一、实验目的
1.掌握C+ +语言多态性的基本概念
2.掌握运算符重载函数的声明和定义方法
二、实验内容
多态性:
在面向对象方法中,所谓多态性就是不同对象收到相同的消息时,产生不同的行为。在C++ 程序设计中,多态性是指用一个名字定义不同的函数,这些函数执行不同但又类似的操作,这样就可以用同一个函数名调用不同内容的函数。
运算符重载:
系统已定义的运算符不适用于新的自定义数据类型,为了解决这一问题,C++允许运算符的重载。算符重载是通过创建运算符重载函数来实现的。
运算符重载格式:
函数类型 operator 运算符名称(形参表)
{
对运算符的重载处理
}
实验要用到三种运算符重载函数:
1.在类外定义的运算符重载函数
2.友元运算符重载函数
3.成员运算符重载函数
1.在类外定义的运算符重载函数
代码如下:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Complex {
public:
double real;
double imag;
Complex(double r = 0, double i = 0)
{
real = r;
imag = i;
}
};
Complex operator+ (Complex co1, Complex co2)
{
Complex temp;
temp.real = co1.real + co2.real;
temp.imag = co1.imag + co2.imag;
return temp;
}
int main(void)
{
Complex com1(1.1, 2.2), com2(3.3, 4.4), total1, total2;
total1 = operator+(com1, com2);
cout << "real1=" << total1.real << " " << "imag1=" << total1.imag << endl;
total2 = com1 + com2;
cout << "real2=" << total2.real << " " << "imag2=" << total2.imag << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果: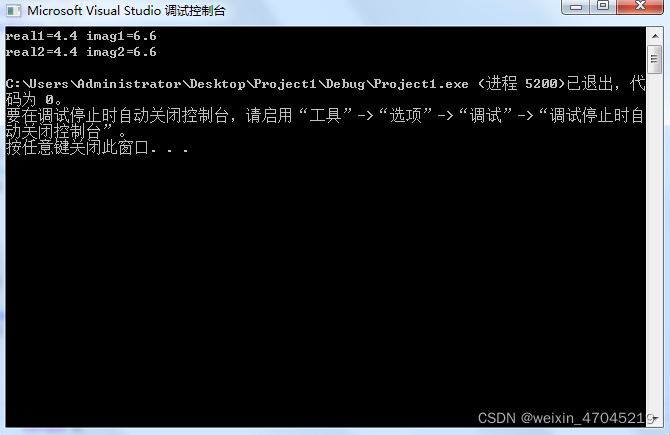
2.友元运算符重载函数
定义友元运算符重载函数的语法形式:
(1 ) 在类的内部,定义友元运算符重载函数的格式如下:
friend 函数类型 operator 运算符(形参表 )
{
函数体
}
(2) 友元运算符重载函数也可以在类中声明友元函数的原型,在类外定义。
在类中,声明友元运算符重载函数原型的格式如下:
class X{
friend 函数类型 operator 运算符(形参表);
};
在类外,定义友元运算符重载函数的格式如下:
函数类型 operator 运算符(形参表 )
{
函数体
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Complex {
public:
double real;
double imag;
