Spring
1.简介
- 首次推出:2002年 Spring框架雏形:interface21
- 正式版:以interface21框架为基础,经过程序设计,并不断丰富内涵,于2004年3月24日,发布了1.0正式版
- Spring理念:使现有技术更加容易使用,整合了现有的技术框架
- SSH: Struct2+Spring+Hibernate
- SSM:SpringMVC+Spring+Mybatis
官网: Spring Framework
中文文档:Spring Framework 中文文档 - Spring Framework 5.1.3.RELEASE Reference | Docs4dev
官方下载地址: repo.spring.io
GitHub: spring-projects/spring-framework: Spring Framework (github.com)
Spring Mavean
Maven Repository: Search/Browse/Explore (mvnrepository.com)
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-webmvc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.21</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-webmvc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.21</version>
</dependency>
2.优点
- Spring是一个开源的免费的框架
- Spring是一个轻量级、非入侵式的框架
- 两个特性:控制反转(IOC)、面向切面编程(AOP)
- 支持事务的处理,对框架整合的支持
Spring是一个轻量级的控制反转(IOC)和面向切面编程(AOP)的框架
3.组成

参考博客:Spring框架七大核心模块_crazy丢的博客-CSDN博客_spring七大模块
4.Spring简化Java开发的策略
- 基于POJO的轻量级和最小侵入性编程
- 通过IOC,依赖注入(DI)和面向接口实现松耦合
- 基于切面(AOP)和惯例进行声明式编程
- 通过切面和末班减少样式代码
5.拓展
- Spring Boot
- 一个快速开发的脚手架
- 基于SprintBoot可以快速开发单个微服务
- Spring Cloud
- 基于SpringBoot实现
IOC
1.理论推导
-
set注入
private UserDao userDao; //利用set进行动态实现值的注入 public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) { this.userDao = userDao; }使用set注入之后,程序由主动创建对象变为被动接受对象
这种思想从本质上解决了问题,大大降低了系统的耦合性
2.本质
控制反转IOC是一种设计思想,DI(依赖注入)是实现IOC的一种方法。
没有IOC的程序中,我们使用面向对象编程,对象的创建与对象间的依赖关系完全硬编码在程序中,对象的创建由程序自己控制,控制反转后将对象的创建转移给第三方。获得依赖对象的方式反转了
IOC是Spring框架的核心内容,可以使用XML配置,也可以使用注解、
Spring容器在初始化时先读取配置文件,根据配置文件或元数据创建与组织对象存入容器,程序使用时再从IOC容器中取出需要的对象

采用XML方式配置Bean时,Bean的定义信息是和实现分离的,而采用注解的方式可以把两者合为一体,Bean的定义信息直接以注解的形式定义在实现类中,从而达到了零配置的目的
控制反转是一种通过描述(XML或注解)并通过第三方去生存或获取特定对象的方式。在Spring中实现控制反转的是IOC容器,其实现方法是依赖注入(DI)
3.控制反转过程
控制:传统应用程序的对象是由程序本身控制创建的,使用Spring后,对象是由Spring创建的
反转:程序本身不创建对象,变成被动的接收对象
依赖注入:利用Set方法进行注入
HelloSpring
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--使用spring创建对象
bean=对象 new Hello();
id=变量名 class=new的对象 property相当于给对象设置一个值
-->
<bean id="hello" class="com.example.pojo.Hello">
<property name="str" value="Spring"/>
</bean>
</beans>
Hello.java
package com.example.pojo;
public class Hello {
private String str;
public String getStr() {
return str;
}
public void setStr(String str) {
this.str = str;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Hello{" +
"str='" + str + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
MyTest.java
import com.example.pojo.Hello;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取Spring上下文对象
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
//对象都在Spring中管理 要使用时直接调用
Hello hello=(Hello) context.getBean("hello");
System.out.println(hello.toString());
}
}
运行结果

- Hello对象由Spring创建
