loong - Java 新特性(8) - Stream
图解
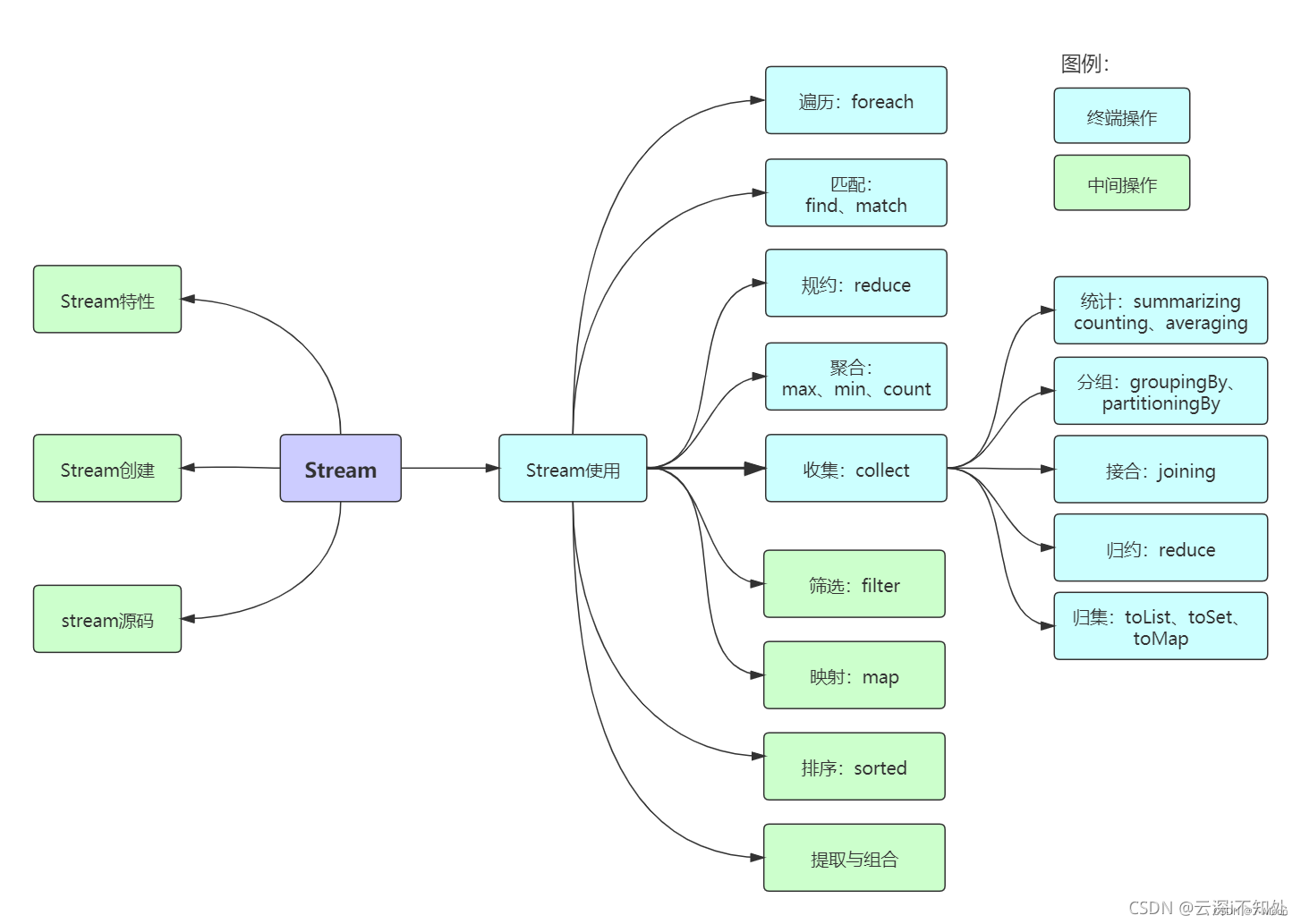
创建流
//返回一个顺序流
default Stream<E> stream()
//返回一个并行流
default Stream<E> parallelStream()
//通过Arrays中得静态方法stream() 获取数组流
IntStream stream = Arrays.stream(new int[]{1,2,3})
//通过Stream类中得of()静态方法获取流
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("a","b","c");
//创建无限流(迭代,生成)
//迭代(需要传入一个种子,也就是起始值,然后传入一元操作)
Stream<Integer> stream=Stream.iterate(2,(x)->x*2);
//生成(无限产生对象)
Stream<Double> stream1=Stream.generate(()->Math.random());
操作符
分类: 中间操作符 终端操作符
中间操作符
| 流操作 | 含义 | 返回值类型 | 链式操作 |
|---|---|---|---|
| filter | 按条件过滤,返回一个新的Stream流 | Stream | 支持 |
| map | 将已有元素转化成另一个对象类型,一对一逻辑 | Stream | 支持 |
| distinct | 去重 | Stream | 支持 |
| sorted | 排序 | Stream | 支持 |
| limit | 限制指定长度 | Stream | 支持 |
| skip | 跳过集合前面指定个数元素 | Stream | 支持 |
| flatMap | 原来一个元素对象可能会转换为1个或多个新类型的元素,一对多逻辑 | Stream | 支持 |
| peek | 对元素进行遍历处理 | Stream | 支持 |
初始化数据
package com.phoenix.learning.Stream;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* @author nieshenglei
*/
@Data
@Builder
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
private String city;
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<User> userList = getUserList();
//操作
}
/**
* 初始化数据
* @return 用户集合
*/
private static List<User> getUserList() {
List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>();
userList.add(new User(1,"张三",18,"上海"));
userList.add(new User(2,"王五",16,"上海"));
userList.add(new User(3,"李四",20,"上海"));
userList.add(new User(4,"张雷",22,"北京"));
userList.add(new User(5,"张超",15,"深圳"));
userList.add(new User(6,"李雷",24,"北京"));
userList.add(new User(7,"王爷",21,"上海"));
userList.add(new User(8,"张三丰",18,"广州"));
userList.add(new User(9,"赵六",16,"广州"));
userList.add(new User(10,"赵无极",26,"赵无极深圳1,赵无极深圳2"));
return userList;
}
}
filter() 过滤
//1、filter:输出ID大于6的user对象
List<User> filterUsers = userList.stream().filter(user -> user.getId() > 6).collect(Collectors.toList());
filterUsers.forEach(System.out::println);
// 结果
User(id=7, name=王爷, age=21, city=上海)
User(id=8, name=张三丰, age=18, city=广州)
User(id=9, name=赵六, age=16, city=广州)
User(id=10, name=赵无极, age=26, city=深圳)
map() 映射
List<String> mapUserList = userList.stream().map(user -> user.getName() + "用户").collect(Collectors.toList());
mapUserList.forEach(System.out::println);
//结果
张三用户
王五用户
李四用户
张雷用户
张超用户
李雷用户
王爷用户
张三丰用户
赵六用户
赵无极用户
//多个Map()
List<String> mapUserList1 =
userList.stream().map(user -> user.getName() + "用户").map(name -> name.substring(0,3)).collect(Collectors.toList());
mapUserList1.forEach(System.out::println);
//结果
张三用
王五用
李四用
张雷用
张超用
李雷用
王爷用
张三丰
赵六用
赵无极
distinct() 去重
List<String> distinctUsers = userList.stream().map(User::getCity).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
distinctUsers.forEach(System.out::println);
//结果
上海
北京
深圳
广州
sorted() 排序
//4、sorted:排序,根据名字倒序
