C语言实现BMP图像的读写
对于刚接触数字图像的同学,应该都有一个疑问,如何把一个BMP格式的图像用纯C语言读入呢,我相信这也是数字图像处理的第一步,如果有幸看到这篇文档,我就有幸的成为你数字图像处理路上的第一盏明灯!
了解BMP的构成
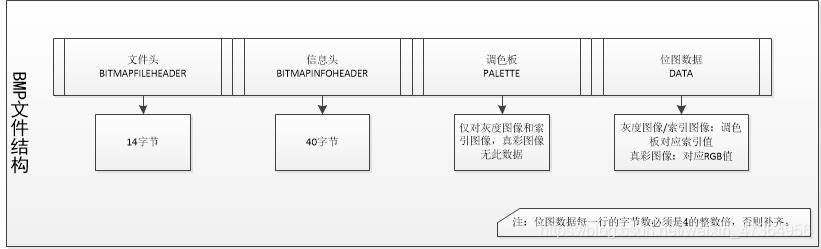
这就是BMP图像的理论知识,有个大概的了解就行,最主要的是从理论到实践!!!
废话不多说,直接上干货。
代码
定义头文件为“bmp.h”,定义read_bmp函数为读函数,write_bmp函数为写函数
读bmp图
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <Windows.h>
#include "bmp.h"
/*存储原图的像素宽度高度和位图深度*/
FILE* fpbmp;
FILE* fpout;
unsigned char* fpBmpHeader; //位图头
unsigned char* fpFileHeader; //位图信息
RGBQUAD* pColorTable; //BMP 调色板
int read_bmp(const char* path, unsigned char *pBmpBuf,int *Width,int *Height,int * bitCount)
{
fpbmp = fopen(path, "rb");//path为图像路径
unsigned short s;
fread(&s, 1, 2, fpbmp);
//判断读入的图像是否为BMP图 字符串"BM"=19778
if (s == 19778)
{
printf("Open bmp success!!!\n");
}
else
{
printf("Open bmp fail!!!\n");
return -1;
}
fseek(fpbmp, 0, SEEK_SET);
BITMAPFILEHEADER fileHead;
fread(&fileHead, sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER), 1, fpbmp);
BITMAPINFOHEADER infoHead;
fread(&infoHead, sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER), 1, fpbmp);
*Width = infoHead.biWidth;//图像的宽
*Height = infoHead.biHeight;//图像的高
*bitCount = infoHead.biBitCount;
int lineByte = (*Width * *bitCount / 8 + 3) / 4 * 4;
fseek(fpbmp, sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER) + sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER) ,SEEK_SET);
fread(pBmpBuf, lineByte * *Height, 1, fpbmp);//pBmpBuf为图像的RGB数据,也是我们将要处理的数据
return 0;
}
写BMP图
int write_bmp(unsigned char* img, int* Width, int* Height, int* bitCount)
{
fpout = fopen("out.bmp", "wb+");
if (fpbmp == NULL)
{
printf("read bmp failed!!!\n");
return -1;
}
int lineByte = (*Width * *bitCount / 8 + 3) / 4 * 4;
if (lineByte == 0)
{
printf("err");
return -1;
}
fpFileHeader = new unsigned char[(sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER))];
fseek(fpbmp, 0, SEEK_SET); //定位原图 偏移位置
fseek(fpout, 0, SEEK_SET); //定位新图 偏移位置
fread(fpFileHeader, 1, sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER), fpbmp);
fwrite(fpFileHeader, 1, sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER), fpout);
/*复制原图中 位图 信息到新图像*/
fpBmpHeader = new unsigned char[(sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER))];
fseek(fpbmp, sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER), SEEK_SET);
fseek(fpout, sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER), SEEK_SET);
fread(fpBmpHeader, 1, sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER), fpbmp);
fwrite(fpBmpHeader, 1, sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER), fpout);
fseek(fpout, sizeof(BITMAPFILEHEADER) + sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER) , SEEK_SET);
fwrite(img, lineByte * *Height, sizeof(char), fpout);
fclose(fpout);
fclose(fpbmp);
return 0;
}
main函数调用
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <Windows.h>
#include "bmp.h"
int main()
{
int width, height, bitCount = 0;
unsigned char* pBmpBuf = (unsigned char*)malloc(1000 * 1000 * 3);//申请空间
const char* path = "D:\\test\\read_bmp_image\\1-B.bmp";//图的路径
read_bmp(path, pBmpBuf, &width, &height, &bitCount);
write_bmp(pBmpBuf, &width, &height, &bitCount);
}
总结,将read_bmp函数返回的pBmpBuf参数,赋值给write_bmp函数的img参数,就实现了BMP图从读到写的全部过程,有兴趣的同学动手实践下,会有意向不到的收获。
注:在线转换BMP图的网址,可以将任何格式的照片转换为BMP格式。亲测好用。链接奉上BMP图像转换网址






















 4210
4210











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