- Hello对象的属性由Spring容器设置(依赖注入)
IOC创建对象
-
使用无参构造创建对象(默认)
-
有参构造
-
下标赋值
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--下标赋值--> <bean id="user" class="com.example.pojo.User"> <constructor-arg index="0" value="张三"/> </bean> </beans> -
通过类型创建
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--通过类型创建--> <bean id="user" class="com.example.pojo.User"> <constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="张三"/> </bean> </beans> -
通过参数名赋值
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--通过参数名赋值--> <bean id="user" class="com.example.pojo.User"> <constructor-arg name="name" value="张三"/> </bean> </beans>
-
Spring配置
1 别名
<alias name="user" alias="用户"/>
在程序中可以使用别名获取对象
2 Bean的配置
<bean id="user" class="com.example.pojo.User" name="user2,用户">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="张三"/>
</bean>
<!--
id:bean的唯一标识符,相当于对象名
class:bean对象所对应的全限定名(包名+类名)
name:作用等同alias,可以同时取多个别名
-->
3 import
一般用于团队开发,可以将多个配置文件导入合并为一个文件
依赖注入
注入方式:
- 构造器注入
- Set方式注入
- 拓展方式注入
1 Set方式注入
依赖:bean对象的创建依赖于容器
注入:bean对象中的所有属性,由容器注入
环境搭建
复杂类型 Address.java
package com.example.pojo;
public class Address {
private String address;
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Address{" +
"address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
真实测试对象 Student.java
package com.example.pojo;
import java.util.*;
public class Student {
private String name;
private Address address;
private String[] books;
private List<String> hobby;
private Map<String,String> card;
private Set<String> games;
private Properties info;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String[] getBooks() {
return books;
}
public void setBooks(String[] books) {
this.books = books;
}
public List<String> getHobby() {
return hobby;
}
public void setHobby(List<String> hobby) {
this.hobby = hobby;
}
public Map<String, String> getCard() {
return card;
}
public void setCard(Map<String, String> card) {
this.card = card;
}
public Set<String> getGames() {
return games;
}
public void setGames(Set<String> games) {
this.games = games;
}
public Properties getInfo() {
return info;
}
public void setInfo(Properties info) {
this.info = info;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", address=" + address.toString() +
", books=" + Arrays.toString(books) +
", hobby=" + hobby +
", card=" + card +
", games=" + games +
", info=" + info +
'}';
}
}
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="address" class="com.example.pojo.Address">
<property name="address" value="杭州"/>
</bean>
<bean id="student" class="com.example.pojo.Student">
<!--普通值注入 value-->
<property name="name" value="张三"/>
<!--bean注入 ref-->
<property name="address" ref="address"/>
<!--数组注入 array value-->