Complex(double r = 0, double i = 0)
{
real = r;
imag = i;
}
void print();
friend Complex operator+(Complex co1, Complex co2);
};
Complex operator+ (Complex co1, Complex co2)
{
Complex temp;
temp.real = co1.real + co2.real;
temp.imag = co1.imag + co2.imag;
return temp;
}
void Complex::print()
{
cout << "total real=" << real << " " << "total imag=" << imag << endl;
}
int main(void)
{
Complex com1(1.1, 2.2), com2(3.3, 4.4), total1;
total1 = com1 + com2;
total1.print();
return 0;
}
运行结果: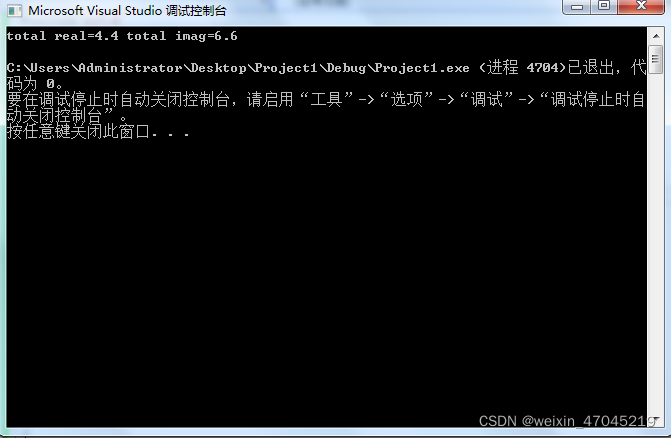
3.成员运算符重载函数
定义成员运算符重载函数的语法形式
(1) 在类的内部,定义成员运算符重载函数的格式如下:
函数类型 operator 运算符(形参表)
{
函数体
}
(2) 成员运算符重载函数也可以在类中声明成员函数的原型,在类外定义。
在类的内部,声明成员运算符重载函数原型的格式如下:
class X {
函数类型 operator 运算符(形参表);
}
在类外,定义成员运算符重载函数的格式如下:
函数类型 X::operator 运算符(形参表 )
{
函数体
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Complex {
public:
double real;
double imag;
Complex(double r = 0.0, double i = 0.0);
void print();
Complex operator+(Complex c);
};
Complex::Complex(double r, double i)
{
real = r;
imag = i;
}
Complex Complex::operator+ (Complex c)
{
Complex temp;
temp.real = real + c.real;
temp.imag = imag + c.imag;
return temp;
}
void Complex::print()
{
cout << "total real=" << real << " " << "total imag=" << imag << endl;
}
int main()
{
Complex com1(2.3, 4.6), com2(3.6, 2.8), total1;
total1 = com1 + com2;
total1.print();
return 0;
}
运行结果: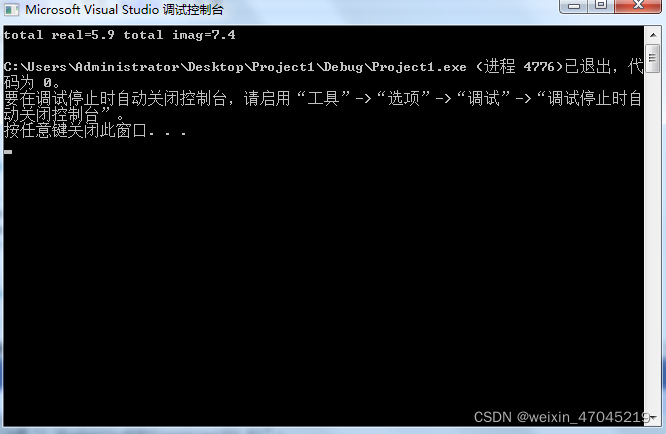
