条件循环结构
一、条件语句
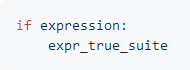
- if语句
<注>:
1.if 语句的 expr_true_suite 代码块只有当条件表达式 expression 结果为真时才执行,否则将继续执行紧跟在该代码块后面的语句。
2.单个 if 语句中的 expression 条件表达式可以通过布尔操作符 and,or和not 实现多重条件判断。
例:
if 2 > 1 and not 2 > 3:
print('Correct Judgement!')
# Correct Judgement!
- if-else语句
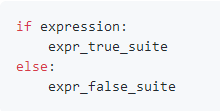
例:
temp = input("guess which number i'm thinking of")
guess = int(temp)
if guess == 666:
print("yes")
else:
print("no")
print("thanks ,game over")
运行结果:
guess which number i'm thinking of666
yes
game over
guess which number i'm thinking of77
no
thanks ,game over
<注>:
if语句支持嵌套,即在一个if语句中嵌入另一个if语句,从而构成不同层次的选择结构。Python 使用缩进而不是大括号来标记代码块边界。
例:
h= input("please input a number:")
hi = int(h)
if hi>2:
print("ok")
if hi>6:
print("very good")
else:
print("sorry")
运行结果:
please input a number:1
sorry
please input a number:6
ok
please input a number:8
ok
very good
例:
temp = input("guess which number i'm thinking :")
guess = int(temp)
if guess > 8:
print("too big")
else:
if guess == 8:
print("you are right")
else:
print("too small")
print("game over,thanks")
运行结果:
guess which number i'm thinking :7
too small
game over,thanks
- if-elif-else语句

<注>
elif 语句即为 else if,用来检查多个表达式是否为真,并在为真时执行特定代码块中的代码。
例:
temp = input('please input grades:')
source = int(temp)
if 100 >= source >= 90:
print('A')
elif 90 > source >= 80:
print('B')
elif 80 > source >= 60:
print('C')
elif 60 > source >= 0:
print('D')
else:
print('wrong!')
# please input grades:80
# B
- assert关键词
assert这个关键词我们称之为“断言”,当这个关键词后边的条件为 False 时,程序自动崩溃并抛出AssertionError的异常。
assert 3 > 7
# AssertionError
二、循环语句
- while循环

<注>
1.while循环的代码块会一直循环执行,直到布尔表达式的值为布尔假。
2.如果布尔表达式不带有<、>、==、!=、in、not in等运算符,仅仅给出数值之类的条件,也是可以的。当while后写入一个非零整数时,视为真值,执行循环体;写入0时,视为假值,不执行循环体。也可以写入str、list或任何序列,长度非零则视为真值,执行循环体;否则视为假值,不执行循环体。
例:
count = 0
while count < 5:
temp = input("guess which number i'm thinking of")
guess = int(temp)
if guess > 8:
print("too big")
else:
if guess == 8:
print("good!you are right")
count =5
else:
print("too small")
count = count + 1
print("game over ,thanks")
运行结果:
guess which number i'm thinking of5
too small
guess which number i'm thinking of6
too small
guess which number i'm thinking of7
too small
guess which number i'm thinking of8
good!you are right
game over ,thanks
例:
string='12345'
while string:
print(string)
string=string[1:]
#12345
#2345
#345
#45
#5
- while - else 循环