<property name="books">
<array>
<value>红楼梦</value>
<value>水浒传</value>
<value>西游记</value>
<value>三国演义</value>
</array>
</property>
<!--List注入-->
<property name="hobby">
<list>
<value>听音乐</value>
<value>打游戏</value>
<value>看电影</value>
</list>
</property>
<!--Map注入-->
<property name="card">
<map>
<entry key="IDCard" value="1234567890"/>
<entry key="Credit" value="1234561234"/>
</map>
</property>
<!--Set注入-->
<property name="games">
<set>
<value>LOL</value>
<value>GenShin</value>
</set>
</property>
<!--properties注入-->
<property name="info">
<props>
<prop key="学号">1001</prop>
<prop key="性别">男</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
测试类 MyTest.java
import com.example.pojo.Student;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Student student=(Student) context.getBean("student");
System.out.println(student.getName());
}
}
2 拓展方式注入
p命名空间和c命名空间不能直接使用,需要导入xml约束
p命名空间:
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
c命名空间
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
<!--p命名空间注入 可以直接注入属性的值 property-->
<bean id="user" class="com.example.pojo.User" p:name="张三" p:age="20"/>
<!--c命名空间注入 通过构造器注入 construct-args-->
<bean id="user1" class="com.example.pojo.User" c:age="21" c:name="李四"/>
bean的作用域

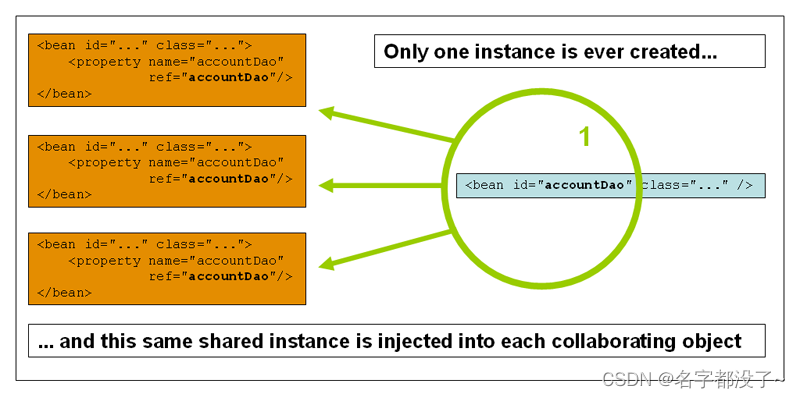
单例模式 singleton
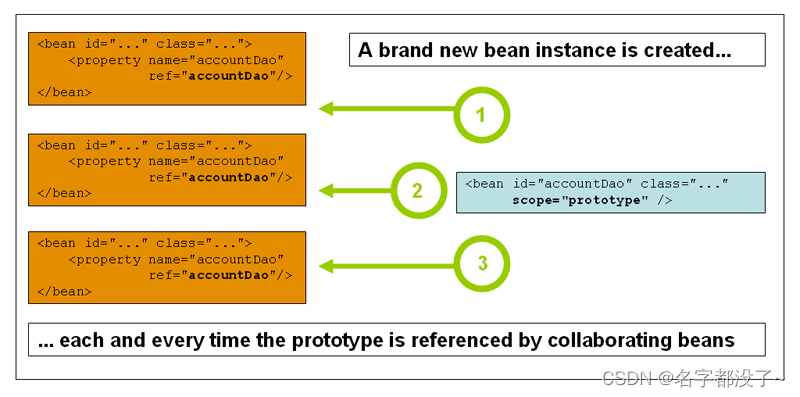
原型模式 prototype
每次从容器中get时产生一个新对象
Bean的自动装配
Spring在上下文中自动寻找,并为bean自动装配属性
装配方式
- 在xml中显式的配置
- 在java中显式配置
- 隐式的自动装配
1 自动装配
<bean id="cat" class="com.example.pojo.Cat"/>
<bean id="dog" class="com.example.pojo.Dog"/>
<!--
byName:根据属性名和id匹配
byType:根据属性的类型和class匹配
-->
<!--<bean id="person" class="com.example.pojo.Person" autowire="byName">
<property name="name" value="张三"/>
</bean>-->
<bean id="person" class="com.example.pojo.Person" autowire="byType">
<property name="name" value="张三"/>
</bean>
-
byName需要保证所有bean的id唯一,并且这个bean需要和自动注入的属性的set方法的值一致
-
byType需要保证所有的bean的class唯一,并且这个bean需要和自动注入的属性的类型一致
2 使用注解实现自动装配
-
导入约束 context约束
-
配置注解的支持
<context:annotation-config/>
@Autowired
- 直接在属性或set方法上使用
- 当自动装配的属性在IOC容器中存在且符合byName时,可以省略set方法
@Nullable //标记字段可以为null,作用同@Autowired(required=false)
package com.example.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class Person {
@Autowired
private Cat cat;
@Autowired
private Dog dog;
private String name;
public Cat getCat() {
return cat;
}
public Dog getDog() {
return dog;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"cat=" + cat +
", dog=" + dog +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
@Qualifier(value=“xxx”)
配合**@Autowired**使用,指定唯一的bean对象注入
@Resource
@Resource
private Cat cat;
@Resource和@Autowired区别
- @Autowired通过byTame方式实现,且对象必须存在
