简介
原始jdbc操作
1--查询数据

2--插入数据
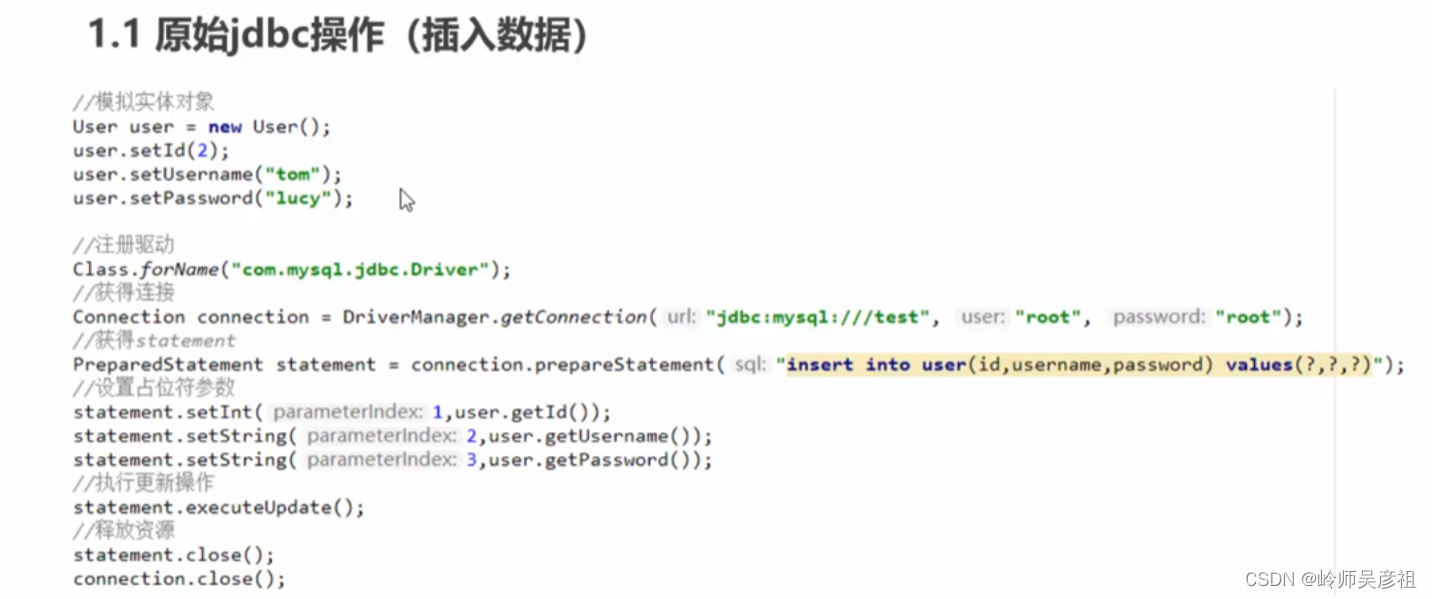
原始jdbc操作的分析:
很多重复代码,变化的,只有sql语句。每次都要创建连接,和关闭资源,比较耗资源。

以上解决方案不会写?不怕,Mybatis就是为了这个而来的
什么是Mybatis?

开发步骤

1--导入坐标
<!--操作dao层必须引入的坐标start-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.4.6</version>
</dependency>
<!--操作dao层必须引入的坐标end-->2--创建数据库表
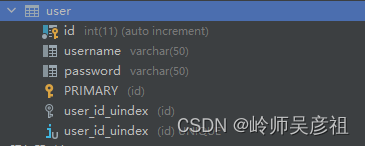
3--创建实体类
@Data
public class User {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
}
4--编写映射文件UserMapper.xml(写sql)
映射文件的约束头:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
例子:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="userMapper" >
<!-- resultType指定查询返回对象的类型 -->
<select id="findAll" resultType="com.example.pojo.User">
select * from user
</select>
</mapper>5--编写核心配置文件SqlMapConfig.xml
Mybatis核心配置文件的约束头:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>例子:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 数据源环境-->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- 加载映射文件-->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper/UserMapper.xml"></mapper>
<!-- <mapper resource="mapper.UserMapper.xml"></mapper> 这里不能用.号分隔 -->
</mappers>
</configuration>6--测试类
public class MybatisTest {
@Test
public void test1() throws IOException {
//获取核心配置文件
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml");
//获取Session工程对象
SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
//获取session会话对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sessionFactory.openSession();
//指定操作,参数:namespace+id
List<User> userList = sqlSession.selectList("userMapper.findAll");
//打印
System.out.println(userList);
//释放资源
sqlSession.close();
}
}MyBatis的映射文件概述

