前言
此知识点都来源于项目实战,对此进行科普总结,使得之后项目游刃有余
对于Spring的基本知识,推荐阅读:
1. 基本知识
在Java中,@Around注解通常与AspectJ框架一起使用,用于定义一个环绕通知(around advice)。
- AspectJ是一个面向切面编程的框架,它允许开发者通过切面(aspects)来模块化横切关注点。
- 环绕通知是AspectJ中的一种通知类型,用于在目标方法执行前后完全控制目标方法的执行。
此处着重加深一下环绕通知以及切面这两个抽象名词的概念,有助于加深@Around注解
👇👇👇
环绕通知(Around Advice)概念:
-
定义:
切面中的一种通知类型,它允许在目标方法执行前后完全控制目标方法的执行。
可以决定是否继续执行目标方法,以及是否修改目标方法的输入参数和返回值。 -
特点:
最灵活的通知类型,提供了对目标方法的完全控制。它能够在目标方法执行前后执行自定义逻辑,包括修改方法的输入和输出。 -
执行步骤:
1.在目标方法执行之前,环绕通知执行前置逻辑。
2.调用ProceedingJoinPoint.proceed()来执行目标方法。
3.在目标方法执行之后,环绕通知执行后置逻辑。 -
使用场景:
记录方法执行时间
权限验证
缓存控制
事务管理等
👇👇👇
切面(Aspect)概念:
-
定义:
切面是一种模块化的方式,用于将横切关注点(cross-cutting concerns)从业务逻辑中分离出来
横切关注点包括日志记录、性能统计、安全性等,它们通常涉及多个对象和方法 -
主要组成:
1.切入点(Join Point): 在应用程序执行期间的某个特定点,如方法调用、异常抛出等。
2.通知(Advice): 定义在切入点上执行的操作,包括前置、后置、环绕、异常等不同类型的通知。
3.切入点表达式(Pointcut): 用于匹配切入点的表达式,决定在哪些切入点上执行通知。 -
主要作用:
将横切关注点集中管理,避免散布在各处的重复代码
提高代码的模块化和可维护性
2. Demo
以下两种Demo示例大同小异
其中不带参数与带参数章节,差异在于切面类是否可以携带参数(大白话:自定义的注解中是否携带参数,增强处理类就是否有参数)
导入依赖:使用@Around注解,先导入AspectJ库
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId>
<version>1.9.7</version> <!-- 根据实际情况调整版本号 -->
</dependency>
2.1 不带参数
- 创建自定义注解:创建一个自定义的注解
@LogExecutionTime,该注解用于标记需要记录执行时间的方法
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface LogExecutionTime {
}
- 创建切面类:创建一个切面类
LoggingAspect,其中包含一个使用@Around注解的环绕通知
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
public class LoggingAspect {
// @Around("@annotation(com.example.demo.LogExecutionTime)")表示该环绕通知仅在使用@LogExecutionTime注解的方法上执行
@Around("@annotation(com.example.demo.LogExecutionTime)")
public Object logExecutionTime(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 执行目标方法
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(
joinPoint.getSignature() + " executed in " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
return result;
}
}
- 创建控制器类:创建一个简单的Spring Boot控制器类,其中包含一个被
@LogExecutionTime注解标记的方法
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class DemoController {
@LogExecutionTime
@GetMapping("/demo")
public String demoEndpoint() {
// 模拟业务逻辑
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "Demo endpoint executed";
}
}
- 启动应用程序:创建一个Spring Boot应用程序入口类,启动Spring Boot应用
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
- 访问端点:启动应用程序后,访问
http://localhost:8080/demo,可在控制台中可以看到输出的执行时间信息
(由于代码模块中8080已被占用,此处在配置文件中修改为8088端口,并且使用测试接口测试)
# application.properties 文件
server.port=8088
以上是测试模块的代码,为了书写规整,博主将其归类如下,大致也差不多
输出截图如下:
结果先出这个,这个是执行过程输出!