- @Resource默认通过byName方式实现,若找不到名字,就通过byType实现。如果两种方式都找不到,就报错
使用注解开发
1 bean
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:annotation-config/>
<!--指定要扫描的包,使包下的注解生效-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.example.pojo"/>
</beans>
2 属性如何注入
package com.example.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component //相当于<bean id="user" class="com.example.pojo.User"/>
public class User {
public String name;
//相当于<property name="name" value="张三"/>
@Value("张三")
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
3 衍生的注解
@Component的衍生注解
- dao 【@Repository】
- service 【@Service】
- controller 【@Controller】
都代表将某个类注册到Spring中,并装配bean
使用java配置spring
JavaConfig:Spring的子项目,在Spring4之后成为核心功能
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.example.pojo")
public class MyConfig {
@Bean
//id为方法名 class属性为方法返回值
public User getUser(){
return new User();//返回要注入到bean的对象
}
}
测试类
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context=new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MyConfig.class);
User user= (User) context.getBean("getUser");
System.out.println(user.name);
}
}
代理模式
分类
- 静态代理
- 动态代理
1 静态代理
角色分析
- 抽象角色:一般使用抽象类或接口解决
- 真实角色:被代理的角色
- 代理角色:代理真实角色
- 客户:访问代理对象的角色
好处
- 可以使真实角色的操作更纯粹
- 公共业务由代理角色管理,实现了业务的分工
- 公共业务发生扩展时,方便集中管理
缺点
- 一个真实角色会产生一个代理角色,降低了开发效率
代码步骤
接口
package com.example.demo1;
//租房
public interface Rent {
public void rent();
}
真实角色
package com.example.demo1;
//房东
public class Host implements Rent{
@Override
public void rent() {
System.out.println("房东出租房子");
}
}
代理角色
package com.example.demo1;
public class Proxy {
private Host host;
public Proxy(){}
public Proxy(Host host){
this.host=host;
}
public void rent(){
host.rent();
}
//看房
public void seeHouse(){
System.out.println("看房");
}
//收中介费
public void fare(){
System.out.println("收中介费");
}
//签租赁合同
public void agreement(){
System.out.println("签合同");
}
}
客户端访问代理角色
package com.example.demo1;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//房东要出租房子
Host host=new Host();
//代理角色一般会有附属操作
Proxy proxy=new Proxy(host);
//越过房东 和中介对接
proxy.rent();
}
}
2 动态代理
- 动态代理和静态代理角色一致
- 动态代理的代理类是动态生成的
- 动态代理分类
- 基于接口的动态代理
- JDK动态代理
- 基于类的动态代理
- cglib
- Java字节码实现
- JAVAssist
- 基于接口的动态代理
动态代理的好处:
- 一个动态代理类代理一个接口,对应一类业务
- 只要实现同一个接口,一个动态代理类可以代理多个类
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
//使用这个类自动生成代理类
public class ProxyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
// Foo f = (Foo) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Foo.class.getClassLoader(),
// new Class<?>[] { Foo.class },
// handler);
//被代理的接口
private Object target;
public void setTarget(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
//生成得到代理类
public Object getProxy(){
