Scanner输入
Next和NextLine区别

NextLine 用的会多点 因为Next遇到空格就断开了
next语法使用
package com.SunAo.scanner;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建扫描器用来接收 键盘输入
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("使用next方法接收:");
//判断用户有没有输入字符串
if(scanner.hasNext()==true){
String str=scanner.next();
System.out.println("输出的内容为:"+str);
}
//使用IO流的类如果不关闭会一直占用资源,要养成良好习惯
scanner.close();
}
}
-
语法
if(scanner.hasNext()==true) 等于 if(scanner.hasNext())
true可以省略
-
关闭输入
scanner.close();
使用IO流的类如果不关闭会一直占用资源,要养成良好习惯
-
测试输入hello world! 输出为 hello
nextline语法使用
package com.SunAo.scanner;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("使用nextline接收数据");
if (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
String str = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("输出的内容为:" + str);
}
scanner.close();
}
}
-
输入hello world!输出hello world!
-
主要是这一行的区别
if (scanner.hasNextLine())
Scanner升级
Scanner的使用
package com.SunAo.scanner;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo03
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int i=0;
float f=0.0f;
System.out.println("请输入整数");
//如果..那么..
if(scanner.hasNextInt()){
i = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("整数数据:"+i);
}else{
System.out.println("输入的不是整数数据!");
}
System.out.printl n("请输入小数");
//如果..那么..
if(scanner.hasNextFloat()){
f = scanner.nextFloat();
System.out.println("小数数据:"+f);
}else{
System.out.println("输入的不是小数数据!");
}
scanner.close();
}
}
题目练习
- 我们可以输入多个数字,并且求其总和和平均数,没输入一个数字用回车确认,通过输入非数字来结束输入并且输出执行结果
package com.SunAo.scanner;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//我们可以输入多个数字,并且求其总和和平均数,没输入一个数字用回车确认,通过输入非数字来结束输入并且输出执行结果
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
//和
double sum=0;
//统计输入多少数字
int m=0;
System.out.println("请输入");
//通过while语句进行判断是否还有输入,并且在里面每一次进行求和和统计
while(scanner.hasNextDouble()){
double x= scanner.nextDouble();
++m;
sum=sum+x;
}
System.out.println(m+"个数的和是"+sum);
System.out.println(m+"个数的平均数是"+(sum/m));
scanner.close();
} }
顺序结构
- 顺序结构就是从上到下
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-sGO37GUc-1673511790593)(C:/Users/%E5%AD%99%E5%A5%A5/AppData/Roaming/Typora/typora-user-images/image-20230111212336629.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/04f03aa6cfc34b0d8d3ead45aee5e9aa.png)
选择结构
if判断语句的使用
if单选择结构
- 判断输入数据是否与要求数据相同相同则返回这个数据,不同则返回end
package com.SunAo.struct;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class IfDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个内容");
String s=scanner.nextLine();
//判断字符串是否相等
if (s.equals("Hello"))
System.out.println(s);
else{
System.out.println("End");
}
scanner.close();
}
}
- 考试成绩大于60则及格否则不及格
package com.SunAo.struct;
import java.util.Scanner;
//考试成绩大于60则及格否则不及格
public class IfDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("其输入成绩");
int score=scanner.nextInt();
if(score>60)
System.out.println("及格");
else
System.out.println("不及格");
scanner.close();
}
}
语法格式
if(布尔表达式){
//如果表达式的值为true
}
else
{
//如果表达式的值为false
}
if多选择结构
- 判断成绩
package com.SunAo.struct;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class IfDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("其输入成绩");
int score = scanner.nextInt();
if (score == 100)
System.out.println("恭喜满分");
else if (score < 100 && score >= 80)
System.out.println("良好");
else if (score < 80 && score >= 60)
System.out.println("及格");
else if (score<60)
System.out.println("不及格");
