Map和Set/二分搜索树
map和set概念
Map:存储Key-value键值对,存储的数据是映射关系,需要根据不重复的key对应value.
Set:存储不重复元素的线性表,只判定元素是否存在,或者过滤重复元素.
Map和Set是一种专门用来进行搜索的数据结构,是一种适合动态查找的集合容器;用它来进行遍历操作效率极低。
- Key-Value键值对
Key:搜索的数据(关键字)
Value:和关键字相对应(值)
Map中存储的是键值对,而Set中只存储Key.
Map的使用

迭代器:用于遍历集合,有了for-each循环,在不需改原集合的前提下,直接用for-each循环即可。只有需要修改原集合的内容,才会用到迭代器。
关于Map的说明
Map是一个接口类,该类没有继承自Collection,该类中存储的是<Key,Value>结构的键值对,并且Key一定是唯一的,不能重复。
Map集合内部元素之间的先后顺序与插入顺序关系不大。
关于Map集合的常用操作
| 操作 | 方法 |
|---|---|
| 添加元素 | put( Key,Value) |
| 根据Key取得Value | get(Key) |
| 根据Key取得Value | getOrDefault(Object key, V defaultValue) |
| 删除操作 | remove(Object key) |
| 遍历Key的不重复集合 | Set KeySet() |
| 遍历Value的不重复集合 | Collection Values() |
| 返回所有Key-Value的映射关系 | Set<Map.Entry<K, V>> entrySet() |
| 查询是否包含Key | boolean containsKey(Object key) |
| 查询是否包含Value | boolean containsValue(Object Value) |
代码示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
//添加元素
map.put("周杰伦", "告白气球");
map.put("陈奕迅", "富士山下");
map.put("林俊杰", "她说");
map.put("沈以诚", "告白");
System.out.println(map.put("林俊杰","手心的蔷薇"));
System.out.println(map);
//查找成功
System.out.println(map.get("林俊杰"));
//查找不成功返回null
System.out.println(map.get("彭于晏"));
//删除元素
System.out.println(map.remove("周杰伦","告白气球"));
System.out.println(map);
运行结果:

遍历操作 (遍历Key的不重复集合/遍历Value的不重复集合 )
有遍历Map集合,就需要把Map集合转为Set集合,然后进行遍历操作,
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
//添加元素
map.put("周杰伦", "告白气球");
map.put("陈奕迅", "富士山下");
map.put("林俊杰", "她说");
map.put("沈以诚", "告白");
//获取map中所有key值
//快捷生成临时变量 ,接收返回值 Alt+Enter
Set<String> strings = map.keySet();
//获取map中所有的value值
Collection<String> values = map.values();
System.out.println(strings);
System.out.println(values);
}

二分搜索树
向BST中添加元素——add(int value)
1.若该二分搜索树为空树,则返回null;
2.若该二分搜索树不为空,则按照逻辑确定插入元素的位置,在此插入新节点。
//向BST中添加一个新元素
public void add(int value) {
root = add(root, value);
}
//向以root为很节点得的BST中添加一个新元素value,返回添加元素后的根节点
private Node add(Node root, int value) {
//当root为空时,此时走到叶子节点,创建新节点并插入值
if (root == null) {
root = new Node(value);
size++;
return root;
}
//比较根节点和value的大小
if (value < root.val) {
//连接
root.left = add(root.left, value);
return root;
}
//连接
root.right = add(root.right, value);
return root;
}
//打印
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
generateBSTString (root,0,sb);
return sb.toString();
}
//先序遍历二分搜索树,将根节点,树的深度,
private void generateBSTString(Node root,int depth,StringBuilder sb){
if(root == null){
sb.append(generateBSTDepth(depth)).append("null\n");
return;
}
//先访问根节点
sb.append(generateBSTDepth(depth)).append(root.val).append("\n");
//递归访问左子树
generateBSTString(root.left,depth+1,sb);
//递归访问右子树
generateBSTString(root.right, depth+1, sb);
}
//打印当前BST的深度,每进入下一层就多两个--
private String generateBSTDepth(int depth){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < depth; i++) {
sb.append("--");
}
return sb.toString();
}
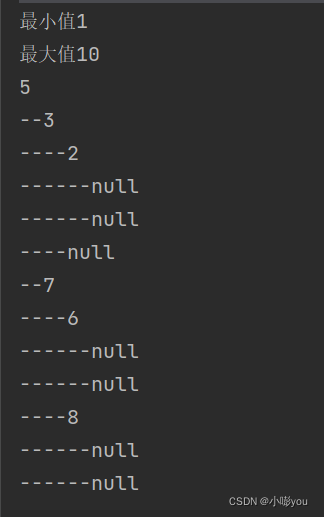
测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
BST bst = new BST();
int[] data={5,10,7,3,6,2,8};
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
bst.add(data[i]);
}
bst.add();
System.out.println(bst);
}

