异常
一、异常的概述
异常:程序出现了不正常的情况。
1、异常的分类

Error:严重问题,不需要处理
Exception:异常类,表示程序本身可以处理的问题
RuntimeException:在编译期不检查,出现问题后需要我们回来修改代码。
CheckedException:编译期就必须处理的,否则程序不能通过编译。
2、JVM的默认处理方案
- 把异常的名称,异常原因及异常出现的位置等信息输出在了控制台
- 程序停止执行
二、异常处理
try…catch…
try{
可能出现异常的代码;
}catch(Exception e){
异常的处理代码;
//当异常发生时,系统将异常封装成Exception对象e,传递给catch
}finally{
//不管是否有异常发生,始终要执行finally
通常将释放资源的代码放在finally中。
}
示例代码:
try{
int div=10/0;//异常发生处,程序运行到这里后异常被捕获,后面的代码内容不再执行,跳转到catch里面的代码块。
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}catch (ArithmeticException e){ //catch语句块可以有多个。
System.out.println("捕获了运算异常。");
e.printStackTrace(); //显示异常追踪信息
}catch (ClassCastException e){
System.out.println("捕获类型转换异常。");
} finally {//不强制要求有finally选项
System.out.println("finally语句块无论是否产生异常都会执行。");
//释放资源,删除临时文件等操作!
}
//若try中存在某种异常没有编写捕获程序,则程序无法捕获异常,执行完finally后程序无法向下执行,程序终止。
执行流程:
- 程序从try里面的代码开始执行
- 出现异常,会自动生成一个异常类对象,该异常对象将被提交给Java运行时系统
- 当Java运行时系统接收到异常对象时,会到catch中去找匹配的异常类,找到后进行异常的处理。如果异常发生,则异常后面的代码不会执行,直接进入catch块。
- 执行完毕之后,程序还可以继续往下执行
注意点:
- 一个try可以匹配多个catch语句
- 如果try中产生了异常对象,那么会跳出try到相应的catch中处理异常,从上到下匹配。
- 如果是多个catch语句,小的异常捕获处理写在前面,大的异常捕获处理写后面。如:Exception异常要写在ArithmeticException(运算异常)后面。
- finally是可选的。
- 快捷键:Ctrl+alt+t :try ,catch ,finally语句块;Ctrl+alt+L :格式化代码
- 如果catch块中有return语句,先不允许,等运行完finally块的代码后再执行return语句,但返回值仍是该return后的返回值(会有一个指针记录该值)。如果catch块和finally块中均含有return语句,执行finally块中的语句。
练习:利用try-catch语句来实现输入一个整数,如果输入的不是整数就循环输入。
package Exception_Learn;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class TryCatchInput {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
String inputString="";
int result;
while (true) {
System.out.print("请输入一个整数:");
inputString=sc.next();
try {
result = Integer.parseInt(inputString);//将字符串转成int型数据
break;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("你输入的内容不是整数!!!");
}
}
System.out.println("你输入的整数为:"+result);
}
}
throws声明异常
方法级别上,向外抛出异常。
示例代码:
public class Throws_Learn {
public static void Learn() throws ArithmeticException{//声明这个方法有异常,谁调用方法谁处理
int div =10/0;//运算异常
}
public static void Learn2() throws ArithmeticException{
Learn();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ArithmeticException {
//在main方法中,可以用try-catch处理异常,也可以在main方法声明时将异常抛给jvm
try {
Learn2();
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("执行完毕!");
}catch(NullPointerException e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
 注意点:
注意点:
- 运行时异常的抛出,不一定要处理。
- 检查异常的抛出,必须处理。(编译器不通过的异常)
- 重写的时候,子类不能抛出比父类更大的异常(同级异常可以)。
三、自定义异常
throw关键字
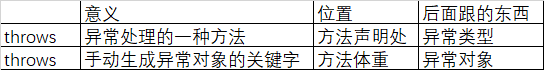
throw主动抛出一个异常的对象。打断程序的执行。配合try-catch或throws使用。
区别:throws是在定义方法的时候,声明该方法将异常抛出。
public class Throw_Learn {
public static int div(int x,int y) throws Exception{
if(y==0){//如果除数等于0,抛出一个异常。
throw new Exception("除数不能为0!");
}
return x/y;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
div(9,0);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
System.out.println("Hello,World!");
}
}
}
需要继承Exception或Exception的子类,代表特定问题。
作用:异常类型名称望文生义,可在发生特定问题的时候抛出对应的异常。
常用构造方法:
- 无参数构造方法
- String message参数构造方法。(见下)
示例代码:
People.java文件
public class People {
int age;
public void setAge(int age) {
if(age<0){//年龄小于0时抛出异常
throw new AgeException("年龄输入不合法!");
}
this.age=age;//等号左边的age为People类中的age,右边的age为setAge方法中的age。
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
People man=new People();
try {//处理异常
man.setAge(-1);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
}
}
}
AgeException.java文件
//自定义异常
public class AgeException extends RuntimeException {
public AgeException(String message){
super(message);
}
}





















 2887
2887











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