userList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(User::getName).reversed()).collect(Collectors.toList()).forEach(System.out::println);
//结果
User(id=10, name=赵无极, age=26, city=深圳)
User(id=9, name=赵六, age=16, city=广州)
User(id=7, name=王爷, age=21, city=上海)
User(id=2, name=王五, age=16, city=上海)
User(id=6, name=李雷, age=24, city=北京)
User(id=3, name=李四, age=20, city=上海)
User(id=4, name=张雷, age=22, city=北京)
User(id=5, name=张超, age=15, city=深圳)
User(id=8, name=张三丰, age=18, city=广州)
User(id=1, name=张三, age=18, city=上海)
limit() 取指定长数据
//5、limit:取前5条数据
userList.stream().limit(5).collect(Collectors.toList()).forEach(System.out::println);
//结果
User(id=1, name=张三, age=18, city=上海)
User(id=2, name=王五, age=16, city=上海)
User(id=3, name=李四, age=20, city=上海)
User(id=4, name=张雷, age=22, city=北京)
User(id=5, name=张超, age=15, city=深圳)
skip() 跳过指定长度数据
//6、skip:跳过第几条取后几条
userList.stream().skip(7).collect(Collectors.toList()).forEach(System.out::println);
//结果
User(id=8, name=张三丰, age=18, city=广州)
User(id=9, name=赵六, age=16, city=广州)
User(id=10, name=赵无极, age=26, city=深圳)
flatMap()
7、flatMap:数据拆分一对多映射
userList.stream().flatMap(user -> Arrays.stream(user.getCity().split(","))).forEach(System.out::println);
//结果
上海
上海
上海
北京
深圳
北京
上海
广州
广州
赵无极深圳1
赵无极深圳二
peek()
//8、peek:对元素进行遍历处理,每个用户ID加1输出
userList.stream().peek(user -> user.setId(user.getId()+1)).forEach(System.out::println);
//结果
User(id=2, name=张三, age=18, city=上海)
User(id=3, name=王五, age=16, city=上海)
User(id=4, name=李四, age=20, city=上海)
User(id=5, name=张雷, age=22, city=北京)
User(id=6, name=张超, age=15, city=深圳)
User(id=7, name=李雷, age=24, city=北京)
User(id=8, name=王爷, age=21, city=上海)
User(id=9, name=张三丰, age=18, city=广州)
User(id=10, name=赵六, age=16, city=广州)
User(id=11, name=赵无极, age=26, city=赵无极深圳1,赵无极深圳2)
终止操作符
| 操作符 | 含义 | 返回类型 |
|---|---|---|
| collect | 收集器,将流转换为其他形式 | 集合 |
| count | 统计个数 | long |
| findFirst | 返回第一个元素 | T |
| findAny | 将返回当前流中的任意元素 | T |
| noneMatch | 检查是否没有匹配所有元素 | boolean |
| allMatch | 检查是否匹配所有元素 | boolean |
| anyMatch | 检查是否至少匹配一个元素 | boolean |
| forEach | 遍历流 | void |
| max | 最大值 | Optional |
| min | 最小值 | Optional |
| sum | 求和 | |
| reduce | 可以将流中元素反复结合起来,得到一个值 |
forEach()
//forEach:遍历流
userList.stream().forEach(user -> System.out.println(user));
System.out.println("===================================");
userList.stream().filter(user -> "上海".equals(user.getCity())).forEach(System.out::println);
//结果
User(id=1, name=张三, age=18, city=上海)
User(id=2, name=王五, age=16, city=上海)
User(id=3, name=李四, age=20, city=上海)
User(id=4, name=张雷, age=22, city=北京)
User(id=5, name=张超, age=15, city=深圳)
User(id=6, name=李雷, age=24, city=北京)
User(id=7, name=王爷, age=21, city=上海)
User(id=8, name=张三丰, age=18, city=广州)
User(id=9, name=赵六, age=16, city=广州)
User(id=10, name=赵无极, age=26, city=赵无极深圳1,赵无极深圳2)
===================================
User(id=1, name=张三, age=18, city=上海)
