动态规划
一、309.最佳买卖股票时机含冷冻期
题目:
给定一个整数数组,其中第 i 个元素代表了第 i 天的股票价格 。
设计一个算法计算出最大利润。在满足以下约束条件下,你可以尽可能地完成更多的交易(多次买卖一支股票):
- 你不能同时参与多笔交易(你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票)。
- 卖出股票后,你无法在第二天买入股票 (即冷冻期为 1 天)。
示例:
- 输入: [1,2,3,0,2]
- 输出: 3
- 解释: 对应的交易状态为: [买入, 卖出, 冷冻期, 买入, 卖出]
思路:
动规五部曲,分析如下:
1、确定dp数组以及下标的含义
dp[i][j],第i天状态为j,所剩的最多现金为dp[i][j]。
其实本题很多同学搞的比较懵,是因为出现冷冻期之后,状态其实是比较复杂度,例如今天买入股票、今天卖出股票、今天是冷冻期,都是不能操作股票的。
具体可以区分出如下四个状态:
- 状态一:持有股票状态(今天买入股票,或者是之前就买入了股票然后没有操作,一直持有)
不持有股票状态,这里就有两种卖出股票状态:
- 状态二:保持卖出股票的状态(两天前就卖出了股票,度过一天冷冻期。或者是前一天就是卖出股票状态,一直没操作)
- 状态三:今天卖出股票
- 状态四:今天为冷冻期状态,但冷冻期状态不可持续,只有一天。
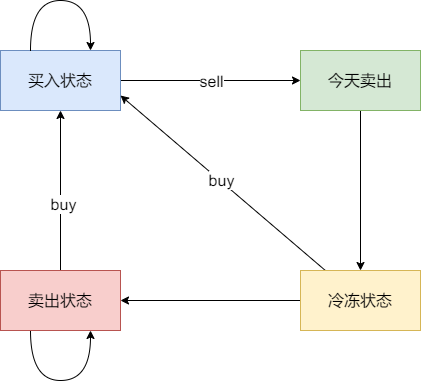
j的状态为:
- 0:状态一
- 1:状态二
- 2:状态三
- 3:状态四
2、确认递推状态
dp[i][0] = max(dp[i - 1][0], max(dp[i - 1][3], dp[i - 1][1]) - prices[i]);
dp[i][1] = max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][3]);
dp[i][2] = dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i];
dp[i][3] = dp[i - 1][2];3、dp数组如何初始化
这里主要讨论一下第0天如何初始化。
如果是持有股票状态(状态一)那么:dp[0][0] = -prices[0],一定是当天买入股票。
保持卖出股票状态(状态二),这里其实从 「状态二」的定义来说 ,很难明确应该初始多少,这种情况我们就看递推公式需要我们给他初始成什么数值。
如果i为1,第1天买入股票,那么递归公式中需要计算 dp[i - 1][1] - prices[i] ,即 dp[0][1] - prices[1],那么大家感受一下 dp[0][1] (即第0天的状态二)应该初始成多少,只能初始为0。想一想如果初始为其他数值,是我们第1天买入股票后 手里还剩的现金数量是不是就不对了。
今天卖出了股票(状态三),同上分析,dp[0][2]初始化为0,dp[0][3]也初始为0。
4、确定遍历顺序
从递归公式上可以看出,dp[i] 依赖于 dp[i-1],所以是从前向后遍历。
5、举例推导dp数组
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
if (prices == null || prices.length < 2) {
return 0;
}
int[][] dp = new int[prices.length][2];
// bad case
dp[0][0] = 0;
dp[0][1] = -prices[0];
dp[1][0] = Math.max(dp[0][0], dp[0][1] + prices[1]);
dp[1][1] = Math.max(dp[0][1], -prices[1]);
for (int i = 2; i < prices.length; i++) {
// dp公式
dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] + prices[i]);
dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 2][0] - prices[i]);
}
return dp[prices.length - 1][0];
}
}
// 一维数组优化
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int[] dp=new int[4];
dp[0] = -prices[0];
dp[1] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= prices.length; i++){
// 使用临时变量来保存dp[0], dp[2]
// 因为马上dp[0]和dp[2]的数据都会变
int temp = dp[0];
int temp1 = dp[2];
dp[0] = Math.max(dp[0], Math.max(dp[3], dp[1]) - prices[i-1]);
dp[1] = Math.max(dp[1], dp[3]);
dp[2] = temp + prices[i-1];
dp[3] = temp1;
}
return Math.max(dp[3],Math.max(dp[1],dp[2]));
}
}
//另一种解题思路
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int[][] dp = new int[prices.length + 1][2];
dp[1][0] = -prices[0];
