技术要求:
- 技术栈: (1)java+mysql+反射+自定义注解+泛型+jdbc.
- 持久层框架: 与数据库交互的一层称为持久层(dao)。完成orm操作。
- o:(Object对象) r:(relative关系) m:(mapping映射)。 实体类---数据库表 属性--表的字段 实体类对象--一条记录 集合---表中多条记录。
- 手撕持久层框架: 自己编写持久层框架 可以完成无需写sql语句即可完成对单表的CRUD操作。
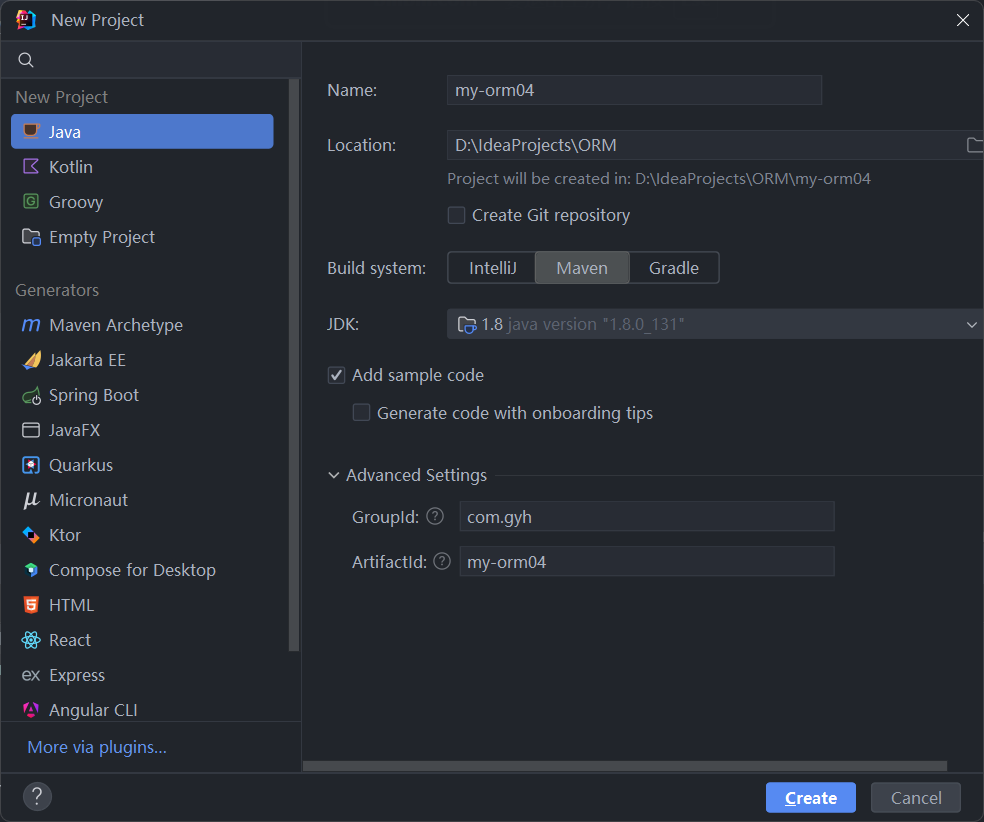
一、创建一个空的 maven 工程 及引入 相关的依赖
二、pom 的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.33</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.16</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.28</version>
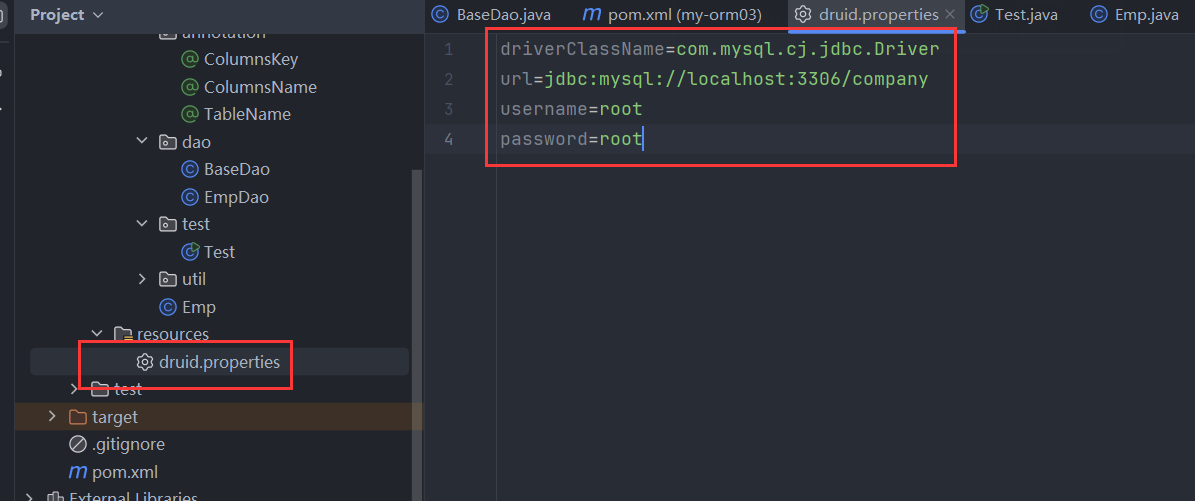
</dependency>三、创建数据源的属性文件
四、创建 DbUtil 工具类(用于连接数据库)【这里使用静态方法方便在 dao 中直接调用】
public class DbUntil {
/**
* 数据源实例,用于获取数据库连接。
*/
private static final DataSource dataSource;
static {
// 加载druid配置文件
Properties props = new Properties();
InputStream inputStream = DbUntil.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("druid.properties");
try {
props.load(inputStream);
// 根据配置文件创建Druid数据源实例
dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(props);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 配置文件加载或数据源创建失败时,抛出运行时异常
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
/**
* 获取数据库连接。
*
* @return 数据库连接
*/
public static Connection getConnection(){
try {
// 从数据源获取连接
return dataSource.getConnection();
} catch (Exception e) {
// 获取连接失败时,抛出运行时异常
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
/**
* 关闭数据库连接和相关资源。
*/
public static void close(Connection connection, PreparedStatement ps, ResultSet...rs){
try {
// 检查并关闭数据库连接
if(connection != null){
connection.close();
}
// 检查并关闭PreparedStatement
if(ps != null){
ps.close();
}
// 遍历并关闭所有的ResultSet实例
for (ResultSet resultSet : rs) {
if(resultSet != null){
resultSet.close();
}
}
}catch (Exception e) {
// 捕获并抛出运行时异常,以便调用者可以对其进行适当处理
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}五、操作
1、通用的添加操作
/**
* 插入数据方法
* 通过反射机制获取对象的字段信息,构建SQL语句,然后执行SQL语句插入数据。
*
* @param t 要插入的数据对象
* @return 执行SQL语句的结果
*/
public int insert(T t) {
// 构建SQL语句的起始部分
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("insert into ");
// 这里掉用封装好的 获取表名方法
sb.append(getTableName()+" ");
// 用于存储字段名和字段值的列表
ArrayList<String> fields = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> values = new ArrayList<>();
// 获取当前类的所有字段
Field[] declaredFields = tClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field f : declaredFields){
// 设置字段可访问
f.setAccessible(true);
// 跳过注有ColumnsKey注解的字段
