一、ThreadLocal概述
ThreadLocal是JDK包提供的,它提供了线程本地变量,也就是如果你创建了一个ThreadLocal变量,那么访问这个变量的每个线程都会有这个变量的一个本地副本。当多个线程操作这个变量时,实际操作的是自己本地内存里面的变量,从而避免了线程安全问题
举例
package lockTest;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Description:
* @Author: Aiguodala
* @CreateDate: 2021/4/23 17:15
*/
public class ThreadLocalTest {
static ThreadLocal<Dog> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
threadLocal.set(new Dog("Aiguodala"));
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ " : " + threadLocal.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ " : " + threadLocal.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
}
class Dog {
String name;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
public Dog(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
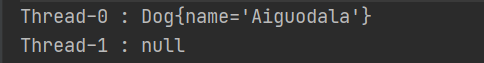
- 第一个线程可以取出自己set的值
- 而第二个线程取不出
- 说明ThreadLocal 对于线程来说是隔离的
二、原理解析
首先应该清楚Thread 类有两个重要的字段,分别用来维护每个Thread线程自己的ThreadLocalMap,具体的应用会在下面分析
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap inheritableThreadLocals = null;
1. set( ) 方法
public void set(T value) {
// 获取当前线程
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
// 通过当前线程获取到一个ThreadLocalMap
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
// 然后对每一个线程独自维护的ThreadLocalMap 进行操作
if (map != null)
// key是当前ThreadLocal value 是放置进入的值
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
if (k == null) {
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
set 其实就是将数值放置在ThreadLocalMap 中的 private Entry[] table 数组中 ,观看源码可知,Entry继承于WeakReference,所以是弱引用,那为什么要将它设置成弱引用呢?
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
原因其实很简单,例如,当构造出该ThreadLocal 类的线程将该连接ThreadLocal 的引用断开,此时,说明该ThreadLocal 已经没用,应该被垃圾回收,但是,该ThreadLocal作为key,将引用存在于该Entry数组中以至于迟迟不能回收,将造成内存泄漏。但是如果设置为弱引用,一旦与该ThreadLocal 相连的强引用被中断,那么在下一次垃圾回收则会无视弱引用而对该ThreadLocal 进行回收。
与此同时,因为该ThreadLocal被回收,此时这对键值对的key为null,则无法通过key访问该value,也会导致内存泄漏,所以一旦不使用,建议调用remove() 方法。
2. get() 和 remove()
理解了上面内容。则对于get() 和 remove() 则也不难理解,就不多赘述,就是从Entry数组中获取相关元素或者删除相关元素的操作
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}
private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
if (e.get() == key) {
e.clear();
expungeStaleEntry(i);
return;
}
}
}
三、InheritableThreadLocal 概述
读懂了上面的知识,很容易发现ThreadLocal 是线程独立的,但是,如果我想共享ThreadLocal 的数据应该怎么办呢,这时候InheritableThreadLocal 就应运而生,InheritableThreadLocal 可以支持子线程访问到父线程的放置其中的数据
举例:
package lockTest;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Description:
* @Author: Aiguodala
* @CreateDate: 2021/4/23 17:15
*/
public class ThreadLocalTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadLocal<String> stringThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
InheritableThreadLocal<String> stringInheritable = new InheritableThreadLocal<>();
// 主线程赋对上面两个变量进行赋值
stringThreadLocal.set("this is threadLocal");
stringInheritable.set("this is inheritableThreadLocal");
// 创建线程
Thread thread1 = new Thread(()->{
// 获得ThreadLocal中存放的值
System.out.println(stringThreadLocal.get());
// 获得InheritableThreadLocal存放的值
System.out.println(stringInheritable.get());
});
thread1.start();
}
}
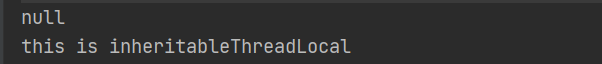
- 分别在ThreadLocal 中和 InheritableThreadLocal 中放置了数据
- 最终子线程只能获取到InheritableThreadLocal 中放置的值
四、原理解析
InheritableThreadLocal 继承自 ThreadLocal 并重写了它下面三个方法,当调用getMap () 或者 createMap()的时候就不是给threadLocal赋值,而是给Thread的inheritableThreadLocals 字段赋值
public class InheritableThreadLocal<T> extends ThreadLocal<T> {
protected T childValue(T parentValue) {
return parentValue;
}
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.inheritableThreadLocals;
}
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.inheritableThreadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
}
那么,这个inheritableThreadLocals 又是如何传递的呢?
当创建线程的时候(以博主的例子,主线程为例)
先调用了无参构造,里面又会不断的调用重载的init方法
public Thread() {
init(null, null, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0);
}
private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name,
long stackSize) {
init(g, target, name, stackSize, null, true);
}
private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name,
long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc,
boolean inheritThreadLocals) {
if (name == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("name cannot be null");
}
this.name = name;
Thread parent = currentThread();
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (g == null) {
/* Determine if it's an applet or not */
/* If there is a security manager, ask the security manager
what to do. */
if (security != null) {
g = security.getThreadGroup();
}
/* If the security doesn't have a strong opinion of the matter
use the parent thread group. */
if (g == null) {
g = parent.getThreadGroup();
}
}
/* checkAccess regardless of whether or not threadgroup is
explicitly passed in. */
g.checkAccess();
/*
* Do we have the required permissions?
*/
if (security != null) {
if (isCCLOverridden(getClass())) {
security.checkPermission(SUBCLASS_IMPLEMENTATION_PERMISSION);
}
}
g.addUnstarted();
this.group = g;
this.daemon = parent.isDaemon();
this.priority = parent.getPriority();
if (security == null || isCCLOverridden(parent.getClass()))
this.contextClassLoader = parent.getContextClassLoader();
else
this.contextClassLoader = parent.contextClassLoader;
this.inheritedAccessControlContext =
acc != null ? acc : AccessController.getContext();
this.target = target;
setPriority(priority);
if (inheritThreadLocals && parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null)
this.inheritableThreadLocals =
ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals);
/* Stash the specified stack size in case the VM cares */
this.stackSize = stackSize;
/* Set thread ID */
tid = nextThreadID();
}
有兴趣的可以都看看线程初始化的过程,但是对于inheritableThreadLocals 来说,重要的是这几句
// 这里的currentThread 指的是创建该线程的线程
Thread parent = currentThread();
if (inheritThreadLocals && parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null)
this.inheritableThreadLocals =
ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals);
传入的参数inheritThreadLocals 为true 并且如果父线程的inheritableThreadLocals 不为空,那么在createInheritedMap内部会使用父线程的inheritableThreadLocals变量作为构造函数创建了一个新的ThreadLocalMap变量,然后赋值给了子线程的inheritableThreadLocals变量,相当于将父线程的inheritableThreadLocals传递给了子线程。





















 4191
4191











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