User(id=2, name=王五, age=16, city=上海)
User(id=3, name=李四, age=20, city=上海)
User(id=7, name=王爷, age=21, city=上海)
findFirst()
//findFirst:返回第一个元素
User firstUser = userList.stream().findFirst().get();
User firstUser1 = userList.stream().filter(user -> "上海".equals(user.getCity())).findFirst().get();
System.out.println(firstUser);
System.out.println(firstUser1);
//结果
User(id=1, name=张三, age=18, city=上海)
User(id=1, name=张三, age=18, city=上海)
findAny()
//findAny:将返回当前流中的任意元素
User findUser = userList.stream().findAny().get();
User findUser1 = userList.stream().filter(user -> "上海".equals(user.getCity())).findAny().get();
System.out.println(findUser);
System.out.println(findUser1);
//结果
User(id=1, name=张三, age=18, city=上海)
User(id=4, name=张雷, age=22, city=北京)
count()
//count:返回流中元素总数
long count = userList.stream().filter(user -> user.getAge() > 20).count();
System.out.println(count);
//结果
4
sum()
//sum:求和
int sum = userList.stream().mapToInt(User::getId).sum();
//结果
55
max()
//max:最大值
int max = userList.stream().max(Comparator.comparingInt(User::getId)).get().getId();
System.out.println(max);
//结果
10
min()
//min:最小值
int min = userList.stream().min(Comparator.comparingInt(User::getId)).get().getId();
//结果
1
max() min() 案例二
public class StreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
//max()
Stream<Integer> stream01 = Stream.of(33, 11, 22, 5);
Optional<Integer> max = stream01.max((i1, i2) -> i1 - i2);
System.out.println("最大值:"+max.get());
//min()
Stream<Integer> stream02 = Stream.of(33, 11, 22, 5);
Optional<Integer> min = stream02.min((i1, i2) -> i1 - i2);
System.out.println("最小值:"+min.get());
}
}
//结果
最大值:33
最小值:5
anyMatch()
//anyMatch:检查是否至少匹配一个元素
boolean matchAny = userList.stream().anyMatch(user -> "北京".equals(user.getCity()));
System.out.println(matchAny);
// 结果
true
allMatch()
//allMatch:检查是否匹配所有元素
boolean matchAll = userList.stream().allMatch(user -> "北京".equals(user.getCity()));
//结果
false
noneMatch()
//11、noneMatch:检查是否没有匹配所有元素,返回boolean
boolean nonaMatch = userList.stream().allMatch(user -> "云南".equals(user.getCity()));
//结果
false
anyMatch() allMatch() noneMatch()
public class StreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
Stream<Integer> stream01 = Stream.of(5, 3, 6, 1);
boolean allMatch = stream01.allMatch(i -> i > 0);
System.out.println("allMatch匹配:"+allMatch);
Stream<Integer> stream02 = Stream.of(5, 3, 6, 1);
boolean anyMatch = stream02 .anyMatch(i -> i > 5);
System.out.println("anyMatch匹配:"+anyMatch);
Stream<Integer> stream03 = Stream.of(5, 3, 6, 1);
boolean noneMatch = stream03 .noneMatch(i -> i < 3);
System.out.println("noneMatch匹配:"+noneMatch);
}
}
//结果
allMatch匹配:true
anyMatch匹配:true
noneMatch匹配:false
reduce()
public class StreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
//reduce():求和操作
Stream<Integer> stream01 = Stream.of(4,3,5,6);