if (f.getAnnotation(ColumnsKey.class) != null){
continue;
}
// 处理字段名,优先使用ColumnsName注解指定的字段名,否则使用字段本身的名称
if (f.getAnnotation(ColumnsName.class) != null){
fields.add(f.getAnnotation(ColumnsName.class).value());
}else {
fields.add(f.getName());
}
try {
// 将字段值转换为字符串形式,并添加到values列表中
values.add("'"+f.get(t).toString()+"'");
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
// 抛出运行时异常
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
// 将字段名和字段值列表转换为SQL语句中的格式
sb.append(fields.toString().replace("[","(").replace("]", ")"));
sb.append(" values ");
sb.append(values.toString().replace("[","(").replace("]", ")"));
// 输出构建的SQL语句
System.out.println(sb);
// 执行SQL语句,并返回执行结果
return executeSql(sb.toString());
} // 获取表名 这里使用的构造方法 不用传入 t 对象即可 获取到表名
private String getTableName(){
// 尝试获取tClass上的TableName注解,如果存在则返回注解中的表名
TableName annotation = tClass.getAnnotation(TableName.class);
if (annotation != null){
return annotation.value();
}else {
// 如果没有TableName注解,则返回类的简单类名作为表名
return tClass.getSimpleName();
}
}
// 执行 sql 语句
private int executeSql(String sql){
Connection connection = DbUntil.getConnection();
try {
PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
return ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}2、通用的修改操作
public int update(T t) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("update ");
sb.append(getTableName()+" ");
sb.append("set ");
String key = null;
String value = null;
Field[] declaredFields = tClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field f : declaredFields){
f.setAccessible(true);
if (f.getAnnotation(ColumnsKey.class) != null){
key = f.getAnnotation(ColumnsKey.class).value();
try {
value = f.get(t).toString();
}catch (Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
continue;
}
if(f.getAnnotation(ColumnsName.class) != null){
try {
sb.append(f.getAnnotation(ColumnsName.class).value()+" = '"+f.get(t)+"',");
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}else {
try {
sb.append(f.getName()+" = '"+f.get(t)+"',");
}catch (IllegalAccessException e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
System.out.println(sb);
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length()-1);
sb.append(" where ");
sb.append(key+" = '"+value+"'");
System.out.println(sb);
return executeSql(sb.toString());
}3、通用的删除操作
public int delete(int id) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("delete from ");