for (int i = 2; i <= prices.length; i++) {
/*
dp[i][0] 第i天持有股票收益;
dp[i][1] 第i天不持有股票收益;
情况一:第i天是冷静期,不能以dp[i-1][1]购买股票,所以以dp[i - 2][1]买股票,没问题
情况二:第i天不是冷静期,理论上应该以dp[i-1][1]购买股票,但是第i天不是冷静期说明,第i-1天没有卖出股票,
则dp[i-1][1]=dp[i-2][1],所以可以用dp[i-2][1]买股票,没问题
*/
dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 2][1] - prices[i - 1]);
dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1], dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i - 1]);
}
return dp[prices.length][1];
}
}二、714.买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费
题目:
给定一个整数数组 prices,其中第 i 个元素代表了第 i 天的股票价格 ;非负整数 fee 代表了交易股票的手续费用。
你可以无限次地完成交易,但是你每笔交易都需要付手续费。如果你已经购买了一个股票,在卖出它之前你就不能再继续购买股票了。
返回获得利润的最大值。
注意:这里的一笔交易指买入持有并卖出股票的整个过程,每笔交易你只需要为支付一次手续费。
示例 1: 输入: prices = [1, 3, 2, 8, 4, 9], fee = 2 输出: 8
解释: 能够达到的最大利润: 在此处买入 prices[0] = 1 在此处卖出 prices[3] = 8 在此处买入 prices[4] = 4 在此处卖出 prices[5] = 9 总利润: ((8 - 1) - 2) + ((9 - 4) - 2) = 8.
注意:
- 0 < prices.length <= 50000.
- 0 < prices[i] < 50000.
- 0 <= fee < 50000.
思路:
相对122.买卖股票的最佳时机II ,本题只需要在计算卖出操作的时候减去手续费就可以了,代码几乎是一样的
相对122.买卖股票的最佳时机II ,本题只需要在计算卖出操作的时候减去手续费就可以了,代码几乎是一样的
/**
* 卖出时支付手续费
* @param prices
* @param fee
* @return
*/
public int maxProfit(int[] prices, int fee) {
int len = prices.length;
// 0 : 持股(买入)
// 1 : 不持股(售出)
// dp 定义第i天持股/不持股 所得最多现金
int[][] dp = new int[len][2];
dp[0][0] = -prices[0];
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] - prices[i]);
dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i] - fee, dp[i - 1][1]);
}
return Math.max(dp[len - 1][0], dp[len - 1][1]);
}
/**
* 买入时支付手续费
* @param prices
* @param fee
* @return
*/
public int maxProfit(int[] prices, int fee) {
int len = prices.length;
// 0 : 持股(买入)
// 1 : 不持股(售出)
// dp 定义第i天持股/不持股 所得最多现金
int[][] dp = new int[len][2];
// 考虑买入的时候就支付手续费
dp[0][0] = -prices[0] - fee;
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0], dp[i - 1][1] - prices[i] - fee);
dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][0] + prices[i], dp[i - 1][1]);
}
return Math.max(dp[len - 1][0], dp[len - 1][1]);
}
// 一维数组优化
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices, int fee) {
int[] dp = new int[2];
dp[0] = -prices[0];
dp[1] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= prices.length; i++) {
dp[0] = Math.max(dp[0], dp[1] - prices[i - 1]);
dp[1] = Math.max(dp[1], dp[0] + prices[i - 1] - fee);
}
return dp[1];
}
}




















 309
309











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








