr.end(), test.begin(), test.end()) << endl;
前两个参数代表父序列范围,后两个为子序列范围

查找数组或容器中第一个大于或小于val的位置:lower_bound()u,pper_bound()
lower_bound(first,last,val) 用来寻找在数组或容器的[first,last)范围内第一个值大于等于val元素的位置,如果是数组,返回该位置的指针;若果是容器,返回该位置的迭代器
upper_bound(first,last,val) 用来寻找在数组或容器的[first,last)范围内第一个值大于val元素的位置,如果是数组,返回该位置的指针;若果是容器,返回该位置的迭代器
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[10]={1,2,2,3,3,4,4,5,6,7};
int *lowerPos=lower_bound(a,a+10,3);
int *upperPos=upper_bound(a,a+10,3);
cout<<"lower_bound(a,a+10,3)="<<lowerPos-a<<endl;
cout<<"upper_bound(a,a+10,3)="<<upperPos-a<<endl;
return 0;
}

——归并——
将两个 有序 序列归并为一个:merge()
int arr[]={ 1, 2, 5 };
int test[]{ 2, 5, 7 };
int C[6];
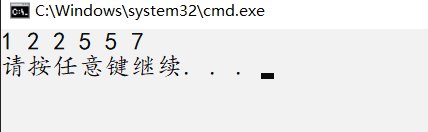
merge(arr, &arr[3], test, &test[3], C);
for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i){
cout << C[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
——比较——
判断两个序列是否相等:equal()
相等返回 true
int arr[]={ 1, 2, 5 };
int test[]{ 2, 5, 7 };
int C[6];
cout << equal(arr, arr + 3, test) << endl;

——赋值——
把数组或容器中的某一段区间赋为某个相同的值: fill()
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[5];
fill(a,a+5,957);
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}






















 2040
2040











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