sb.append(getTableName()+" ");
sb.append("where ");
Field[] declaredFields = tClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field f : declaredFields){
f.setAccessible(true);
if (f.getAnnotation(ColumnsKey.class) != null){
try {
sb.append(f.getName()+" = "+id);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
System.out.println(sb);
return executeSql(sb.toString());
}4、通用的查询全部操作
// 查询全部的方法
public List<T> select(){
try {
// 这使用一个查询的工具类
return selectUtil();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}5、通用的查询单条数据操作
// 条件查询啊全部的方法
public T selectById(int id) {
try {
T t = tClass.newInstance();
List<T> ts = selectUtil(id);
for (T t1 :ts){
t=t1;
}
return t;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}上面查询单条和多条数据都使用了一个工具方法
// 查询 单条数据和 多条数据的 工具方法
private List<T> selectUtil(Integer... id){
StringBuilder sql = new StringBuilder("select * from ");
// 获取 表名
sql.append(getTableName());
if (id != null && id.length > 0){
sql.append(" where ");
Field[] fields = tClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field f : fields){
f.setAccessible(true);
if (f.getAnnotation(ColumnsKey.class) != null){
sql.append(f.getName()+"='" + id[0] + "'");
}
}
}
ResultSet resultSet = null;
Connection connection = DbUntil.getConnection();
PreparedStatement ps = null;
// 用于存放结果的集合
List<T> list = new ArrayList<>();
try {
ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql.toString());
resultSet = ps.executeQuery();
// 结果 循环 遍历装入到 集合中
while (resultSet.next()){
T tt = (T) tClass.newInstance();
Field[] declaredFields = tClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field f : declaredFields){
if (f.getAnnotation(ColumnsKey.class) != null){
String value = f.getAnnotation(ColumnsKey.class).value();
f.setAccessible(true);
f.set(tt,resultSet.getObject(value));
}else {
if (f.getAnnotation(ColumnsName.class) != null){
String value = f.getAnnotation(ColumnsName.class).value();
f.setAccessible(true);
f.set(tt,resultSet.getObject(value));
}else {
f.setAccessible(true);
f.set(tt,resultSet.getObject(f.getName()));
}
}
}
list.add(tt);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
DbUntil.close(connection, ps, resultSet);
}
return list;
}思想:
通过是否传入参数来区别 是 查询全部 还是单条数据 这里 七 八 可以看成是一个中转的方法,来限制使用者只能选择传入一个 参数 或 使用查询全部的方法 并将此工具方法 私有化 使其不能被 继承






















 670
670











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