1--查询数据操作
<!-- 查询操作 resultType指定查询返回对象的类型 -->
<select id="findAll" resultType="user">
select * from user
</select>
<!-- 单条件查询操作 resultType指定查询返回对象的类型 -->
<select id="findById" resultType="user">
select * from user where id=#{id}
</select>
<!-- 多条件查询操作 resultType指定查询返回对象的类型 -->
<select id="findBySome" resultType="user">
select * from user where username=#{username} and password=#{password}
</select>2-- 插入数据操作
<!-- 插入操作 #{}里面放的是实体的属性名,不是数据表的字段名-->
<insert id="save" parameterType="user">
insert into user values(#{id},#{username},#{password})
</insert> 3--修改数据操作
3--修改数据操作
<!-- 修改操作-->
<insert id="update" parameterType="com.example.pojo.User">
update user set username=#{username},password=#{password} where id=#{id}
</insert>
4--删除数据操作
<!-- 修改操作 传过来一个参数时,#{}内写任何值都可以 下面用到了别名 int 是java.lang.Integer的别名 -->
<delete id="delete" parameterType="int">
delete from user where id=#{id}
</delete>
5--知识小结

P156
MyBatis核心配置文件的概述
标签定义请求顺序(要遵循,否则报错)
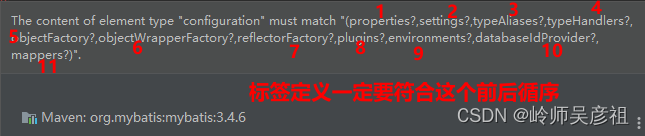
(一)environments标签
1--介绍:


2--模板:
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>(二)mapper标签
1--介绍:

2--模板:
<!-- 加载映射文件(配置sql语句)下面:src/main/resources/mapper/UserMapper.xml-->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper/UserMapper.xml"></mapper>
</mappers>(三)Properties标签
加载一个properties配置文件。