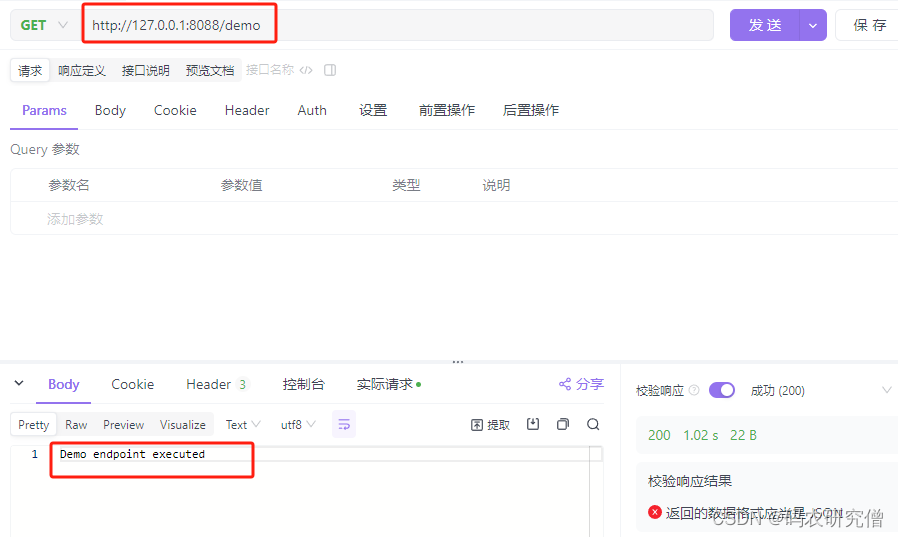
最后是环绕后置通知:
通过切面和环绕通知,实现在不修改业务逻辑的情况下,记录方法执行时间的功能。
切面提供了一种清晰、模块化的方式来处理横切关注点
2.2 带参数
- 带参数自定义注解:(这个注解带有一个value参数,用于传递额外的信息)
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface LogExecutionTime {
String value() default "";
}
- 切面类:
在@Around注解中使用@annotation(logExecutionTime)表示将注解信息传递给切面方法。
通过LogExecutionTime logExecutionTime参数获取注解的值,然后在切面逻辑中使用
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
public class LoggingAspect {
@Around("@annotation(logExecutionTime)")
public Object logExecutionTime(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, LogExecutionTime logExecutionTime) throws Throwable {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 打印传入的参数值
String additionalInfo = logExecutionTime.value();
System.out.println("Additional Info: " + additionalInfo);
// 执行目标方法
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(
joinPoint.getSignature() + " executed in " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
return result;
}
}
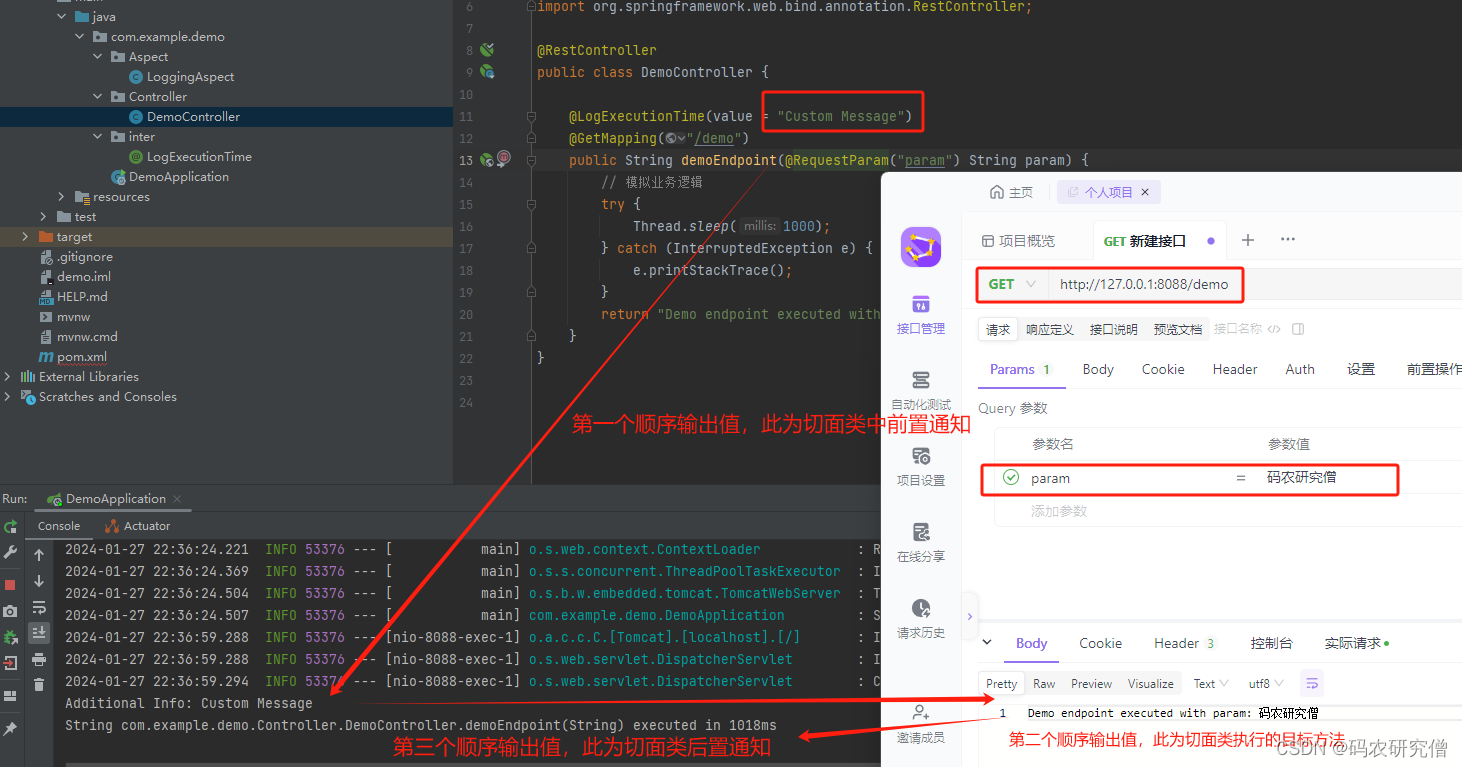
- 控制类:
在控制器类中,@LogExecutionTime(value = "Custom Message")注解传递一个带参数的自定义消息
在demoEndpoint方法中,也接收了一个@RequestParam参数,用于演示带参数的情况。
(对于@RequestParam参数,推荐阅读:
1.详细分析Java中的@RequestParam和@RequestBody
2.@pathvariable 和 @Requestparam的详细区别)
这样,通过@Around注解和ProceedingJoinPoint,能够实现对带参数的自定义注解进行更灵活的处理。
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class DemoController {
@LogExecutionTime(value = "Custom Message")
@GetMapping("/demo")
public String demoEndpoint(@RequestParam("param") String param) {
// 模拟业务逻辑
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "Demo endpoint executed with param: " + param;
}
}
截图如下:
























 1241
1241











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










