Java从入门到“放弃”(精通)之旅🚀——String类⑩
前言
在Java编程中,String类是最常用也是最重要的类之一。无论是日常开发还是面试,对String类的深入理解都是必不可少的。
1. String类的重要性
在C语言中,字符串只能使用字符数组或字符指针表示,操作字符串需要依赖标准库函数。这种方式将数据和操作分离,不符合面向对象思想。Java专门提供了String类来解决这个问题。
String类在开发中无处不在,例如:
- 字符串转数字
- 字符串拼接
- 数据校验等
面试中也经常被问到String相关的问题,如String、StringBuffer和StringBuilder的区别等。
2. 常用方法
2.1 字符串构造
String类提供了多种构造方式,常用的有三种:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用常量串构造
String s1 = "hello bit";
System.out.println(s1);
// 直接new String对象
String s2 = new String("hello bit");
System.out.println(s2);
// 使用字符数组进行构造
char[] array = {'h','e','l','l','o',' ','b','i','t'};
String s3 = new String(array);
System.out.println(s3);
}
注意:String是引用类型,并不是直接保存字符串内容,而是内部通过字符数组存储字符串内容。
代码示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
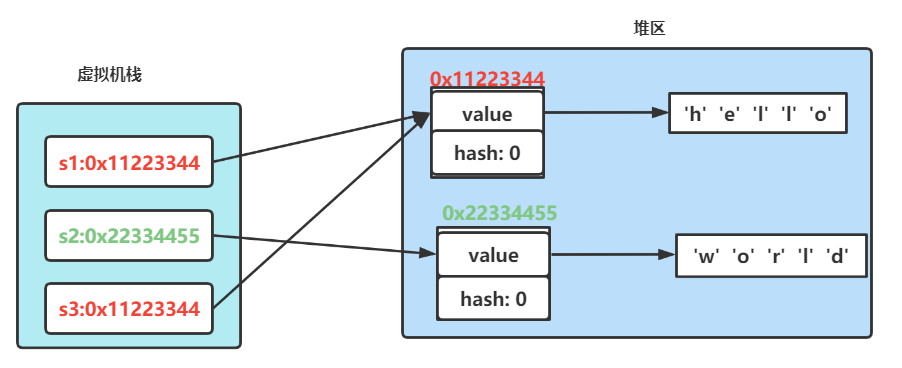
// s1和s2引用的是不同对象 s1和s3引用的是同一对象
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("world");
String s3 = s1;
System.out.println(s1.length()); // 获取字符串长度---输出5
System.out.println(s1.isEmpty()); // 如果字符串长度为0,返回true,否则返回false
}
2.2 String对象的比较
Java提供了4种字符串比较方式:
- ==比较引用地址
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("hello");
String s3 = new String("world");
String s4 = s1;
System.out.println(s1 == s2); // false
System.out.println(s2 == s3); // false
System.out.println(s1 == s4); // true
}
- equals()方法:按字典序比较
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("hello");
String s3 = new String("Hello");
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); // true
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3)); // false
}
- compareTo()方法:按字典序比较并返回差值
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("abc");
String s2 = new String("ac");
String s3 = new String("abc");
String s4 = new String("abcdef");
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2)); // -1
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s3)); // 0
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s4)); // -3
}
- compareToIgnoreCase()方法:忽略大小写的compareTo
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String("abc");
String s2 = new String("ac");
String s3 = new String("ABC");
String s4 = new String("abcdef");
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2)); // -1
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s3)); // 0
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s4)); // -3
}
2.3 字符串查找
常用查找方法:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
char charAt(int index) | 返回index位置上字符,如果index为负数或者越界,抛出IndexOutOfBoundsException异常 |
int indexOf(int ch) | 返回ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始找ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
int indexOf(String str) | 返回str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始找str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
int lastIndexOf(int ch) | 从后往前找,返回ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始找,从后往前找ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
int lastIndexOf(String str) | 从后往前找,返回str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始找,从后往前找str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "aaabbbcccaaabbbccc";
System.out.println(s.charAt(3)); // 'b'
System.out.println(s.indexOf('c')); // 6
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf('c')); // 17
}
2.4 字符串转化
- 数值和字符串互转
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 数字转字符串
String s1 = String.valueOf(1234);
String s2 = String.valueOf(12.34);
// 字符串转数字
int data1 = Integer.parseInt("1234");
double data2 = Double.parseDouble("12.34");
}
- 大小写转换
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "HELLO";
System.out.println(s1.toUpperCase()); // HELLO
System.out.println(s2.toLowerCase()); // hello
}
- 字符串与数组互转
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hello";
// 字符串转数组
char[] ch = s.toCharArray();
// 数组转字符串
String s2 = new String(ch);
}
2.5 字符串替换
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloworld";
System.out.println(str.replaceAll("l", "_")); // he__owor_d
System.out.println(str.replaceFirst("l", "_")); // he_loworld
}
注意:字符串是不可变对象,替换操作会创建新对象。
2.6 字符串拆分
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 基本拆分
String str = "hello world hello bit";
String[] result = str.split(" ");
// 部分拆分
String[] result2 = str.split(" ", 2);
// 拆分IP地址
String ip = "192.168.1.1";
String[] ipParts = ip.split("\\.");
}
2.7 字符串截取
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloworld";
System.out.println(str.substring(5)); // world
System.out.println(str.substring(0, 5)); // hello
}
2.8 其他操作方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 去除首尾空格
String str = " hello world ";
System.out.println(str.trim());
// 大小写转换
String mixed = "Hello%$$%@#$%World";
System.out.println(mixed.toUpperCase());
System.out.println(mixed.toLowerCase());
}
3. 字符串的不可变性
String类被设计为不可变类,主要原因有:
- 方便实现字符串常量池
- 线程安全
- 便于缓存hash code
注意:String不可变不是因为final修饰,而是因为其设计如此。
public final class String {
private final char value[];
// ...