模板:
<!--加载properties文件 jdbc.properties在resource目录下 -->
<properties resource="jdbc.properties"></properties>
<!-- 使用properties文件的数据 数据源环境-->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
(四)typeAliases标签
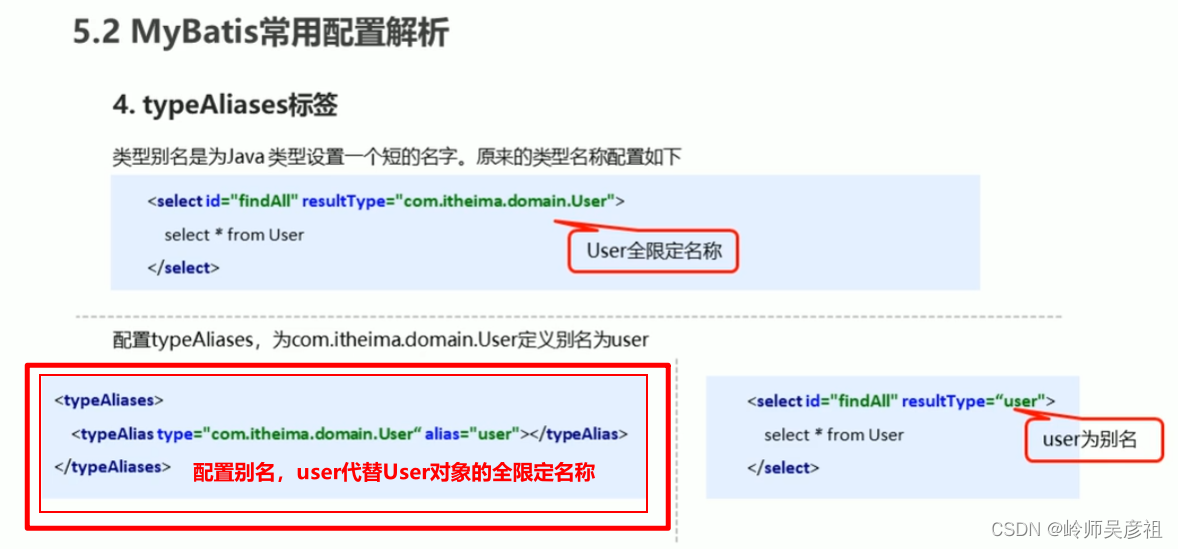
1--现成别名
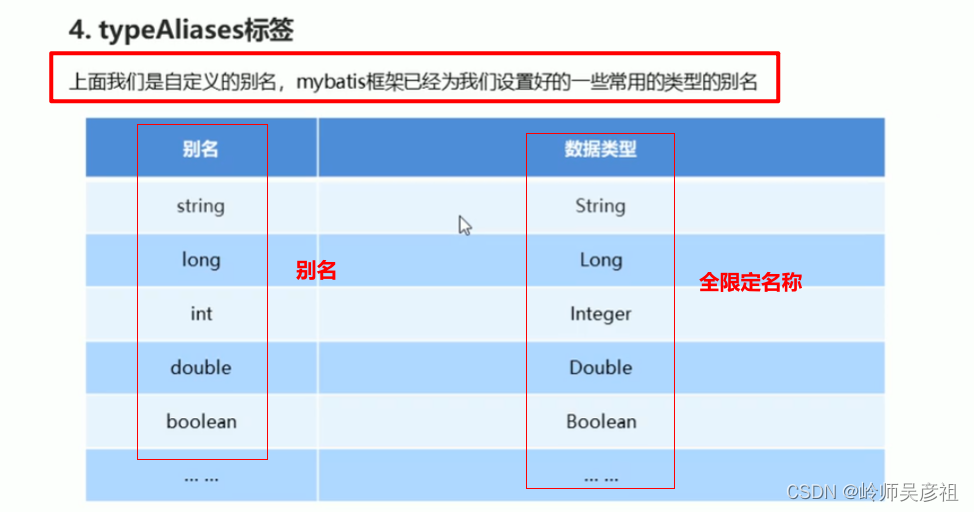
2--自定义别名
注意点:typeAliases标签要在properties后,和environments前声明
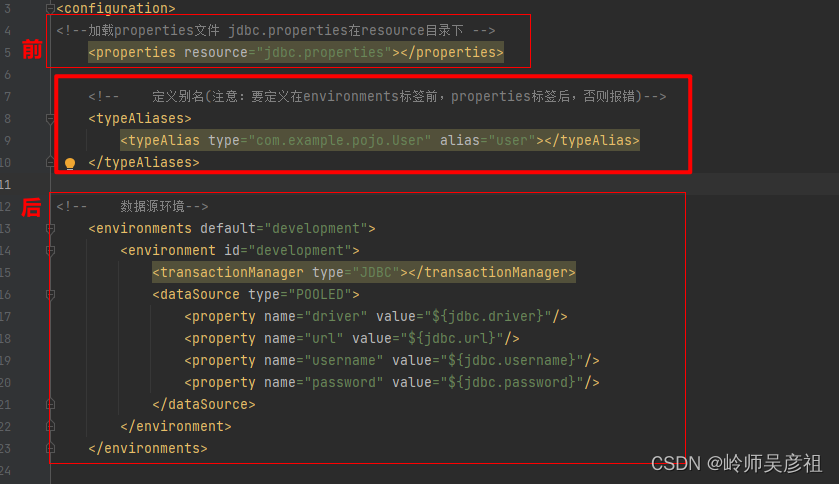