else
System.out.println("成绩不合法");
scanner.close();
}
}
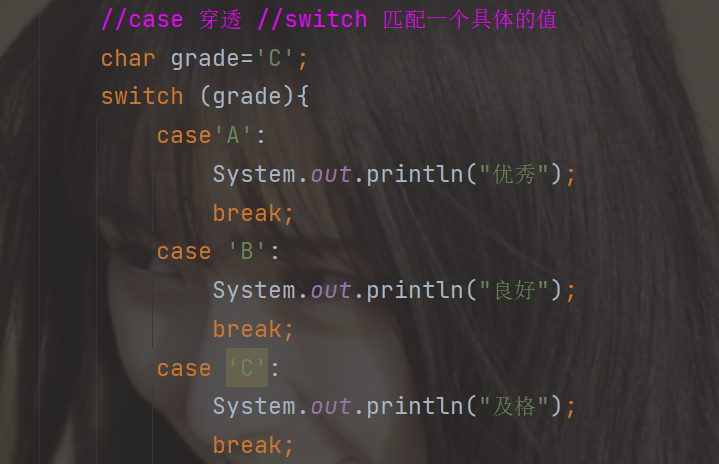
switch多选择结构
-
switch 的穿透需要注意
必须要写上break不然会一直往下执行
循环结构
While循环结构
while(布尔类型){
//循环内容
}
- 一般为在某种情况下程序停止
- 循环条件一直未true的话就会造成死循环,我们正在业务编程中应该尽量避免死循环
public class WhileDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
int sum = 0;
while (i < 100) {
i++;
sum = sum + i;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
do…while循环结构
public class DoWhileDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i=0;
int sum=0;
do{
sum = sum + i;
i++;
}while(i<=100);
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
while与do…while二者区别
public class DoWhileDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a=0;
while(a<0){
System.out.println(a);
a++;}
System.out.println("___________________");
do {
System.out.println(a);
a++;
}while(a<0);
} }
- 二者输出是有区别的前者(while)这种情况是没有进入循环,而(do…while)是有进入循环的🔑
for循环 重点
for(初始化;布尔;更新){
//循环结构
}
for替代while
- while
int a = 1;
while (a <= 100) {
System.out.println(a);
a += 2;//迭代
}
System.out.println("While循环结束!!!");
- for
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
}
System.out.println("for循环结束!!!");
-
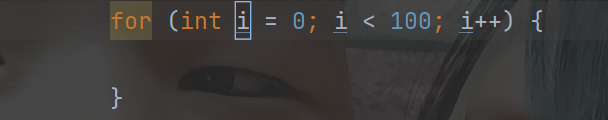
for 循环可以用快捷键
快捷输入
100.for可以生成如下循环
练习题
- 练习题1:for循环实现0到100之间奇数和偶数的和
public class ForDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int oddSum=0;//奇数和
int evenSum=0;//偶数和
for (int i = 0; i <=100; i++) {
if(i%2!=0){
oddSum=oddSum+i;
}else{
evenSum=evenSum+i;
}
}
System.out.println("奇数的和:"+oddSum);
System.out.println("偶数的和:"+evenSum);
}
}
- 练习题2:用while或者for循环输出1-1000之间能被5整除的数,并且每行输出3个
//用while或者for循环输出1-1000之间能被5整除的数,并且每行输出3个
for (int i = 0; i <= 1000; i++) {
if(i%5==0){
System.out.print(i+"\t");
}
if(i%(5*3)==0){//换行
//System.out.println();
System.out.println("\n");
}
}
// \t是空格 \n是换行
-
练习题3:打印出99乘法表
for (int i=1;i<=9;i++){ for (int m=1;m<=i;m++){ System.out.print(m+"*"+i+"="+(m*i)+"\t"); } System.out.println(); }
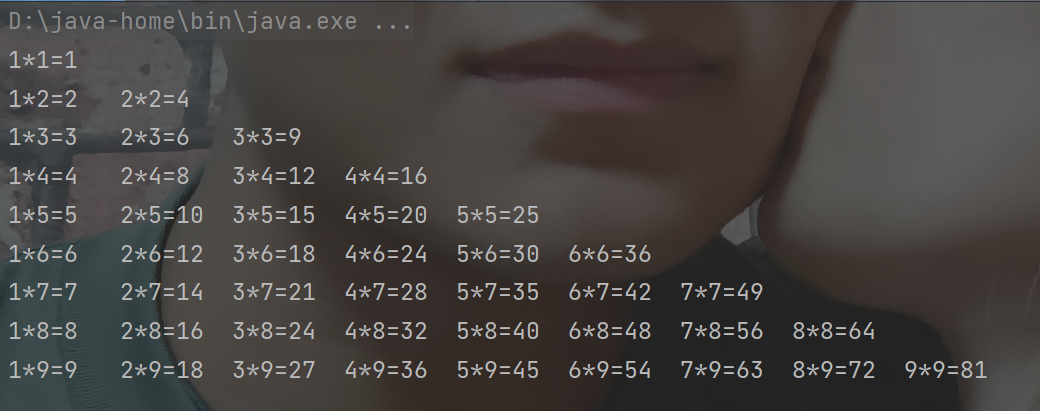
- 我们先打印第一列
- 再把第一列用循环抱起来
- 去掉重复项 i<j
- 调整样式
print和println
- System.out.print与System.out.println
- 前者是正常输出后面必须要有输出参数而后者默认输出带换行可以不需要输出值默认带参数
增强for循环
- 这个语句块等同于下面这个
int [] numbers={10,20,30,40,50};//定义数组
//遍历数组的元素
for (int x:numbers){
System.out.println(x);
}
System.out.println("=========================");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println(numbers[i]);
}
break和continue的区别
-
break在任何循环语句的主体部分均可以用break控制循环的流程
break用于强制退出循环,不执行循环剩余语句 (break语句可在swith语句中使用)
-
continue语句在循环句体重,用于终止某次循环过程,即跳过循环体尚未执行的语句,判断是否下一次执行语句
break语句
public class BreakDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i=0;
while (i < 100) {
i++;
System.out.println(i);
if (i==30){
break;
}
}
System.out.println("1 2 3");
}
}
- 输出结果:到30就终止,但是不影响程序继续运行

continue语句
public class ContinueDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i=0;
while (i<100){
i++;
if(i%10==0){
System.out.println();
continue;
}
System.out.print(i);
}
}
- 输出结果:持续输出跳过这一轮循环,下一轮继续循环
goto语句使用
- 打印101-150之间所有质数
public class LabeDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打印101-150之间所有质数
//质数:是指在大于1的自然数中,除了1和它本身以外不在有其他因数的自然数
int count=0;
//不建议使用!!!
outer:for (int i = 101; i < 150; i++) {
for (int j=2;j<i/2;j++){
if (i % j==0){
continue outer;
}
}
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
}























 2676
2676











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