}
4. 字符串修改
由于String不可变,频繁修改会产生大量临时对象,效率低下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 不推荐的写法
String s = "";
for(int i = 0; i < 10000; ++i){
s += i;
}
// 推荐使用StringBuilder
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int i = 0; i < 10000; ++i){
sb.append(i);
}
}
5. StringBuilder和StringBuffer
5.1 StringBuilder介绍
StringBuilder是可变的字符串类,方法表:
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
StringBuffer append(String str) | 在尾部追加,相当于String的+=,可以追加:boolean、char、char[]、double、float、int、long、Object、String、StringBuffer的变量 |
char charAt(int index) | 获取index位置的字符 |
int length() | 获取字符串的长度 |
int capacity() | 获取底层保存字符串空间总的大小 |
void ensureCapacity(int minimumCapacity) | 扩容 |
void setCharAt(int index, char ch) | 将index位置的字符设置为ch |
int indexOf(String str) | 返回str第一次出现的位置 |
int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始查找str第一次出现的位置 |
int lastIndexOf(String str) | 返回最后一次出现str的位置 |
int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始找str最后一次出现的位置 |
StringBuffer insert(int offset, String str) | 在offset位置插入:八种基类类型 & String类型 & Object类型数据 |
StringBuffer deleteCharAt(int index) | 删除index位置字符 |
StringBuffer delete(int start, int end) | 删除[start, end)区间内的字符 |
StringBuffer replace(int start, int end, String str) | 将[start, end)位置的字符替换为str |
String substring(int start) | 从start开始一直到末尾的字符以String的方式返回 |
String substring(int start, int end) | 将[start, end)范围内的字符以String的方式返回 |
StringBuffer reverse() | 反转字符串 |
String toString() | 将所有字符按照String的方式返回 |
常用方法部分代码示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("hello");
sb.append(" world"); // 追加
sb.insert(5, ","); // 插入
sb.delete(5, 6); // 删除
sb.reverse(); // 反转
String result = sb.toString(); // 转为String
}
5.2 面试题
-
String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder的区别
- String不可变,后两者可变
- StringBuffer线程安全,StringBuilder非线程安全
- StringBuilder性能更高
-
创建了多少个String对象
String str = new String("ab"); // 2个(常量池1个,堆1个)
String str = new String("a") + new String("b"); // 6个
6. String类OJ题解
6.1 第一个只出现一次的字符
class Solution {
public int firstUniqChar(String s) {
int[] count = new int[256];
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i){
count[s.charAt(i)]++;
}
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i){
if(1 == count[s.charAt(i)]){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
6.2 最后一个单词的长度
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNext()){
String s = sc.nextLine();
int len = s.substring(s.lastIndexOf(" ")+1).length();
System.out.println(len);
}
sc.close();
}
}
6.3 检测字符串是否为回文
class Solution {
public static boolean isValidChar(char ch){
return (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') || (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9');
}
public boolean isPalindrome(String s) {
s = s.toLowerCase();
int left = 0, right = s.length()-1;
while(left < right){
while(left < right && !isValidChar(s.charAt(left))) left++;
while(left < right && !isValidChar(s.charAt(right))) right--;
if(s.charAt(left) != s.charAt(right)) return false;
left++;
right--;
}
return true;
}
}
总结
String类是Java中最重要的类之一,理解其不可变特性、掌握常用方法以及了解StringBuilder/StringBuffer的区别,对于编写高效Java程序至关重要。希望本文能帮助大家全面掌握String类的使用!
JavaSE专栏


























 326
326

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