4.编写一个程序,实现复数的乘法。
采用双目成员运算符重载函数来完成。对于双目运算符,成员运算符重载函数的形参表中仅有一个参数,它作为运算符的右
操作数。另一个操作数(左操作数)是隐含的,是该类的当前对象,它是通过 this 指针隐含
地传递给函数的。如下:
class X {
int operator+ (X a);
};
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Complex {
public:
Complex(double r = 0.0, double i = 0.0);
void print();
Complex operator* (Complex c);
private:
double real;
double imag;
};
Complex::Complex(double r, double i)
{ real = r;
imag = i;
}
Complex Complex::operator* (Complex c)
{
Complex temp;
temp.real = real * c.real - imag * c.imag;
temp.imag = real * c.imag + imag * c.real;
return temp;
}
void Complex::print()
{
cout<< real;
if (imag > 0)
cout << "+ ";
if (imag != 0)
cout << imag << 'i' << endl;
}
int main()
{
Complex com1(1.2, 2.5), com2(3.6, 4.7), total;
total = com1 * com2;
total.print();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
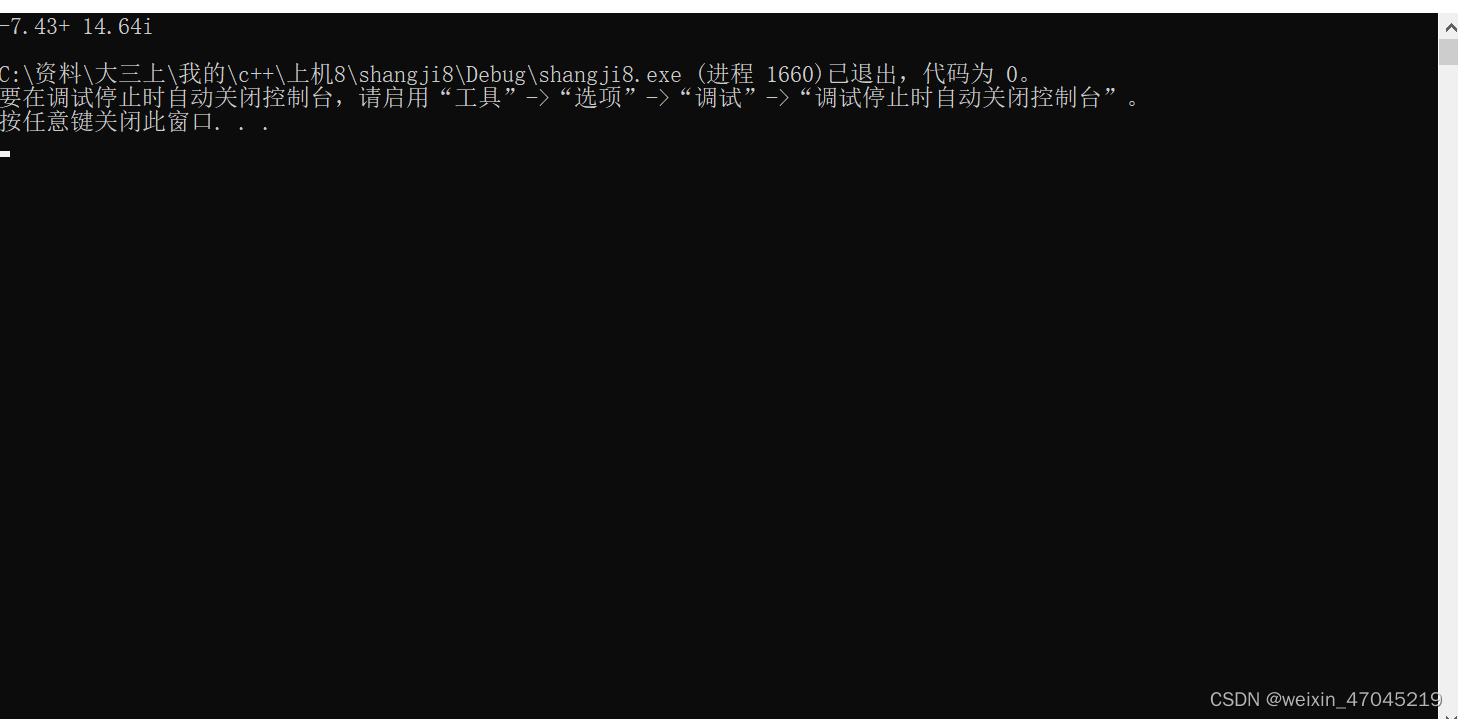
三、实验总结
1.C++ 为运算符重载提供了一种方法,即在进行运算符重载时,必须定义一个运算符重载函数,其名字为 operator,后随一个要重载的运算符。
2.在编译时遇到名为 operator@的运算符重载函数,就检查传递给函数的参数的类型。如果编译器在一个运算符的两边 “看” 到自定义的数据类型,就执行用户自己定义的函数,而不是系统已经定义好的运算符函数。
3.C++只能对已有的C++运算符进行重载,不允许用户自定义新的运算符。运算符重载是针对新类型数据的实际需要,对原有运算符进行适当的改造完成的。




 本文介绍了C++编程中的多态性和运算符重载概念,通过实例展示了如何在类外、作为友元和成员函数定义运算符重载,并实现复数的加法和乘法操作。实验总结强调了运算符重载的规则及其在对象行为差异化中的作用。
本文介绍了C++编程中的多态性和运算符重载概念,通过实例展示了如何在类外、作为友元和成员函数定义运算符重载,并实现复数的加法和乘法操作。实验总结强调了运算符重载的规则及其在对象行为差异化中的作用。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








