视频讲解:[GESP202403 五级] B-smooth 数-信息学奥赛GESP等级考试真题解析
一、原题
题目描述
小杨同学想寻找一种名为 B-smooth 数的正整数。
如果一个正整数的最大质因子不超过 B,则该正整数为 B-smooth 数。小杨同学想知道,对于给定的 n和 B,有多少个不超过 n 的 B-smooth 数。
输入格式
第一行包含两个正整数 n 和 B,含义如题面所示。
输出格式
输出一个非负整数,表示不超过 n 的 B-smooth 数的数量。
输入输出样例
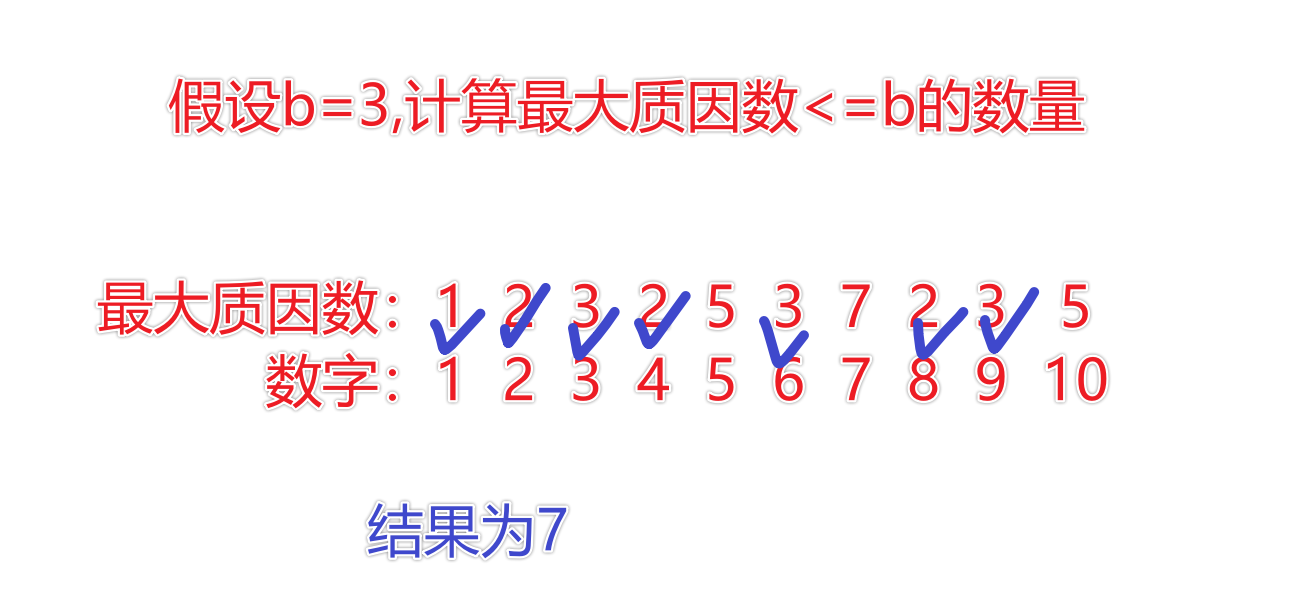
输入 #1
10 3输出 #1
7说明/提示
数据规模与约定
| 子任务 | 得分 | n≤ | B |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30 | 1 ≤ B ≤ | |
| 2 | 30 | n ≤ B ≤ | |
| 3 | 40 | 1 ≤ B ≤ |
对全部的测试数据,保证 1 ≤ n , B ≤ 。
二、做题思路
1)填充数据
//1)确定范围n,条件b
int n,b;
cin>>n>>b;2)埃筛求出最大质因子


//2.1)最小质数2开始
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
//2.2)是质数
if(gpf[i]==0){
//2.3)把当前质数的所有倍数 标记因子
for(int j=i;j<=n;j+=i){
gpf[j]=i;
}
}
}3)计算B-smooth
//3)计算B-smooth
int B_smooth=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(gpf[i]<=b) B_smooth++;
}
cout<<B_smooth;三、答案
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int gpf[1000010]={0,1};
int main(){
//1)确定范围n,条件b
int n,b;
cin>>n>>b;
//2)埃筛求出最大质因子
//2.1)最小质数2开始
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
//2.2)是质数
if(gpf[i]==0){
//2.3)把当前质数的所有倍数 标记因子
for(int j=i;j<=n;j+=i){
gpf[j]=i;
}
}
}
//3)计算B-smooth
int B_smooth=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(gpf[i]<=b) B_smooth++;
}
cout<<B_smooth;
} 
























 1004
1004

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