<注>
当while循环正常执行完的情况下,执行else输出,如果while循环中执行了跳出循环的语句,比如 break,将不执行else代码块的内容。
例:
count = 0
while count < 5:
print("%d is less than 5" % count)
count = count + 1
else:
print("%d is not less than 5" % count)
#0 is less than 5
#1 is less than 5
#2 is less than 5
#3 is less than 5
#4 is less than 5
#5 is not less than 5
例:
count = 0
while count < 5:
print("%d is less than 5" % count)
count = 6
break
else:
print("%d is not less than 5" % count)
#0 is less than 5
- for循环
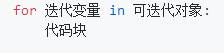
<注>
for循环是迭代循环,在Python中相当于一个通用的序列迭代器,可以遍历任何有序序列,如str、list、tuple等,也可以遍历任何可迭代对象,如dict。
member = ['zhangsan', 'lisi', 'liudehua', 'liuliu', 'zhourunfa']
for i in range(5):
print(member[i])
#zhangsan
#lisi
#liudehua
#liuliu
#zhourunfa
- for - else 循环
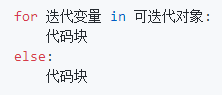
<注>
当for循环正常执行完的情况下,执行else输出,如果for循环中执行了跳出循环的语句,比如 break,将不执行else代码块的内容,与while - else语句一样。
for num in range(10, 20):
for i in range(2, num):
if num % i == 0:
j = num / i
print('%d = %d * %d' % (num, i, j))
break
else:
print(num, 'it is a prime number')
#10 = 2 * 5
#11 it is a prime number
#12 = 2 * 6
#13 it is a prime number
#14 = 2 * 7
#15 = 3 * 5
#16 = 2 * 8
#17 it is a prime number
#18 = 2 * 9
#19 it is a prime number
- range()函数
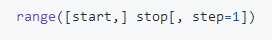
<注>
1.这个BIF(Built-in functions)有三个参数,其中用中括号括起来的两个表示这两个参数是可选的。
2.step=1 表示第三个参数的默认值是1。
3.range 这个BIF的作用是生成一个从start参数的值开始到stop参数的值结束的数字序列,该序列包含start的值但不包含stop的值。
例:
for i in range(1, 10, 2):
print(i)
# 1
# 3
# 5
# 7
# 9
- enumerate()函数
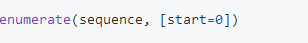
<注>
1.sequence – 一个序列、迭代器或其他支持迭代对象。
2.start – 下标起始位置。
3.返回 enumerate(枚举) 对象
例:
(默认下标从0开始)
seasons = ['Spring', 'Summer', 'Fall', 'Winter']
lst = list(enumerate(seasons))
print(lst)
运行结果:
[(0, 'Spring'), (1, 'Summer'), (2, 'Fall'), (3, 'Winter')]
下标从1开始
seasons = ['Spring', 'Summer', 'Fall', 'Winter']
lst = list(enumerate(seasons,start=1))
print(lst)
运行结果:
[(1, 'Spring'), (2, 'Summer'), (3, 'Fall'), (4, 'Winter')]
- break 语句
import random
secret = random.randint(1, 10)
while True:
temp = input("guess which number i'm thinking of")
guess = int(temp)
if guess > secret:
print("too big")
else:
if guess == secret:
print("yes,you are right")
break
else:
print("too small")
print("game over ,thanks")
#guess which number i'm thinking of7
#too big
#guess which number i'm thinking of1
#too small
#guess which number i'm thinking of4
#too small
#guess which number i'm thinking of5
#too small
#guess which number i'm thinking of5
#too small
#guess which number i'm thinking of6
#yes,you are right
#game over ,thanks
- continue语句

例:
for i in range(10):
if i % 2 != 0:
print(i)
continue
i += 2
print(i)
#2
#1
#4
#3
#6
#5
#8
#7
#10
#9
- pass 语句
<注>
pass是空语句,不做任何操作,只起到占位的作用,其作用是为了保持程序结构的完整性。尽管pass语句不做任何操作,但如果暂时不确定要在一个位置放上什么样的代码,可以先放置一个pass语句,让代码可以正常运行。
例题:
1、编写一个Python程序来查找那些既可以被7整除又可以被5整除的数字,介于1500和2700之间。
for i in range(1500,2700):
if i%5==0 and i%7==0:
print(i,end=" ")
#1505 1540 1575 1610 1645 1680 1715 1750 1785 1820 1855 1890 1925 1960 1995 2030 2065 2100 2135 2170 2205 2240 2275 2310 2345 2380 2415 2450 2485 2520 2555 2590 2625 2660 2695






















 2457
2457











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










