Queue接口
Queue接口提供了新的方法
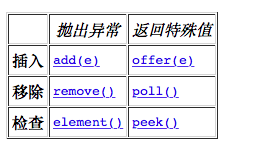
特殊值是null和false
PriortiryQueue优先队列
底层数据结构分析
上图中我给每个元素按照层序遍历的方式进行了编号,就会发现父节点和子节点的编号是有联系的,更确切的说父子节点的编号之间有如下关系: leftNo=parentNo2+1 rightNo=parentNo2+1 parentNo=(nodeNo-1)/2 通过上述三个公式,可以轻易计算出某个节点的父节点以及子节点的下标。这也就是为什么可以直接用数组来存储堆的原因。 小根堆实现:
/**
* desc:小根堆
*/
public class DIYHeap {
Integer [] heap ;//存储数据heap
int count;//表示存储数据个数
public DIYHeap() {
heap = new Integer[13];
count = 0;
}
//添加元素
public void add(Integer v) {
/**
* 1、如果count为0 ,插入根位置
* 2、如果不为空,将数据插入count位置,
* 进行调整,从下往上调整()
* 3、对count加一操作
*/
if (count == 0) {
heap[0] = v;
} else {
//将节点放入最后位置,涉及调整
siftUp(v,count);
}
count++;
}
/**
* 向上调整
* @param v:调整的元素,
* @param index:要调整的位置
*/
private void siftUp(Integer v, int index) {
//找父位置
int parentIndex = 0;
do {
parentIndex = (index - 1) / 2;
if (heap[parentIndex] > v) {
heap[index] = heap[parentIndex];
index = parentIndex;
} else {
break;
}
} while (parentIndex > 0);
heap[index] = v;
}
//删除元素 删除堆顶元素
public Integer remove(){
/**
* 1、判断是否存在元素,不存在元素,返回0
* 2、存在元素,删除堆顶元素,将最后位置元素复制到堆顶,然后从上往下遍历()
* 3、count减一
*/
if (count == 0) return 0;
//存在元素,
Integer oldValue = heap[0];
//将最后元素调整到0号位置,然后调整
Integer v = heap[count-1];
heap[count-1] = null;
count--;
siftDown(v,0);
return oldValue;
}
/**
*
* @return
*/
private void siftDown(Integer v,Integer index){
//利用完全二叉树特征,非叶子节点到2/size大小
int end = count/2;
while (index < end) {
//找到左右孩子最小的
int childIndex = index*2+1;
Integer child = heap[childIndex];
if (((childIndex+1) < count) && child > heap[childIndex+1]) {
child = heap[childIndex+1];
childIndex = childIndex+1;
}
//最小孩子节点和父节点比较
if (v > child) {
//父节点大于最小孩子节点,调整
heap[index] = heap[childIndex];
index = childIndex;
} else {
break;
}
}
heap[index] =v;
}
//获取堆顶元素,但不删除
public Integer peek(){
if (count > 0) {
return heap[0];
} else {
return 0;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DIYHeap diyHeap = new DIYHeap();
diyHeap.add(45);
diyHeap.add(23);
diyHeap.add(66);
diyHeap.add(12);
diyHeap.add(89);
diyHeap.add(11);
System.out.println(diyHeap.remove());
System.out.println(diyHeap.remove());
System.out.println(diyHeap.remove());
}
}源码研究
默认值及基础属性
默认的初始化大小是11
private static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 11;
//数据存储位置是堆
private transient Object[] queue;
//集合中数据个数
private int size = 0;
//comparator 自定义比较器类
private final Comparator<? super E> comparator;
private transient int modCount = 0;构造函数
//通过初始容量和自定义比较器来构造优先级龟裂
public PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity,Comparator<? super E> comparator) {
if (initialCapacity < 1)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.queue = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.comparator = comparator;
}
默认的初始容量是11添加元素:add()和offer
public boolean add(E e) {
return offer(e);
}
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
modCount++;
int i = size;
//插入的数据到达队列最大限度
if (i >= queue.length)
//扩容
grow(i + 1);
size = i + 1;
if (i == 0)
//第一次插入数据,放在0号位置
queue[0] = e;
else
siftUp(i, e);
return true;
}
//扩容方法
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = queue.length;
// Double size if small; else grow by 50%
int newCapacity = oldCapacity +
((oldCapacity < 64) ?(oldCapacity + 2) :(oldCapacity >> 1));
// overflow-conscious code
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
queue = Arrays.copyOf(queue, newCapacity);
}
private void siftUp(int k, E x) {
if (comparator != null)
siftUpUsingComparator(k, x);
else
siftUpComparable(k, x);
}
private void siftUpComparable(int k, E x) {
Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>) x;
while (k > 0) {
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
Object e = queue[parent];
if (key.compareTo((E) e) >= 0)
break;
queue[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
queue[k] = key;
}
private void siftUpUsingComparator(int k, E x) {
while (k > 0) {
int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1;
Object e = queue[parent];
if (comparator.compare(x, (E) e) >= 0)
break;
queue[k] = e;
k = parent;
}
queue[k] = x;
}优先级队列特征: 1、不能存储null值 2、扩容大小问题:如果较小(小于64)按照2倍扩容,否则按照1.5倍扩容
siftUP方法调整图解
查看元素:element()和peek()
方法作用相同,都是后去但不删除堆头的元素,也就是获取最大、最小的值
public E element() {
E x = peek();
if (x != null)
return x;
else
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
public E peek() {
if (size == 0)
return null;
return (E) queue[0];
}删除操作:remove()和poll()
都是删除堆头元素并获取当前元素
public E remove() {
E x = poll();
if (x != null)
return x;
else
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
public E poll() {
//如果为空,返回特殊值null
if (size == 0)
return null;
int s = --size;
modCount++;
E result = (E) queue[0];
E x = (E) queue[s];
queue[s] = null;
if (s != 0)
siftDown(0, x);
return result;
}
private void siftDown(int k, E x) {
if (comparator != null)
siftDownUsingComparator(k, x);
else
siftDownComparable(k, x);
}
private void siftDownComparable(int k, E x) {
Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>)x;
int half = size >>> 1; // loop while a non-leaf
while (k < half) {
int child = (k << 1) + 1; // assume left child is least
Object c = queue[child];
int right = child + 1;
if (right < size &&
((Comparable<? super E>) c).compareTo((E) queue[right]) > 0)
c = queue[child = right];
if (key.compareTo((E) c) <= 0)
break;
queue[k] = c;
k = child;
}
queue[k] = key;
}
private void siftDownUsingComparator(int k, E x) {
//完全二叉树特征,非叶子节点小于size/2
int half = size >>> 1;
while (k < half) {
int child = (k << 1) + 1;
Object c = queue[child];
int right = child + 1;
if (right < size &&
comparator.compare((E) c, (E) queue[right]) > 0)
c = queue[child = right];
if (comparator.compare(x, (E) c) <= 0)
break;
queue[k] = c;
k = child;
}
queue[k] = x;
}
siftDowm调整过程:


























 764
764











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