Integer sum = stream01.reduce(0,(x,y)-> x + y);
System.out.println("求和:"+sum);
//reduce():求最大值操作
Stream<Integer> stream01 = Stream.of(4,3,5,6);
Integer max= stream01.reduce(0,(x,y)-> x > y ? x : y);
System.out.println("最大值为:"+max);
//reduce():求最小值操作
Stream<Integer> stream01 = Stream.of(4,3,5,6);
Optional<Integer> max= stream01.reduce((x, y)-> x < y ? x : y);
System.out.println("最小值为:"+max.get());
//结果
//求和:18
//最大值:6
//最小值:3
}
}
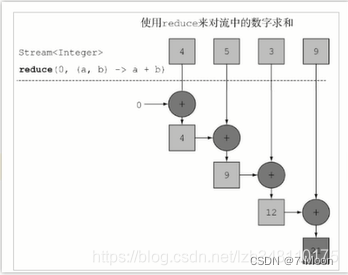
解析(求和解析)
求和流程:
第一次:将默认值赋值给x,取出集合第一个元素赋值给y
第二步:将上一次返回的结果赋值给x,取出集合第二个元素赋值给y
第三步:继续执行第二步(如下图所示)
collect()
PS(注意事项):Stream不调用终止方法,中间的操作不会执行
收集Stream流中的数据到集合中
//1.收集数据到list集合中
stream.collect(Collectors.toList())
//2.收集数据到set集合中
stream.collect(Collectors.toSet())
//3.收集数据到指定的集合中
Collectors.toCollection(Supplier<C> collectionFactory)
示例
/**
* 收集Stream流中的数据到集合中
* 备注:切记Stream流只能被消费一次,流就失效了
* 如下只是示例代码
*/
public class CollectDataToCollection{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Stream 流
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "bbb");
//收集流中的数据到集合中
//1.收集流中的数据到 list
List<String> list = stream.collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list);
//2.收集流中的数据到 set
Set<String> collect = stream.collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(collect);
//3.收集流中的数据(ArrayList)(不收集到list,set等集合中,而是)收集到指定的集合中
ArrayList<String> arrayList = stream.collect(Collectors.toCollection(ArrayList::new));
System.out.println(arrayList);
//4.收集流中的数据到 HashSet
HashSet<String> hashSet = stream.collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));
System.out.println(hashSet);
}
}
测试结果:
[aaa, bbb, ccc, bbb]
[aaa, ccc, bbb]
[aaa, bbb, ccc, bbb]
[aaa, ccc, bbb]
收集Stream流中的数据到数组中
//1.使用无参,收集到数组,返回值为 Object[](Object类型将不好操作)
Object[] toArray();
//2.使用有参,可以指定将数据收集到指定类型数组,方便后续对数组的操作
<A> A[] toArray(IntFunction<A[]> generator);
示例
/**
* 收集Stream流中的数据到数组中
* 备注:切记Stream流只能被消费一次,流就失效了
* 如下只是示例代码
*/
public class CollectDataToArray{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Stream 流
Stream<String> stream = Stream.of("aaa", "bbb", "ccc", "bbb");
//2.1 使用 toArray()无参
Object[] objects = stream.toArray();
for (Object o: objects) {//此处无法使用.length() 等方法
System.out.println("data:"+o);
}
//2.2 使用有参返回指定类型数组
//无参不好的一点就是返回的是 Object[] 类型,操作比较麻烦.想要拿到长度,Object是拿不到长度的
String[] strings = stream.toArray(String[]::new);
for(String str : strings){
System.out.println("data:"+str + ",length:"+str.length());
}
}
}
测试结果
data:aaa
data:bbb
data:ccc
data:bbb
-----------------
data:aaa,length:3
data:bbb,length:3
data:ccc,length:3
data:bbb,length:3
Stream中数据聚合/分组/分区/拼接操作
实体类(Student)
/**
* TODO Student实体类
*
* @author liuzebiao
* @Date 2020-1-10 13:38
*/
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private int score;
