安装influxdb
#下载
wget https://dl.influxdata.com/influxdb/releases/influxdb-1.8.3.x86_64.rpm
#安装
yum localinstall influxdb-1.8.3.x86_64.rpm
#启动
service influxdb start
#检查是否启动成功
service influxdb status
#PS:配置文件位于 vim 进行修改是否需要账号密码登录
/etc/influxdb/influxdb.conf
打开命令窗口
#本机
influx -precision rfc3339
#远程
influx -host 地址 -precision rfc3339
#-precision为设置显示时间格式
#rfc3339表示格式
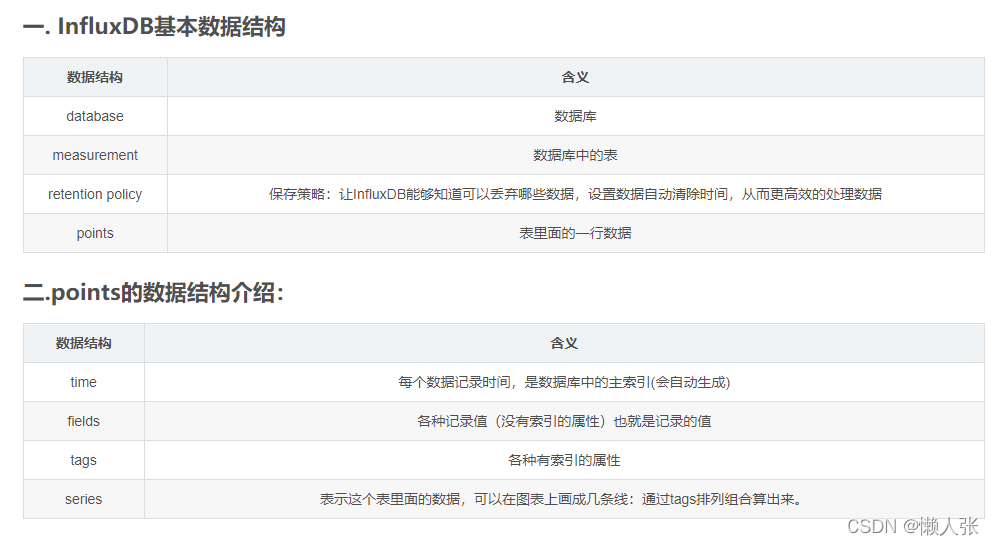
结构

设置密码
打开命令窗口后查看用户
influx
show users;
#查看所有用户
exit
#退出
去配置文件influxdb.conf中,将auth-enabled项设置为true,在重启服务之前添加几个用户,并对其进行授权。
vim /etc/influxdb/influxdb.conf
再次打开influxdb命令窗口
influx
#添加一个管理员用户
create user "root" with password 'root' with all privileges
重启后
influxdb中使用用户名密码登录
influx -username root -password root
简单的增删改查
# 插入一条数据
INSERT cpu,host=serverA,region=us_west value=0.64
# 查看数据
SELECT "host", "region", "value" FROM "cpu"
# 往另一个表中插入数据
INSERT temperature,machine=unit42,type=assembly external=25,internal=37
# 查看所有内容
SELECT * FROM "temperature"
# 使用表名通配符,同时查看多个表中的多条记录
# SELECT * FROM /.*/ LIMIT 10
# 带有查询条件
SELECT * FROM "cpu_load_short" WHERE "value" > 0.9
# 删除数据
delete from "cpu" where host='serverA'
#删除数据的条件不能是field,因为field没有索引.但是可以是tags
#查询数据的条件可以是field
springboot整合influxDb
导包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.influxdb</groupId>
<artifactId>influxdb-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置yml文件
spring:
influx:
url: http://192.168.28.128:8086
password: root
user: root
database: my_sensor1
配置类
package com.zhk.study.influxdb;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import org.influxdb.InfluxDB;
import org.influxdb.InfluxDBFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class InfluxdbConfig {
@Value("${spring.influx.url}")
private String influxDBUrl;
@Value("${spring.influx.user}")
private String userName;
@Value("${spring.influx.password}")
private String password;
@Value("${spring.influx.database}")
private String database;
@Bean
public InfluxDB influxdb(){
InfluxDB influxDB = InfluxDBFactory.connect(influxDBUrl, userName, password);
try {
/**
* 异步插入:
* enableBatch这里第一个是point的个数,第二个是时间,单位毫秒
* point的个数和时间是联合使用的,如果满100条或者60 * 1000毫秒
* 满足任何一个条件就会发送一次写的请求。
*/
influxDB.setDatabase(database).enableBatch(100,1000 * 60, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//设置默认策略
influxDB.setRetentionPolicy("sensor_retention");
}
//设置日志输出级别
influxDB.setLogLevel(InfluxDB.LogLevel.BASIC);
return influxDB;
}
}
使用
package com.zhk.study.influxdb;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.influxdb.InfluxDB;
import org.influxdb.dto.BatchPoints;
import org.influxdb.dto.Point;
import org.influxdb.dto.Query;
import org.influxdb.dto.QueryResult;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/influx/")
public class TestController {
@Autowired
private InfluxDB influxDB;
//measurement 表名字
private final String measurement = "sensor";
@Value("${spring.influx.database}")
private String database;
/**
* 批量插入第一种方式
*/
@GetMapping("insert1")
public String insert1(){
ArrayList<String> strings = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
//一条数据
Point point = Point.measurement(measurement)
//所对应的有索引的字段
.tag("deviceId", "sensor" + i)
//所对应的无索引的字段
.addField("temp", 3)
.addField("voltage", 145 + i)
.addField("A1", "4i")
.addField("A2", "4i").build();
strings.add(point.lineProtocol());
}
log.info("存储数据");
//写入
influxDB.write(strings);
return "succes" ;
}
/**
* 批量插入第二种方式
*/
@GetMapping("insert2")
public String insert2(){
BatchPoints batchPoints = BatchPoints
.database(database)
.consistency(InfluxDB.ConsistencyLevel.ALL)
.build();
//遍历sqlserver获取数据
for(int i=0;i<50;i++){
//创建单条数据对象——表名
Point point = Point.measurement(measurement)
//tag属性——只能存储String类型
.tag("deviceId", "sensor" + i)
.addField("temp", 3)
.addField("voltage", 145+i)
.addField("A1", "4i")
.addField("A2", "4i").build();
//将单条数据存储到集合中
batchPoints.point(point);
}
log.info("存储数据");
influxDB.write(batchPoints);
return "succes" ;
}
/**
* 获取数据
*/
@GetMapping("query")
public String query(@RequestParam(defaultValue = "1") Integer page){
int pageSize = 10;
//InfluxDB支持分页查询,一次可以设置发呢也查询条件
String pageQuery = "limit" + pageSize + "offsiz" + (page -1) * pageSize;
String queryCondition = ""; //查询条件暂且为空
String queryCmd = "SELECT * FROM "
// 查询指定设备下的日志信息
// 要指定从 RetentionPolicyName.measurement中查询指定数据,默认的策略可以不加;
// + 策略name + "." + measurement
+ measurement
// 添加查询条件(注意查询条件选择tag值,选择field数值会严重拖慢查询速度)
+ queryCondition
// 查询结果需要按照时间排序
+ " ORDER BY time DESC"
// 添加分页查询条件
+ pageQuery;
log.info("查询");
QueryResult query = influxDB.query(new Query(queryCmd, database));
return query.toString();
}
}
























 511
511

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










