GitHub同步更新(已分类):Data_Structure_And_Algorithm-Review
公众号:URLeisure 的复习仓库
公众号二维码见文末
以下是本篇文章正文内容,下面案例可供参考。
什么是螺旋矩阵?
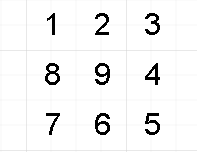
3阶螺旋矩阵:
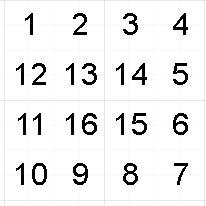
4阶螺旋矩阵:
螺旋矩阵的实现很简单,学习它是为了更好地了解如何在二维数组里进行上下左右的移动操作,强化基础。
创建思路
- 创建方法很简单,别找规律一行一行输就行。
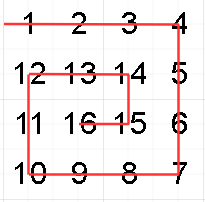
如图,我们本次的螺旋矩阵按照右下左上的顺序完成创建。
-
先一直朝向一个方向创建,创建过程中判断是否需要转向,然后继续创建。
-
我们默认数组操作前数值全部为 0 ,而边界为 -1。
则判断条件为:
- 下一个值是否为 -1;
- 下一个值是否为 0。
(其实只用判断下一个值是否为 0 就行了,不为 0 就转向)
算法设计
- 生成螺旋矩阵就需要转向操作,转向操作也十分的简单。
我们先定义一个转向用的结构体(内部类),包含行(x),列(y)转向信息。
c++代码如下(示例):
struct Position{
int x;
int y;
};
java代码如下(示例):
public static class Position {
int x;
int y;
Position() {
}
Position(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
初始化
- 将边界设为 -1,而其他位置为 0.
c++代码如下(示例):
void Init(int n) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
m[i][j] = 0;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n + 1; i++) {
m[0][i] = m[n + 1][i] = -1;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n + 1; i++) {
m[i][0] = m[i][n + 1] = -1;
}
}
java代码如下(示例):
public static void init(int n) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
m[i][j] = 0;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n + 1; i++) {
m[0][i] = m[n + 1][i] = -1;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n + 1; i++) {
m[i][0] = m[i][n + 1] = -1;
}
}
转向操作
- 向右:行 +0,列 +1;
- 向下:行 +1,列 +0;
- 向左:行 +0,列 -1;
- 向上:行 -1,列 +0。
c++代码如下(示例):
Position DIR[4] = {0, 1, 1, 0, 0, -1, -1, 0};
Position here, nextt;//当前位置 下一个位置
void Solve(int n) {
here.x = 1;
here.y = 1;//当前位置为 1 1
int num = 1;
m[1][1] = 1;//开始位置为数字 1
int dirIndex = 0;
while (num < n * n) {
nextt.x = here.x + DIR[dirIndex].x;
nextt.y = here.y + DIR[dirIndex].y;//更新下一个位置
if (m[nextt.x][nextt.y] == 0) {//判断下一个位置是否合法
m[nextt.x][nextt.y] = ++num;
here = nextt;
} else {
dirIndex = (dirIndex + 1) % 4;
}
}
}
java代码如下(示例):
public static Position here = new Position();//当前位置
public static Position nextt = new Position();//下一个位置
public static Position dir[] = {
new Position(0, 1),
new Position(1, 0),
new Position(0, -1),
new Position(-1, 0)
};
public static void solve(int n) {
here.x = 1;
here.y = 1;
int num = 1;
m[1][1] = 1;
int dirIndex = 0;
while (num < n * n) {
nextt.x = here.x + dir[dirIndex].x;
nextt.y = here.y + dir[dirIndex].y;
if (m[nextt.x][nextt.y] == 0) {
m[nextt.x][nextt.y] = ++num;
here.x = nextt.x;
here.y = nextt.y;
} else {
dirIndex = (dirIndex + 1) % 4;
}
}
}
完整代码
c++代码如下(示例):
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Position {
int x;
int y;
};
Position DIR[4] = {0, 1, 1, 0, 0, -1, -1, 0};
Position here, nextt;
int m[100][100];
void Init(int n) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
m[i][j] = 0;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n + 1; i++) {
m[0][i] = m[n + 1][i] = -1;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n + 1; i++) {
m[i][0] = m[i][n + 1] = -1;
}
}
void Solve(int n) {
here.x = 1;
here.y = 1;
int num = 1;
m[1][1] = 1;
int dirIndex = 0;
while (num < n * n) {
nextt.x = here.x + DIR[dirIndex].x;
nextt.y = here.y + DIR[dirIndex].y;
if (m[nextt.x][nextt.y] == 0) {
m[nextt.x][nextt.y] = ++num;
here = nextt;
} else {
dirIndex = (dirIndex + 1) % 4;
}
}
}
void Print(int n) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
cout << m[i][j] << "\t";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
Init(n);
Solve(n);
Print(n);
}
java代码如下(示例):
import java.util.Scanner;
public class A {
public static class Position {
int x;
int y;
Position() {
}
Position(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
public static int m[][] = new int[100][100];
public static Position here = new Position();
public static Position nextt = new Position();
public static Position dir[] = {
new Position(0, 1),
new Position(1, 0),
new Position(0, -1),
new Position(-1, 0)
};
public static void init(int n) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
m[i][j] = 0;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n + 1; i++) {
m[0][i] = m[n + 1][i] = -1;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n + 1; i++) {
m[i][0] = m[i][n + 1] = -1;
}
}
public static void solve(int n) {
here.x = 1;
here.y = 1;
int num = 1;
m[1][1] = 1;
int dirIndex = 0;
while (num < n * n) {
nextt.x = here.x + dir[dirIndex].x;
nextt.y = here.y + dir[dirIndex].y;
if (m[nextt.x][nextt.y] == 0) {
m[nextt.x][nextt.y] = ++num;
here.x = nextt.x;
here.y = nextt.y;
} else {
dirIndex = (dirIndex + 1) % 4;
}
}
}
public static void print(int n) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
System.out.print(m[i][j] + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
init(n);
solve(n);
print(n);
}
}
关注公众号,感受不同的阅读体验

下期预告:树-概述篇























 439
439











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










