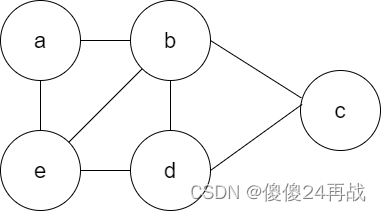
代码实现①建立图(邻接表存储)②邻接表转换成逆邻接表③计算有向图的每个顶点的度④邻接表转换成邻接数组
(1)ALGraph.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#define MAX_VERTEX_NUM 100
#define MAX_LENGTH 100
typedef char VertexType;
//弧结点数据结构
typedef struct ArcNode {
int adjvex;//邻接域
struct ArcNode* nextArc;
int weight;//权值
}ArcNode;
//顶点数据结构
typedef struct VNode {
VertexType data;
ArcNode* firstarc;
}VNode, AdjList[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];
//图的数据结构
typedef struct {
AdjList vertices;
int vexNum, arcNum;
int kind;
}ALGraph;
//建图
void createALGraph(ALGraph& G, VertexType vList[], int vListLength, int arcList[][2], int arcListLength, int kind);
//获得索引下表
int getIndex(ALGraph G, VertexType x);
//插入弧
void insertRALGraph(ALGraph& rG, int v, int w);
//逆邻接表
void reverseALGraph(ALGraph G, ALGraph& rG);
//得到每个顶点的度
void getDegree(ALGraph G, int degreeArr[]);
//邻接矩阵数据结构
typedef struct MGraph {
VertexType vexList[MAX_VERTEX_NUM];//顶点向量
int arcMatrix[MAX_VERTEX_NUM][MAX_VERTEX_NUM];//邻接矩阵
int vexNum, arcNum, kind;//顶点数边数图的种类
}MGraph;
//将邻接表转换成邻接矩阵
void convertAdjList2Matrix(ALGraph G, MGraph& MG);(2)Operate.cpp
#include"ALGraph.h"
/*算法思想:首先将顶点集合存入邻接数组,然后读取每一条边,使用头插法插入相应的链表中,重复上述步骤,直到所有的边访问结束,最后初始化顶点数和边数以及图的种类*/
void createALGraph(ALGraph& G, VertexType vList[], int vListLength, int arcList[][2], int arcListLength, int kind) {
for (int i = 1; i <= vListLength; i++) {
G.vertices[i].data = vList[i];
G.vertices[i].firstarc = NULL;
}
for (int i = 0; i < arcListLength; i++) {
int v = arcList[i][0];
int w = arcList[i][1];
ArcNode* pnode = (ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
pnode->adjvex = w;
pnode->nextArc = G.vertices[v].firstarc;
G.vertices[v].firstarc = pnode;
if (kind == 0) {//无向图
pnode = (ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
pnode->adjvex = v;
pnode->nextArc = G.vertices[w].firstarc;
G.vertices[w].firstarc = pnode;
}
}
G.arcNum = arcListLength;
G.vexNum = vListLength;
G.kind = kind;
}
int getIndex(ALGraph G, VertexType x) {
for (int i = 1; i <= G.vexNum; i++) {
if (G.vertices[i].data == x) {
return i;
break;
}
}
}
/*将邻接表中有向图转换成逆邻接表:在邻接表中首先读取顶点信息存入逆邻接表中,然后从上至下遍历每条链,将读取到的弧结点信息存入逆邻接表中*/
void insertRALGraph(ALGraph& rG, int v, int w) {
ArcNode* pnode = (ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode));
pnode->adjvex = w;
pnode->nextArc = rG.vertices[v].firstarc;
rG.vertices[v].firstarc = pnode;
}
void reverseALGraph(ALGraph G, ALGraph& rG) {
for (int i = 1; i <= G.vexNum; i++) {
rG.vertices[i].data = G.vertices[i].data;