向BST中查找元素——boolean contains(int val)
返回BST的最小值(在左树):root.left = null;
返回BST的最大值(在右树):root.right= null;
查找指定元素
//查找操作,判断以root为根节点的二叉搜索树是否存在指定元素
public boolean contains(int val){
return contains(root,val);
}
private boolean contains(Node root, int val) {
if(root == null){
return false;
//根节点就是待查找元素
}else if(root.val == val)return true;
//在左树中查找
else if(val<root.val)return contains(root.left,val);
//在右树中查找
return contains(root.right, val);
}
测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
BST bst = new BST();
int[] data={5,10,7,3,6,2,8};
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
bst.add(data[i]);
}
bst.add(1);
System.out.println(bst.contains(7));
System.out.println(bst.contains(4));
System.out.println(bst.contains(11));
}
测试结果

查找bst中的最大最小值
public int maximum() {
if (size == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("bst is empty!");
}
Node maxNode = maximum(root);
return maxNode.val;
}
//找到以root为根节点的BST中的最大值
private Node maximum(Node root) {
if (root.right == null) {
return root;
}
return maximum(root.right);
}
//找到以root为根节点的BST中的最小值
public int minimum() {
if (size == 0) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("bst is empty!");
}
Node minNode = minimum(root);
return minNode.val;
}
private Node minimum(Node root){
if(root.left == null){
return root;
}
return minimum(root.left);
}
测试结果
删除元素
删除最大值
最大值的右孩子为空,则只需要把最大值的左子树连接就好
删除最小值
最小值的左子树为空,则只需要把最小值的右孩子连接就好
//删除最小值节点,并返回其val
public int removeMin() {
int min = minimum();
root = removeMin(root);
return min;
}
//删除当前以root为根节点的bst中的最小值,返回删除后的根节点
private Node removeMin(Node root) {
if (root.left == null) {
//说明此时root为当前bst的最小值
//将右树连接即可
Node right = root.right;
//断开原来的连接
root.right = null;
size--;
return root.right;
}
//连接
root.left = removeMin(root.left);
return root;
}
//删除最大值节点,返回其val
public int removeMax() {
int max = maximum();
root = removeMax(root);
return max;
}
//删除当前以root为根节点的bst中的最大值
private Node removeMax(Node root) {
if (root.right == null) {
//说明此时root为当前bst的最大值,将左树连接即可
Node left = root.left;
//断开原来的连接
root.left = null;
size--;
return left;
}
//连接
root.right = removeMax(root.right);
return root;
}
删除任意节点
1.待删除节点为空
2.待删除节点只有一个孩子(类似于删除最大或最小值)
3.待删除结点有左右孩子
找到待删除节点的前驱节点或者后继节点,让它来代替带删除元素,做删除后的原位置的树根,这个前驱或者后继节点Node一定满足:所有左树节点值<Node<所有右树节点值
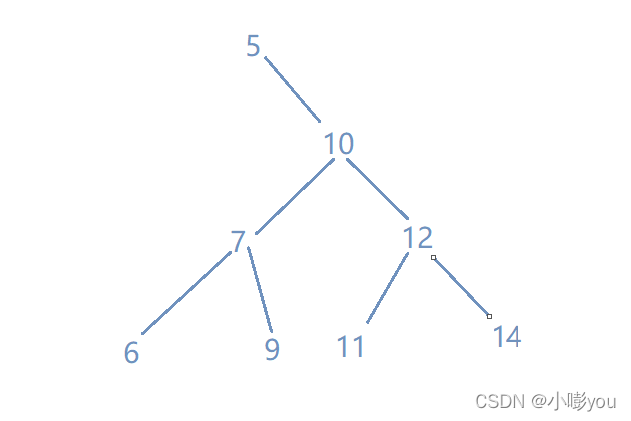
1.先找到10的后继节点11;
2.在右子树中删除最小值11;
3.将10的左子树连接到11的左孩子,11的右子树连接删除后右子树中的最小值;
4.将原来10所有的指向关系断开,返回删除后的新的树根11.
此时11是右子树的最小值,则它小于右子树的所有结点,因为它在右子树,所以它的值大于左子树的所有值。因此选它作为新树根。
删除10之后的BST如图:


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