public Student(String name, int age, int score) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.score = score;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(int score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", score=" + score +
'}';
}
}
聚合操作
//最大值
Collectors.maxBy();
//最小值
Collectors.minBy();
//总和
Collectors.summingInt();/Collectors.summingDouble();/Collectors.summingLong();
//平均值
Collectors.averagingInt();/Collectors.averagingDouble();/Collectors.averagingLong();
//总个数
Collectors.counting();
示例
/**
* Stream流数据--聚合操作
* 备注:切记Stream流只能被消费一次,流就失效了
* 如下只是示例代码
* @author liuzebiao
* @Date 2020-1-10 13:37
*/
public class CollectDataToArray{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of(
new Student("赵丽颖", 58, 95),
new Student("杨颖", 56, 88),
new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 99),
new Student("柳岩", 52, 77)
);
//聚合操作
//获取最大值(Stream流 max()方法亦可)
//max()方法实现
//Optional<Student> max = studentStream.max((s1, s2) -> s1.getScore() - s2.getScore());
//(聚合)实现
Optional<Student> max = studentStream.collect(Collectors.maxBy((s1, s2) -> s1.getScore() - s2.getScore()));
System.out.println("最大值:"+max.get());
//获取最小值(Stream流 min()方法亦可)
//min()方法实现
//Optional<Student> min = studentStream.max((s1, s2) -> s2.getScore() - s1.getScore());
//(聚合)实现
Optional<Student> min = studentStream.collect(Collectors.minBy((s1, s2) -> s1.getScore() - s2.getScore()));
System.out.println("最小值:"+min.get());
//求总和(使用Stream流的map()和reduce()方法亦可求和)
//map()和reduce()方法实现
//Integer reduce = studentStream.map(s -> s.getAge()).reduce(0, Integer::sum);
//(聚合)简化前
//Integer ageSum = studentStream.collect(Collectors.summingInt(s->s.getAge()));
//(聚合)使用方法引用简化
Integer ageSum = studentStream.collect(Collectors.summingInt(Student::getAge));
System.out.println("年龄总和:"+ageSum);
//求平均值
//(聚合)简化前
//Double avgScore = studentStream.collect(Collectors.averagingInt(s->s.getScore()));
//(聚合)使用方法引用简化
Double avgScore = studentStream.collect(Collectors.averagingInt(Student::getScore));
System.out.println("分数平均值:"+avgScore);
//统计数量(Stream流 count()方法亦可)
//count()方法实现
//long count = studentStream.count();
//(聚合)统计数量
Long count = studentStream.collect(Collectors.counting());
System.out.println("数量为:"+count);
}
}
测试结果
最大值:Student{name='迪丽热巴', age=56, score=99}
最小值:Student{name='柳岩', age=52, score=77}
年龄总和:222
分数平均值:89.75
数量为:4
分组操作
//接收一个 Function 参数
groupingBy(Function<? super T, ? extends K> classifier)
示例
/**
* Stream流数据--分组操作
* 备注:切记Stream流只能被消费一次,流就失效了
* 如下只是示例代码
* @author liuzebiao
* @Date 2020-1-10 13:37
*/
public class CollectDataToArray{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of(
new Student("赵丽颖", 52, 56),
new Student("杨颖", 56, 88),
new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 99),
new Student("柳岩", 52, 53)
);
//1.按照具体年龄分组
Map<Integer, List<Student>> map = studentStream.collect(Collectors.groupingBy((s -> s.getAge())));
map.forEach((key,value)->{