3--模板
<!-- 定义别名(注意:要定义在environments标签前,properties标签后,否则报错)-->
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias type="com.example.pojo.User" alias="user"></typeAlias>
</typeAliases>Mybatis的API
获取工程对象
获取SqlSession对象
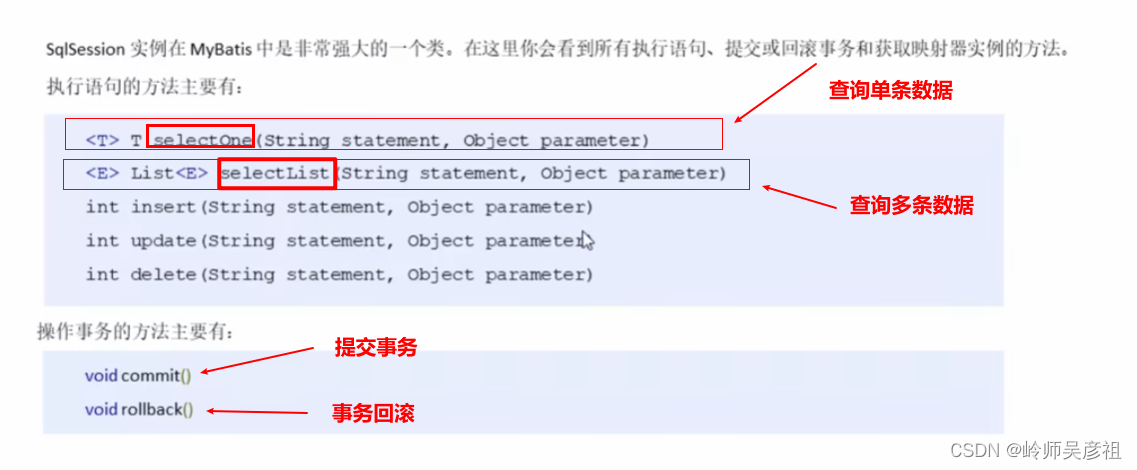
SqlSession会话对象的方法
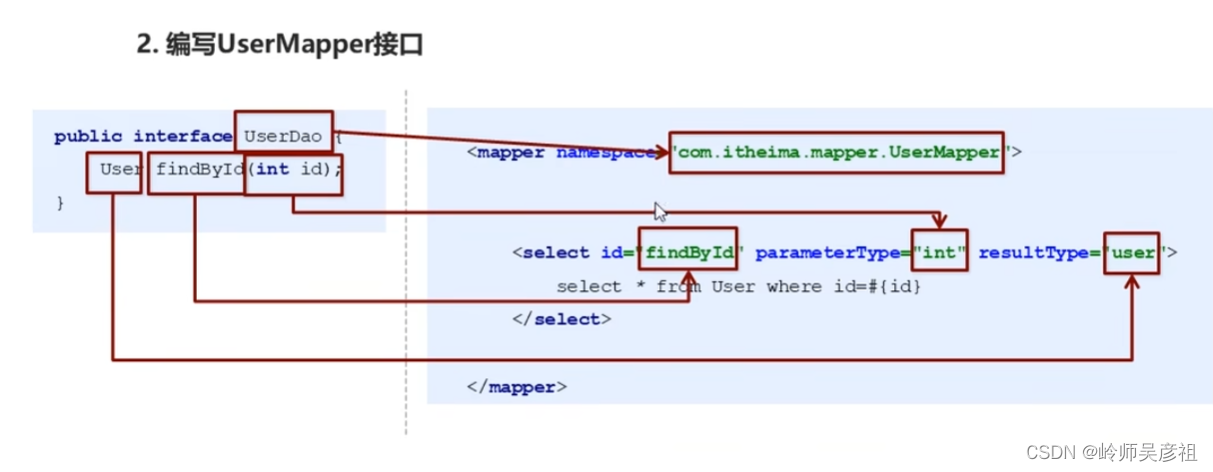
MyBatis的Dao层实现
代理开发方式介绍
通过代理,编写规范的接口,可以让mybatis帮我们实现dao层的实现,不需要手动对dao的接口进行实现。