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.getClass().getClassLoader(),
target.getClass().getInterfaces(),
this);
}
//处理代理实例并返回结果
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
log(method.getName());
Object result=method.invoke(target,args);//使用反射机制实现动态代理
return result;
}
public void log(String msg){
System.out.println("执行了"+msg+"方法");
}
}
AOP(面向切面编程)
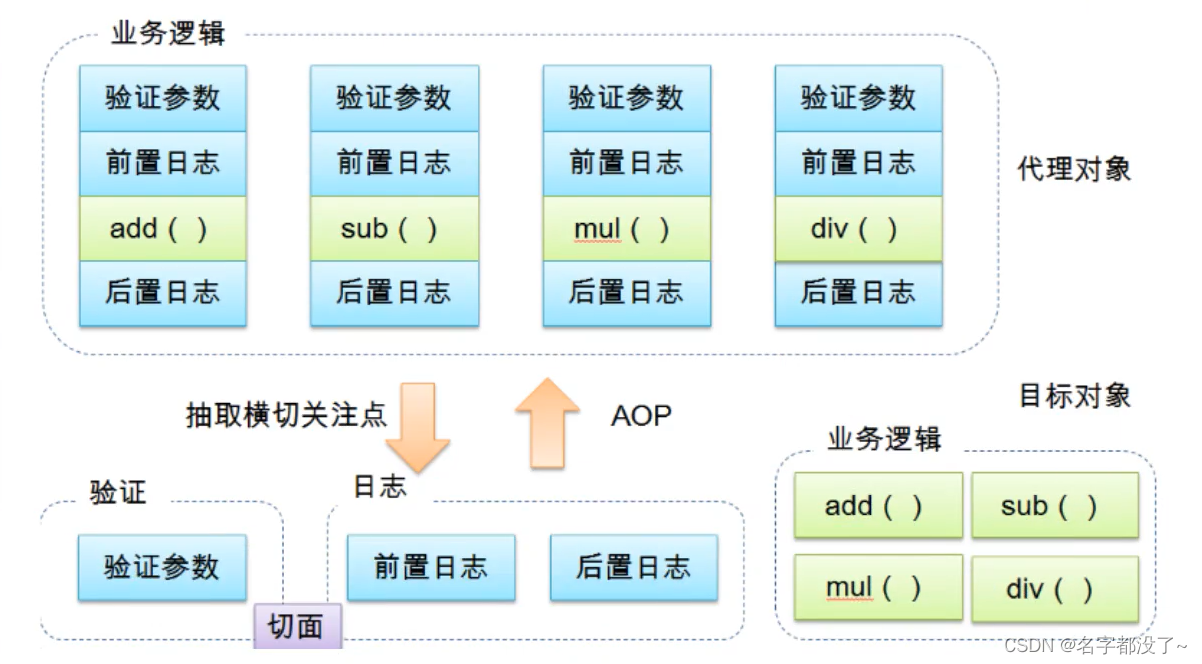
1 AOP在Spring中的作用
提供声明式事务;允许用户自定义切面
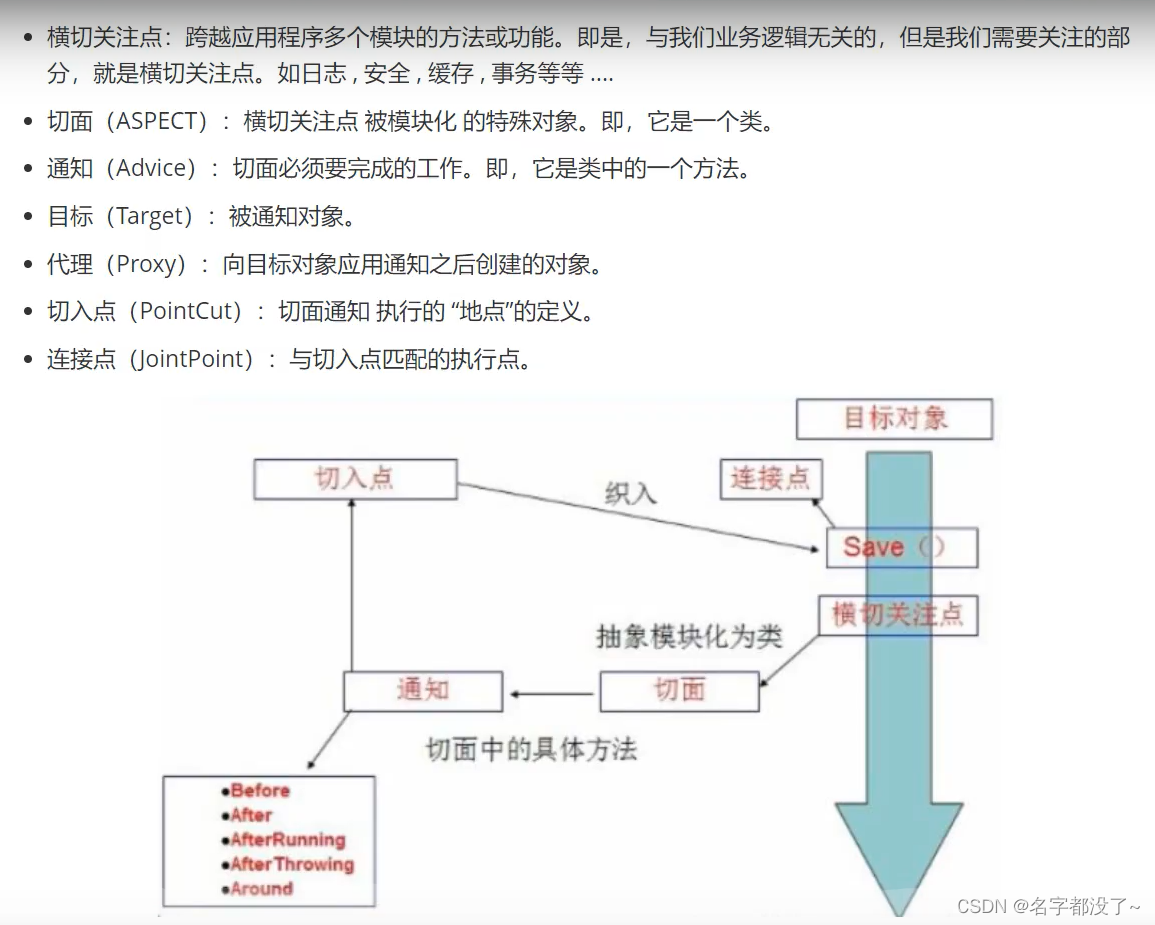
SpringAOP中,通过Advice定义横切逻辑。Spring中支持5中类型的Advice

2 使用Spring实现AOP
导入依赖包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.9.1</version>
</dependency>
方式一:使用Spring的API接口
applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--注册bean-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.example.service.UserServiceImpl"/>
<bean id="log" class="com.example.log.Log"/>
<bean id="afterLog" class="com.example.log.AfterLog"/>
<!--配置AOP-->
<aop:config>
<!--切入点
expression:表达式
-->
<aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.example.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<!--执行环绕增加-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="log" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="afterLog" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
</aop:config>
</beans>
execution表达式参考博客:
关于 expression=“execution(* com.xy.service..(…))”-pudn.com
Log.java
package com.example.log;
import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Log implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
//method:目标对象的方法
//object:参数
//target:目标对象
@Override
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.println(target.getClass().getName()+"的"+method.getName()+"方法被执行了");
}
}
AfterLog.java
package com.example.log;
import org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class AfterLog implements AfterReturningAdvice {
//returnValue:返回值
@Override
public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("执行了"+method.getName()+"方法,返回结果为"+returnValue);
}
}
MyTest.java
import com.example.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//动态代理的是接口
UserService userService=(UserService) context.getBean("userService");
userService.add();
}
}
运行结果

方式二:自定义类实现AOP
<!--自定义类实现AOP-->
<bean id="custom" class="com.example.custom.CustomPointCut"/>
<aop:config>
<!--自定义切面:ref 要引用的类-->
<aop:aspect ref="custom">
<!--切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="point" expression="execution(* com.example.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<!--通知-->
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="point"/>
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="point"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
