索引
一、Thread的常用方法
1.run()方法
作用:子类通常需要重写Thread类中的run()方法,run()中写你想让该线程执行的代码。
//MyThread继承Thread
class MyThread extends Thread{
//1.子类MyThread重写Thread类中的run()方法
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 2;i <= 10;i++){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
2.start()方法
作用:启动当前线程,并调用当前线程中的run()方法
class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 2;i <= 10;i++){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
public class ThreadTest{
public static void main(String args[]){
MyThread m1 = new MyThread();
//2.调用m1的start()方法
m1.start();
}
}
输出结果:

3.currrentThread()方法,返回当前执行代码的线程,该方法为静态方法,直接通过Thread类名调用
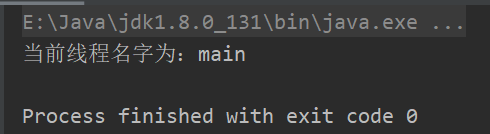
一般要操控某个线程,先通过该方法currentThread()获取到该线程,然后再访问该线程里的方法,对该线程进行操作。例如:我想获取当前线程的名字,代码如下:
public class ThreadTest{
public static void main(String args[]){
//获取主线程的名字
//先通过Thread.currentThread()方法返回当前线程,然后调用该线程里的getName()方法,获取当前线程的名字
System.out.println("当前线程名字为:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
4.getName()方法,获取当前线程的名字
具体代码参见第3点
5.setName()方法,设置当前线程名字
public class ThreadTest{
public static void main(String args[]){
//先通过Thread.currentThread()获取当前线程
//调用当前线程的setName()方法,为当前线程设置名字。
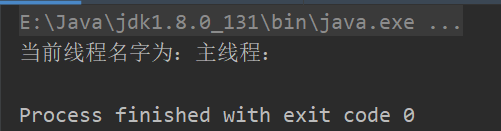
Thread.currentThread().setName("主线程:");
System.out.println("当前线程名字为:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
6.yield()方法,释放当前线程的操作
执行yield()方法,cpu会释放当前线程,去执行其它的线程,过后还是会继续执行该线程,具体什么时候执行该线程,看cpu心情。
class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 1;i <= 10;i++){
System.out.println(i);
if(i % 2 == 0){
//写法一
Thread.currentThread().yield();
//写法二:由于该类继承了Thread类,所以该子类拥有yield()方法,可以直接使用yield()来释放当前线程
//yield();
}
}
}
}
7.join()方法
如果在线程a中调用了线程b的join()方法,此时线程a就会进入阻塞状态,直到线程b完全执行完以后,线程a才会结束阻塞状态,由于join方法中会抛出异常,所以我们还需要try-catch来捕捉处理异常
class MyThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i = 1;i <= 10;i++){
System.out.println(getName() + i);
}
}
}
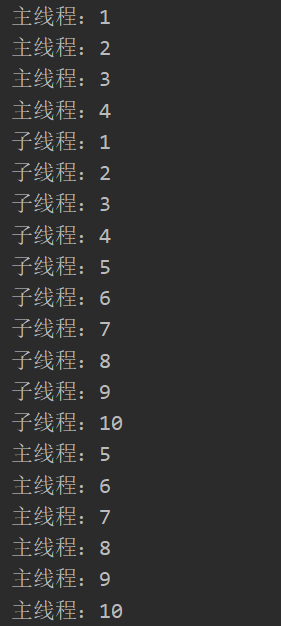
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread.currentThread().setName("主线程:");
MyThread t1 = new MyThread();
t1.setName("子线程:");
t1.start();
for(int i = 1;i <= 10;i++){
if(i == 5){
try {
//在主线程中调用了t1的join()方法,主线程进入阻塞状态,直到t1执行完毕后,才继续执行主线程
t1.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + i);
}
}
}
输出结果:
8.sleep()方法
sleep()方法内的形参为long millitime,调用该方法会让当前线程“睡眠”指定的millitime(毫秒),在指定的millitime毫秒的时间内,当前的线程是阻塞状态。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread.currentThread().setName("主线程:");
try {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
//让该线程睡眠0.5秒
Thread.currentThread().sleep(500);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + i);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
9.isAlive()方法
isAlive()方法用来判断当前线程是否存活,如果当前线程存活,返回true,如果消亡,返回false
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + i);
}
//输出当前的线程是否存活
//由于判断的是主线程是否存活,所以主线程执行isAlive()方法时,肯定是存活的
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().isAlive());
}
}
运行结果:

二、线程的优先级
3个优先级静态常量
MAX_PRIORITY:10(最高优先级)
MIN_PRIORITY:1(最低优先级)
NORM_PRIORITY:5(默认优先级)
如何获取和设置当前线程的优先级
获取当前线程的优先级:getPriority()
设置当前线程的优先级:setPriority(int p),p的取值范围为1~10
说明:高优先级的线程从概率上来讲会有较高的概率抢占低优先级线程的cup执行权,并不意味着只有当高优先级的线程执行完之后,低优先级的线程才执行。
class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
System.out.println(getName() + i);
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread.currentThread().setName("主线程:");
MyThread t1 = new MyThread();
t1.setName("子线程1:");
t1.start();
//获取线程的优先级
System.out.println("修改前子线程的优先级为:" + t1.getPriority());
//设置线程的优先级
t1.setPriority(10);
System.out.println("修改后子线程的优先级为:" + t1.getPriority());
}
}






















 338
338











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








