1.Thread.sleep
sleep 设置休眠时间单位是毫秒
public class TestThread01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable mr1=new MyRunnable();
Thread t1=new Thread(mr1,"t1");
t1.start();
Thread t2=new Thread(mr1,"t2");
t2.start();
}
}
class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
String name=Thread.currentThread().getName();
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
System.out.println(name+"\t\t\t"+i);
if(i%10==0){
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}}}}}
2. Thread.yield
public static void yield()
和sleep相似,我们不能进行时间的设置!!!
public class TestThread02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable r=new MyRunnable1();
Thread t1=new Thread(r,"t1");
t1.start();
Thread t2=new Thread(r,"t2");
t2.start();
}
}
class MyRunnable1 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"\t"+i);
if(i%10==0){
Thread.yield();
}
}
}
}3.Thred.join()
当线程可以调用另一个线程的join方法,调用后当前线程会被阻塞不再执行,直到被调用的线程执行完毕,当前线程才会被执行。
public class TestThread03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable mr = new MyRunnable3();
Thread t1 = new Thread(mr,"t1");
t1.start();
try {
t1.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Thread t2 = new Thread(mr,"t2");
t2.start();
System.out.println("---------end");
}
}
class MyRunnable3 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+",,"+i);
}
}
}4.interrupt()的使用,下面例子中当第二个sleep小于等于第一个sleep时候,
因为主线程的sleep小,所以主线程先被唤醒,执行了t1.interrupt(),然后输出的中断。
public class TestThread04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable mr = new MyRunnable04();
Thread t1 = new Thread(mr,"t1");
t1.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(800);/第二个sleep
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
t1.interrupt();
}
}
class MyRunnable04 implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "," + i);
if(i%50==0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);/第一个sleep
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("-----中断------");
break;
}
}}}}5.利用私有属性的set方法去中断Runnable的任务线程
当sleep设置的时间大,就不会中断,因为t1线程会先跑完,再去执行mri1.setFlag();
public class TestThread05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyRunnable05 mr1=new MyRunnable05();
Thread t1=new Thread(mr1,"t1");
t1.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(2);sleep方法
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
mr1.setflag(true);
}
}
class MyRunnable05 implements Runnable{
private boolean flag;
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+","+i);
if(flag){
System.out.println("结束");
break;
}
}
}
public void setflag(boolean flag){
this.flag=flag;
}
}6.下面是为了演示 synchronized的例子,当两个线程作用到一个任务上面,并且牵扯到成员变量num的时候,num的值不一样,明明是独立的线程,产生了数据的混乱。
public class TestThread07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable r = new MyRunnable07();
Thread t1 = new Thread(r,"t1");
t1.start();
Thread t2 = new Thread(r,"t2");
t2.start();
}}
class MyRunnable07 implements Runnable{
private int num=0;
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (this) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
num += i;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+",,"+num);
}
num=0;
}}}
加了synchronized()之后的运行????
public class TestThread07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable r = new MyRunnable07();
Thread t1 = new Thread(r,"t1");
t1.start();
Thread t2 = new Thread(r,"t2");
t2.start();
}
}
class MyRunnable07 implements Runnable{
private int num=0;
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (this) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
num += i;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+",,"+num);
}
num=0;
}
}
}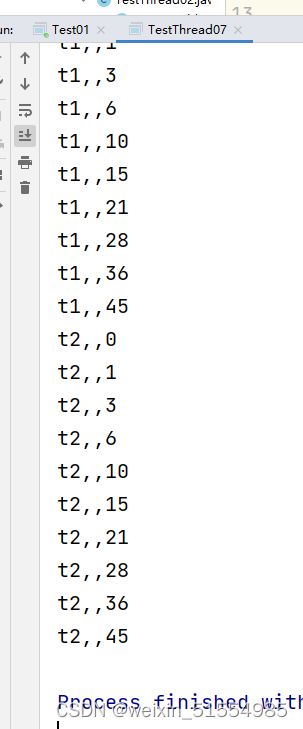
t1会先运行完,t2再运行,有了先后数据,并且 num=0;也将数据清0了。
为什么需要同步?
通过demo06的演示得出结论,代码线程不安全!!! 如何解决 ,采用线程同步,加锁,让改变量不能共享!!!
线程同步: 某一个时刻,允许一个线程来访问共享资源,线程同步是对 对象进行加锁
如果对象中的方法都是同步方法,那么某一时刻只能执行一个方法 采用线程同步就能解决上述问题!






















 1307
1307











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








