在学习数据结构时,我们学习的二叉树是基于链表进行存储,每个节点包含左子节点、右子节点等信息,组成的基于链表存储的二叉树。
但最近我二叉树其实也是可以通过数组也就是说顺序表来实现的。
如图所示。
上代码:
package BTreeV1.ListToBTree;
import BTreeV1.MyArrayList.MyArrayList;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
// 在二叉树中,根节点的编号为1,所在层为1
// 对于编号为n的节点来说,左子节点编号:2n,右子节点编号:2n+1,所在层数为 [log2 (10)] + 1
public class Func1 {
// 判断节点是否存在
public boolean isExist(List list, int index) {
// 越界和索引对应值为null
if (index > list.size() || list.get(index - 1) == null) {
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
// 层序便利
// 在通过链表存储的二叉树中,层序遍历是借助队列完成的,但在通过数组存储的二叉树中,并不需要分配额外的队列空间来实现层序遍历
public void levelOrder(List list) {
// 顺序表长度
int listLength = list.size();
// 二叉树的深度
int depth = (int) (Math.log10(listLength) / Math.log10(2)) + 1;
// 二叉树每层的最大容量计数
int count = 1;
// 当前节点
int current = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < depth; i++) {
for (int k = 0; k < depth - i; k++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
for (int j = 0; j < count && current < listLength; j++, current++) {
System.out.print(list.get(current));
if (list.get(current) == null) {
System.out.print(" ");
} else {
System.out.print(" ");
}
if (current < listLength - 1 && list.get(current + 1) == null) {
System.out.print("");
} else {
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
count *= 2;
System.out.println();
}
}
// 递归的先序遍历
public void preOrderRecur(List list, int index) {
if (isExist(list, index)) {
System.out.print(list.get(index - 1) + " ");
preOrderRecur(list, 2 * index);
preOrderRecur(list, 2 * index + 1);
}
}
// 非递归的先序遍历
public void preOrder(List list, int index) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
while (isExist(list, index) || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (isExist(list, index)) {
System.out.print(list.get(index - 1) + " ");
stack.push(index);
index *= 2;
}
index = stack.pop() * 2 + 1;
}
}
// 非递归的中序遍历
public void inOrder(List list, int index) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
while (isExist(list, index) || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (isExist(list, index)) {
stack.push(index);
index *= 2;
}
int temIndex = stack.pop();
System.out.print(list.get(temIndex - 1) + " ");
index = temIndex * 2 + 1;
}
}
// 非递归的后序遍历
public void postOrder(List list, int index) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
// 记录上一个被访问的节点
int flag = 0;
while (isExist(list, index) || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (isExist(list, index)) {
stack.push(index);
index *= 2;
}
// 访问但不弹出
int temIndex = stack.peek();
if (!isExist(list, 2 * temIndex + 1) || flag == (2 * temIndex + 1)) {
temIndex = stack.pop();
System.out.print(list.get(temIndex - 1) + " ");
flag = temIndex;
} else {
index = 2 * temIndex + 1;
}
}
}
}
测试功能:
package BTreeV1.ListToBTree;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// root index = 1
int index = 1;
Func1 func = new Func1();
Integer[] a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, null, null, 8};
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
list.add(null);
list.add(null);
list.add(7);
System.out.println("层序遍历:");
func.levelOrder(list);
System.out.println("递归的先序遍历:");
func.preOrderRecur(list, index);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("非递归的先序遍历:");
func.preOrder(list, index);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("非递归的中序遍历:");
func.inOrder(list, index);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("非递归的后序遍历:");
func.postOrder(list, index);
System.out.println();
}
}
输出:
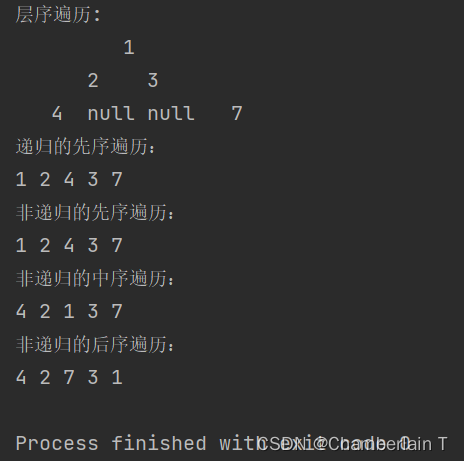
我们实现了基于顺序表存储的二叉树,但这种存储方式是存在浪费空间的(完全二叉树除外),所以基于链表存储的二叉树是我们平时使用较多的。

























 752
752











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