rG.vertices[i].firstarc = NULL;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= G.vexNum; i++) {
int v = getIndex(G,G.vertices[i].data);
ArcNode* pnode = G.vertices[i].firstarc;
while (pnode != NULL) {
int w = pnode->adjvex;
insertRALGraph(rG, w, v);//注意插入顺序
pnode = pnode->nextArc;
}
}
rG.arcNum = G.arcNum;
rG.vexNum = G.vexNum;
rG.kind = G.kind;
}
//得到每个顶点的度
/*算法思想:依次访问邻接表每一个头结点和每一条链中的每一个弧结点,获得每一条弧信息,将每条弧头弧尾度加1*/
void getDegree(ALGraph G, int degreeArr[]) {
for (int i = 1; i <= G.vexNum; i++) {
int v = (getIndex(G, G.vertices[i].data));
ArcNode* pnode = G.vertices[i].firstarc;
while (pnode != NULL) {
int w = pnode->adjvex;
pnode = pnode->nextArc;
degreeArr[v] += 1;
degreeArr[w] += 1;
}
}
}
#define INF 9999999//无穷大
/*邻接表转换成邻接矩阵算法思想:读取图的邻接表中顶点信息将其存入到邻接矩阵的顶点向量中,然后初始化邻接矩阵,从上到下遍历每条链,获取弧<v,x>,并将赋值邻接矩阵v行w列*/
void convertAdjList2Matrix(ALGraph G, MGraph& MG) {
//读取邻接表顶点信息并将其存入邻接矩阵的顶点向量中
for (int i = 1; i <= G.vexNum; i++) {
MG.vexList[i] = G.vertices[i].data;
}
//初始化邻接矩阵,若为不带权图,则初始化为0,若为带权图,则初始化为无穷
//因为建立图的时候邻接数组索引域从1开始,故邻接矩阵下表从1开始
for (int i = 1; i <= G.vexNum; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= G.vexNum; j++) {
if (G.kind == 2) {//带权图初始化无穷
MG.arcMatrix[i][j] = INF;
}
else {//不带权图初始化为0
MG.arcMatrix[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
//读取弧信息,并赋值邻接矩阵
for (int i = 1; i <= G.vexNum; i++) {
int v = getIndex(G, G.vertices[i].data);
ArcNode* pnode = G.vertices[i].firstarc;
while (pnode != NULL) {
int w = pnode->adjvex;
pnode = pnode->nextArc;
if (G.kind == 2) {//带权图获得图的权
MG.arcMatrix[v][w] = pnode->weight;
}
else if (G.kind == 1) {//无向图,矩阵v行w列赋值1
MG.arcMatrix[v][w] = 1;
}
else {//无向图,v行w列和w行v列均需赋值1
MG.arcMatrix[v][w] = 1;
MG.arcMatrix[w][v] = 1;
}
}
}
MG.kind = G.kind;//0为无向图,1为有向图,2为带权图
MG.arcNum = G.arcNum;
MG.vexNum = G.vexNum;
}
(3)main.cpp
#include"ALGraph.h"
int main() {
ALGraph G, rG;//邻接表
MGraph MG;//邻接矩阵
char ch;//处理换行符
int vListLength;
VertexType vList[MAX_LENGTH];
int arcListLength;
int arcList[MAX_LENGTH][2];
int kind;
scanf("%d", &vListLength);
scanf("%c", &ch);
for (int i = 1; i <= vListLength; i++) {
scanf("%c ", &vList[i]);
}
scanf("%d", &arcListLength);
for (int i = 0; i < arcListLength; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
scanf("%d", &arcList[i][j]);
}
}
scanf("%d", &kind);
createALGraph(G, vList, vListLength, arcList, arcListLength, kind);建图
reverseALGraph(G,rG);//转换逆邻接表
int degreeArr[MAX_LENGTH] = { 0 };
getDegree(G, degreeArr);//获得度
convertAdjList2Matrix(G, MG);//转换成逆邻矩阵
return 0;
}(4)样例输入格式






















 1275
1275











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