例子:
Dao层接口:
public interface UserMapper {
public List<User> findAll() throws IOException;
public User findById(int id);
}映射文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.dao.UserMapper" >
<!-- 查询操作 resultType指定查询返回对象的类型 -->
<select id="findAll" resultType="user" >
select * from user
</select>
<!-- 根据id查询 resultType指定查询返回对象的类型 -->
<select id="findById" parameterType="int" resultType="user" >
select * from user where id=#{id}
</select>
</mapper>Service动态代理实现Dao层:
public class ServiceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sessionFactory.openSession(true);
//得到dao层代理对象
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
//执行方法
List<User> userList = mapper.findAll();
System.out.println(userList);
}
@Test
public void test1() throws IOException {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sessionFactory.openSession(true);
//得到dao层代理对象
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
//执行方法
User user = mapper.findById(2);
System.out.println(user);
}
}动态 SQL
语句类型:

if和where语句
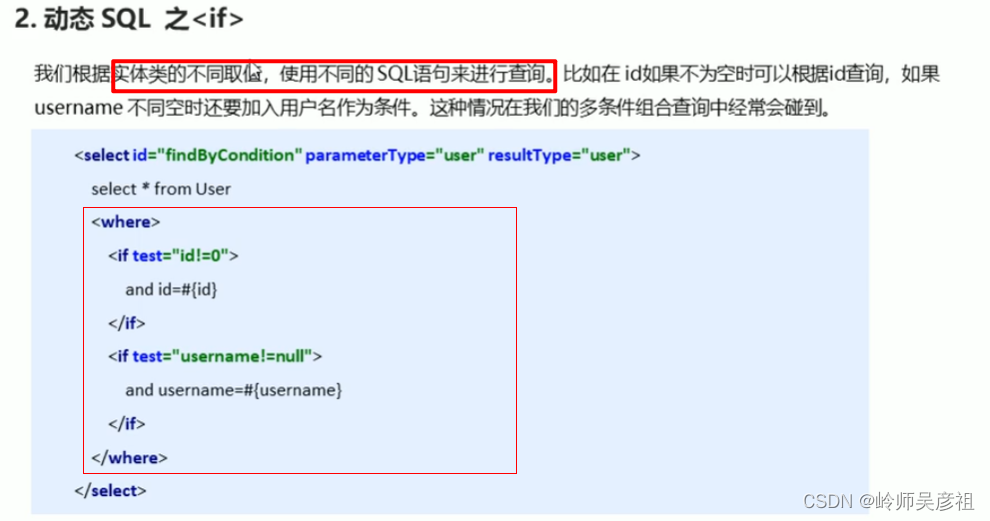
![]()
在<where></where>标签里面添加判断语句,注意的是每个if里面的and不能删掉,因为可能会进行多条件判断,需要and来连接起来。最前面的if中的and,<where>会自动把它去掉

<mapper namespace="com.example.dao.UserMapper">
<select id="findByCondition" parameterType="user" resultType="user">
select * from user
<where>
<if test="id!=0">
and id=#{id}
</if>
<if test="username!=null">
and username=#{username}
</if>
<if test="password!=null">
and passwrod=#{passwrod}
</if>
</where>
</select>
</mapper>foreach语句
(实现了范围比较运算in语句的动态特性)
如果传入参数为数据:collection="array",如果为List集合,则collection="list"
如果为map集合,则collection="map"


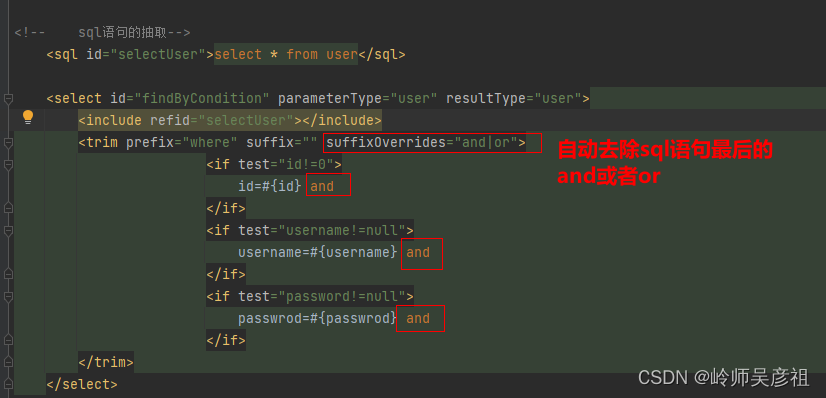
trim语句

choose,when,otherwise语句

choose,when,otherwise三个标签是组合语句,必须一起使用,when相当于if或者elseif,后面接判断语句,otherwise相当于else。
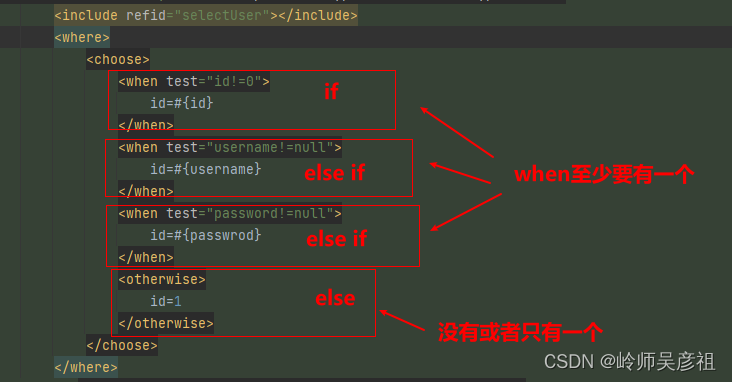
<where>
<choose>#if
<when test="id!=0">#else if
id=#{id}
</when>
<when test="username!=null">#else if
id=#{username}
</when>
<when test="password!=null">#else if
id=#{passwrod}
</when>
<otherwise>#else
id=1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>sql语句的抽取

总结























 540
540











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