System.out.println(key + "---->"+value);
});
//2.按照分数>=60 分为"及格"一组 <60 分为"不及格"一组
Map<String, List<Student>> map = studentStream.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(s -> {
if (s.getScore() >= 60) {
return "及格";
} else {
return "不及格";
}
}));
map.forEach((key,value)->{
System.out.println(key + "---->"+value.get());
});
//3.按照年龄分组,规约求每组的最大值最小值(规约:reducing)
Map<Integer, Optional<Student>> reducingMap = studentStream.collect(
Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getAge,
Collectors.reducing(
BinaryOperator.maxBy(
Comparator.comparingInt(Student::getScore)
)
)
)
);
reducingMap .forEach((key,value)->{
System.out.println(key + "---->"+value);
});
}
}
测试结果
52---->[Student{name='赵丽颖', age=52, score=56}, Student{name='柳岩', age=52, score=53}]
56---->[Student{name='杨颖', age=56, score=88}, Student{name='迪丽热巴', age=56, score=99}]
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
不及格---->[Student{name='赵丽颖', age=52, score=56}, Student{name='柳岩', age=52, score=53}]
及格---->[Student{name='杨颖', age=56, score=88}, Student{name='迪丽热巴', age=56, score=99}]
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
52---->Student{name='赵丽颖', age=52, score=95}
56---->Student{name='杨颖', age=56, score=88}
多级分组操作
当我们使用 Stream 流处理数据后,可以根据某个属性来将数据进行分组。
//接收两个参数: 1.Function 参数 2.Collector多级分组
groupingBy(Function<? super T, ? extends K> classifier,Collector<? super T, A, D> downstream)
示例
/**
* Stream流数据--多级分组操作
* 备注:切记Stream流只能被消费一次,流就失效了
* 如下只是示例代码
* @author liuzebiao
* @Date 2020-1-10 13:37
*/
public class CollectDataToArray{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of(
new Student("赵丽颖", 52, 95),
new Student("杨颖", 56, 88),
new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 55),
new Student("柳岩", 52, 33)
);
//多级分组
//1.先根据年龄分组,然后再根据成绩分组
//分析:第一个Collectors.groupingBy() 使用的是(年龄+成绩)两个维度分组,所以使用两个参数 groupingBy()方法
// 第二个Collectors.groupingBy() 就是用成绩分组,使用一个参数 groupingBy() 方法
Map<Integer, Map<Integer, Map<String, List<Student>>>> map = studentStream.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(str -> str.getAge(), Collectors.groupingBy(str -> str.getScore(), Collectors.groupingBy((student) -> {
if (student.getScore() >= 60) {
return "及格";
} else {
return "不及格";
}
}))));
map.forEach((key,value)->{
System.out.println("年龄:" + key);
value.forEach((k2,v2)->{
System.out.println("\t" + v2);
});
});
}
}
测试结果
年龄:52
{不及格=[Student{name='柳岩', age=52, score=33}]}
{及格=[Student{name='赵丽颖', age=52, score=95}]}
年龄:56
{不及格=[Student{name='迪丽热巴', age=56, score=55}]}
{及格=[Student{name='杨颖', age=56, score=88}]}
分区操作
我们在前面学习了 Stream流中数据的分组操作,我们可以根据属性完成对数据的分组。接下来我们介绍分区操作,我们通过使用 Collectors.partitioningBy() ,根据返回值是否为 true,把集合分为两个列表,一个 true 列表,一个 false 列表。

**分组和分区的区别就在:**分组可以有多个组。分区只会有两个区( true 和 false)
//1.一个参数
partitioningBy(Predicate<? super T> predicate)
//2.两个参数(多级分区)