CustomPointCut.java
package com.example.custom;
public class CustomPointCut {
public void before(){
System.out.println("方法执行前");
}
public void after(){
System.out.println("方法执行后");
}
}
方式三:使用注解实现AOP
AnnotationPointCut.java
package com.example.custom;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
@Aspect //将这个类标记为切面
public class AnnotationPointCut {
@Before("execution(* com.example.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void before(){
System.out.println("方法执行前");
}
@After("execution(* com.example.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void after(){
System.out.println("方法执行后");
}
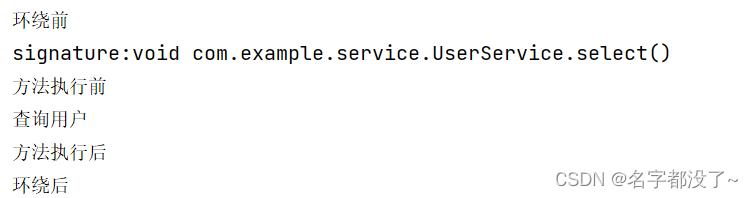
@Around("execution(* com.example.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{
System.out.println("环绕前");
//获得签名
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("signature:"+signature);
Object proceed = joinPoint.proceed();//执行方法
System.out.println("环绕后");
}
}
运行结果
整合MyBatis
-
导入相关jar包
-
junit
<dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>4.12</version> </dependency> -
mybatis
<dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> <version>3.5.10</version> </dependency> -
mysql数据库
<dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>8.0.29</version> </dependency> -
Spring相关
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId> <version>5.3.20</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>5.3.21</version> </dependency> -
aop织入
<dependency> <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId> <version>1.9.9.1</version> </dependency> -
mybatis-spring
<dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId> <version>2.0.7</version> </dependency>
-
方式一
-
编写实体类
-
编写mapper接口
-
实现mapper接口 mappe.xml
-
编写mapper接口实现类 mapperImpl.java
package org.example.mapper; import org.example.pojo.User; import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate; import java.util.List; public class UserMapperImmpl implements UserMapper{ //原先使用SqlSession执行的操作,现在使用SqlSessionTemplate执行 private SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate; public void setSqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate) { this.sqlSessionTemplate = sqlSessionTemplate; } @Override public List<User> queryUsers() { UserMapper mapper = sqlSessionTemplate.getMapper(UserMapper.class); return mapper.queryUsers(); } } -
