说在前头:本人为大二在读学生,书写文章的目的是为了对自己掌握的知识和技术进行一定的记录,同时乐于与大家一起分享,因本人资历尚浅,能力有限,文章难免存在一些错漏之处,还请阅读此文章的大牛们见谅与斧正。若在阅读时有任何的问题,也可通过评论提出,本人将根据自身能力对问题进行一定的解答。
前言
在前面的文章中,我们介绍了简单排序中的冒泡排序算法与选择排序算法,此篇文章将再介绍一种简单排序算法——插入排序算法。对于随机的数据而言,插入排序比冒泡排序效率高一倍,比选择排序略快,且其时间复杂度也为O(N2)。这三种算法被称为简单排序算法或基本排序算法,也是最稳定的算法。
01—算法思想
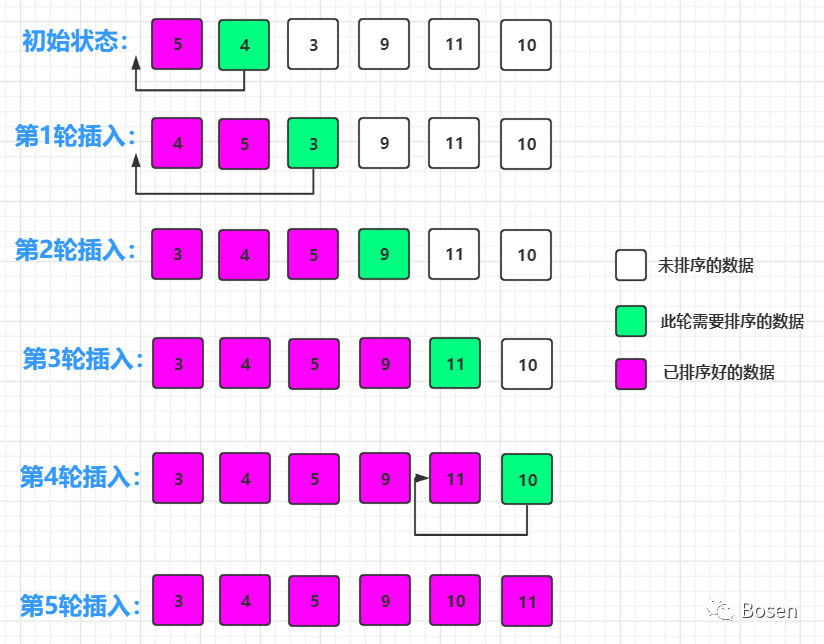
插入排序算法的思想:自左往右对数据进行排序,在进行第1轮插入时,下标为1的数据为待插入的数据,如果前面的数据大于这个待插入的数据时,前面的数据需要进行后移操作,然后再将待插入的数据插入,以此类推进行后面几轮的插入,直到数据排序完成为止。(具体流程如下图)
02—具体代码
Insert.java
package com.bosen.insert;
/**
* <p>插入排序</p>
* @author Bosen 2021/5/29 0:13
*/
public class Insert {
/*
* 待排序的数组
*/
private int[] array;
public Insert(int[] array) {
this.array = array;
}
/*
* 执行排序
*/
public void sort() {
display("初始状态:");
for (int i=1; i<array.length; i++) {
int tempValue = array[i]; // 此轮需要插入的数据
int beforeIndex = i-1; // 前面已排序好的数据
// 当待排序的数据小于已排序的数据时,对应的数据位置需后移
while (beforeIndex>=0 && array[beforeIndex] > tempValue) {
array[beforeIndex+1] = array[beforeIndex];
beforeIndex--;
}
array[beforeIndex+1] = tempValue;
display("第"+i+"轮插入:");
}
}
/*
* 打印排序信息
*/
public void display(String msg) {
System.out.print(msg);
for (int i : array) {
System.out.print("\t"+i);
}
System.out.println();
}
}Test.java
package com.bosen.insert;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
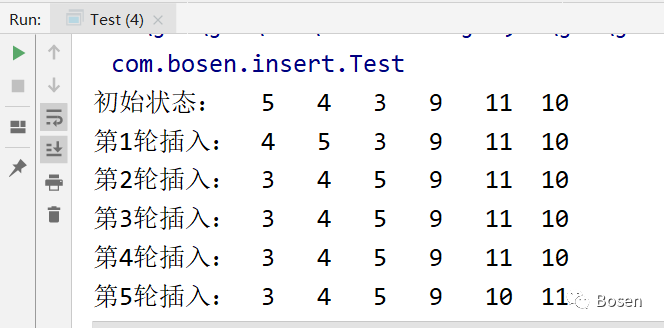
int[] array = {5, 4, 3, 9, 11, 10};
Insert insert = new Insert(array);
insert.sort();
}
}输出结果:
03—算法优化
在前面的算法中,当待插入的数据需要执行插入操作时,需要对已经排序好的数组进行一个全扫描,以确定待插入数组需要插入的具体位置。但当已经排序好的数组的数据量非常大时,这个扫描是十分耗时与不合理的,因此,在查找具体的插入位置时,我们可以对算法引入二分查找的思想。
04—优化代码
package com.bosen.insert;
/**
* <p>插入排序</p>
* @author Bosen 2021/5/29 0:13
*/
public class Insert {
/*
* 待排序的数组
*/
private int[] array;
public Insert(int[] array) {
this.array = array;
}
/*
* 执行排序
*/
public void sort() {
display("初始状态:");
for (int i=1; i<array.length; i++) {
int tempValue = array[i]; // 此轮需要插入的数据
if (array[i-1] > tempValue) {
int beforeIndex = binarySearch(0, i-1, tempValue); // 前面已排序好的数据
for (int j=i; j>beforeIndex; j--) {
array[j] = array[j-1];
}
array[beforeIndex] = tempValue;
}
display("第"+i+"轮插入:");
}
}
/*
* 二分查找
*/
public int binarySearch(int min, int max, int flag) {
int curIndex;
while (min < max) {
curIndex = (min+max)/2;
if (array[curIndex] > flag) {
max = curIndex - 1;
} else {
min = curIndex + 1;
}
}
return min;
}
/*
* 打印排序信息
*/
public void display(String msg) {
System.out.print(msg);
for (int i : array) {
System.out.print("\t"+i);
}
System.out.println();
}
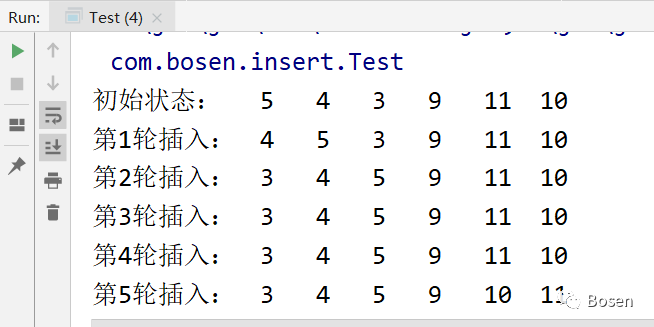
}输出结果:
总结
此篇章节,主要介绍了插入排序算法的基本算法思想,通过具体代码来实现,并引入二分查找法对算法进行优化。
👇扫描二维码关注
























 511
511











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