partitioningBy(Predicate<? super T> predicate, Collector<? super T, A, D> downstream)
示例
/**
* Stream流数据--多级分组操作
* 备注:切记Stream流只能被消费一次,流就失效了
* 如下只是示例代码
* @author liuzebiao
* @Date 2020-1-10 13:37
*/
public class CollectDataToArray{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of(
new Student("赵丽颖", 52, 95),
new Student("杨颖", 56, 88),
new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 55),
new Student("柳岩", 52, 33)
);
//分区操作
Map<Boolean, List<Student>> partitionMap = studentStream.collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(s -> s.getScore() > 60));
partitionMap.forEach((key,value)->{
System.out.println(key + "---->" + value);
});
}
}
测试结果
false---->[Student{name='迪丽热巴', age=56, score=55}, Student{name='柳岩', age=52, score=33}]
true---->[Student{name='赵丽颖', age=52, score=95}, Student{name='杨颖', age=56, score=88}]
拼接操作
Collectors.joining() 会根据指定的连接符,将所有元素连接成一个字符串。
//无参数--等价于 joining("");
joining()
//一个参数
joining(CharSequence delimiter)
//三个参数(前缀+后缀)
joining(CharSequence delimiter, CharSequence prefix,CharSequence suffix)
示例
/**
* Stream流数据--多级分组操作
* 备注:切记Stream流只能被消费一次,流就失效了
* 如下只是示例代码
* @author liuzebiao
* @Date 2020-1-10 13:37
*/
public class CollectDataToArray{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of(
new Student("赵丽颖", 52, 95),
new Student("杨颖", 56, 88),
new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 55),
new Student("柳岩", 52, 33)
);
//拼接操作
//无参:join()
String joinStr1 = studentStream.map(s -> s.getName()).collect(Collectors.joining());
System.out.println(joinStr1);
//一个参数:joining(CharSequence delimiter)
String joinStr2 = studentStream.map(s -> s.getName()).collect(Collectors.joining(","));
System.out.println(joinStr2);
//三个参数:joining(CharSequence delimiter, CharSequence prefix,CharSequence suffix)
String joinStr3 = studentStream.map(s -> s.getName()).collect(Collectors.joining("—","^_^",">_<"));
System.out.println(joinStr3);
}
}
测试结果
赵丽颖杨颖迪丽热巴柳岩
赵丽颖,杨颖,迪丽热巴,柳岩
^_^赵丽颖—杨颖—迪丽热巴—柳岩>_<
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stream<Student> studentStream = Stream.of(
new Student("赵丽颖", 52, 95),
new Student("杨颖", 56, 88),
new Student("迪丽热巴", 56, 55),
new Student("柳岩", 52, 33)
);
//拼接操作
//无参:join()
String joinStr1 = studentStream.map(s -> s.getName()).collect(Collectors.joining());
System.out.println(joinStr1);
//一个参数:joining(CharSequence delimiter)
String joinStr2 = studentStream.map(s -> s.getName()).collect(Collectors.joining(","));
System.out.println(joinStr2);
//三个参数:joining(CharSequence delimiter, CharSequence prefix,CharSequence suffix)
String joinStr3 = studentStream.map(s -> s.getName()).collect(Collectors.joining("—","^_^",">_<"));
System.out.println(joinStr3);
}
}
测试结果
赵丽颖杨颖迪丽热巴柳岩
赵丽颖,杨颖,迪丽热巴,柳岩
^_^赵丽颖—杨颖—迪丽热巴—柳岩>_<






















 324
324











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










