GCD算法
使用辗转相除法
python:
def gcd(a,b):
if b==0:
return a
else:
return gcd(b,a%b)
EGCD算法
常使用EGCD求 c 1 , c 2 c1,c2 c1,c2在 以对方为模数 M o d Mod Mod 时的乘法逆元
python:
版本1:手动算法的递归
根据手动算法的方式实现
{
a
1
∗
x
+
b
1
∗
y
=
c
1
a
2
∗
x
+
b
2
∗
y
=
c
2
\begin{cases} a1*x+b1*y=c1 \\a2*x+b2*y=c2\end{cases}
{a1∗x+b1∗y=c1a2∗x+b2∗y=c2
当c2==1时,结束递归
def egcd1(c1, c2, a1=1, b1=0, a2=0, b2=1):
if c2 == 1:
return a2, b2
else:
times = c1//c2
return egcd1(c2, c1 % c2, a2, b2, a1-a2*times, b1-b2*times)
版本2:循环版本,输出中间过程:
输出中间过程(while循环)
def egcd2(c1,c2):
检查 c1、c2 是否互素
g=gcd(c1,c2)
if g!=1:
print("The gcd of numbers is not 1,but",g)
return 0,0
last=[1,0,c1]
now=[0,1,c2]
print("{:5}x+({:5})y = {:5}".format(last[0],last[1],last[2]))
while(now[2]!=1):
times=last[2]//now[2]
print("{:5}x+({:5})y = {:5}\t\t{}".format(now[0],now[1],now[2],times))
转移
tmp=[]
for i in now:
tmp.append(i)
now[0]=last[0]-now[0]*times
now[1]=last[1]-now[1]*times
now[2]=last[2]%now[2]
last=tmp
print("{:5}x+({:5})y = {:5}".format(now[0],now[1],now[2]))
如果结果小于0,返回大于0的值
return now[0]%c2 ,now[1]%c1
测试程序:
if __name__ == "__main__":
a,b=egcd2(262,57)
print(a,b)
运行结果:
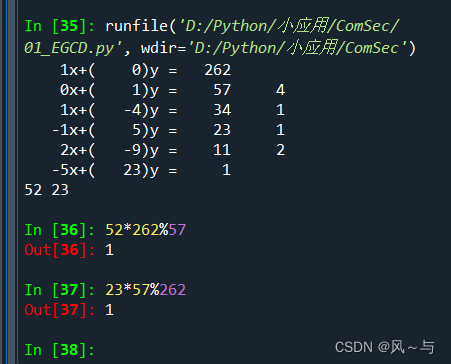
版本3:简化后的递归版本:
经过简化,只关注等式的右边,直接获取结果。
return返回的是第二条等式的2个参数
a
2
,
b
2
a2,b2
a2,b2
def egcd(a, b):
if b == 0:
return 1, 0
else:
x, y = egcd(b, a % b)
return y, x-a//b*y
C:
A B 作为计算结果 通过形参的值传递传出
其他参数对应手工计算时的系数:
{
a
1
∗
x
+
b
1
∗
y
=
c
1
a
2
∗
x
+
b
2
∗
y
=
c
2
\begin{cases} a1*x+b1*y=c1 \\a2*x+b2*y=c2\end{cases}
{a1∗x+b1∗y=c1a2∗x+b2∗y=c2
版本1:递归版本,直接输出结果
void egcd(LL& A, LL& B, LL c1, LL c2, LL a1 = 1,
LL b1 = 0, LL a2 = 0, LL b2 = 1) {
if (c2 == 1) {
A = a2;
B = b2;
return;
} else {
LL time = c1 / c2;
egcd(A, B, c2, c1 % c2, a2, b2, a1 - a2 * time, b1 - b2 * time);
// printf("%5lldx + (%5lld)y = %5lld\t %5lld\n", a2, b2, x % y,times);
return;
}
}
版本2:循环版本,输出中间过程
与Python的循环版本类似
void egcd1(LL& A, LL& B, LL c1, LL c2) {
LL last[3] = {1, 0, c1};
LL now[3] = {0, 1, c2};
while (now[2] != 1) {
LL times = last[2] / now[2];
LL tmp[3] = {};
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
tmp[i] = now[i];
now[0] = last[0] - now[0] * times;
now[1] = last[1] - now[1] * times;
now[2] = last[2] % now[2];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
last[i] = tmp[i];
printf("%5lldx+(%5lld)y=%5lld\t%5lld\n", now[0], now[1], now[2], times);
}
A = now[0];
B = now[1];
}
测试程序:
int main() {
LL a = 0, b = 0;
LL X = 0, Y = 0;
printf("Input The Two Numbers:");
scanf("%lld %lld", &X, &Y);
egcd1(a, b, X, Y);
printf("X=%5lld Y=%5lld\n", X, Y);
printf("a=%5lld b=%5lld\n", a, b);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
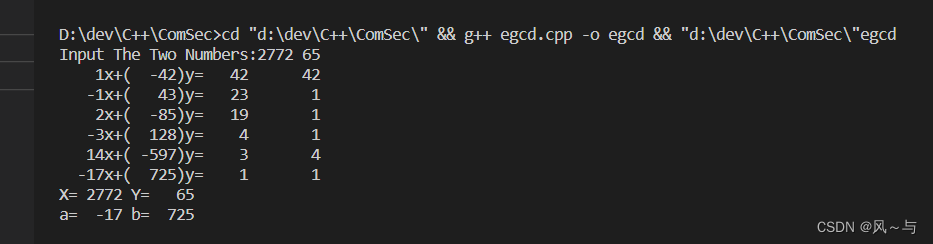






















 9274
9274











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