编写spring-dao.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd"> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/> <!--编写数据源配置 DataSource:使用Spring的数据源替换MyBatis的配置 org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource--> <bean id="datasource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="${driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${url}"/> <property name="username" value="${jdbc_username}"/> <property name="password" value="${password}"/> </bean> <!--sqlSessionFactory--> <bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean"> <property name="dataSource" ref="datasource"/> <!--绑定MyBatis配置文件--> <property name="configLocation" value="mybatis-config.xml"/> <property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:org/example/mapper/userMapper.xml"/> </bean> <!--sqlSessionTemplate=sqlSession--> <bean id="sqlSessionTemplate" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate"> <!--只能使用构造器注入sqlSessionFactory,因为没有set方法--> <constructor-arg index="0" ref="sqlSessionFactory"/> </bean> <bean id="userMapper" class="org.example.mapper.UserMapperImmpl"> <property name="sqlSessionTemplate" ref="sqlSessionTemplate"/> </bean> </beans>-
可能遇到的问题
-
Caused by: java.sql.SQLException: Access denied for user 'XXX'@'localhost' (using password: YES)错误原因:上面spring-dao.xml中第15行,username的值存在歧义
解决办法:修改db.properties中的username的变量名,使其唯一,例如修改为jdbc_username
-
Property or field 'driver' cannot be found on object of type 'org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanExpressionContext' - maybe not public or not valid?错误原因:在注册datasource时,driver的值应该由${}引入
解决办法:检查driver的值,改为${}引入
如果报错的原因不是driver,检查field后的变量名即可
-
Mapped Statements collection already contains value for错误原因:同时在mapper核心配置文件及spring-dao.xml中注册了mapper
解决办法:删除mapper核心配置文件中对mapper的注册
-
-
-
测试
方式二
修改方式一中的实现类MapperImpl.java,继承SqlSessionDaoSupport类
package org.example.mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.example.pojo.User;
import org.mybatis.spring.support.SqlSessionDaoSupport;
import java.util.List;
public class UserMapperImpl extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements UserMapper{
@Override
public List<User> queryUsers() {
SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
return mapper.queryUsers();
}
}
修改spring-dao.xml中注册userMapper的语句
<bean id="userMapper" class="org.example.mapper.UserMapperImpl2">
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
声明式事务
- 声明式事务:AOP
- 编程式事务:需要在代码中进行事务的管理
<!--结合AOP实现事务织入-->
<!--配置事务通知的类-->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<!--需要配置事务的方法-->
<!--配置事务的传播特性 propagation 默认为REQUIRED-->
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!--配置事务切入-->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="txPointcut" expression="execution(* org.example.mapper.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPointcut"/>
</aop:config>
为什么需要事务
- 如果不配置事务,可能存在数据提交时不一致的情况





















 1894
1894











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








