函数(1):Scala数组常用函数(1)_后季暖的博客-CSDN博客
目录
四十六.-def isTraversableAgain: Boolean
四十七.-def iterator: collection.Iterator[T]
四十九.-def lastIndexOf(elem: T): Int
五十.-def lastIndexOf(elem: T, end: Int): Int
五十一.-def lastIndexOfSlice[B >: A](that: GenSeq[B]): Int
五十二.-def lastIndexOfSlice[B >: A](that: GenSeq[B], end: Int): Int
五十三.-def lastIndexWhere(p: (T) ⇒ Boolean): Int
五十四.-def lastOption: Option[T]
五十六.-def lengthCompare(len: Int): Int
五十八.-def minBy[B](f: (A) ⇒ B): A
六十.-def padTo(len: Int, elem: A): Array[A]
六十二.-def partition(p: (T) ⇒ Boolean): (Array[T], Array[T])
六十三.-def patch(from: Int, that: GenSeq[A], replaced: Int): Array[A]
六十四.-def permutations: collection.Iterator[Array[T]]
六十五.-def prefixLength(p: (T) ⇒ Boolean): Int
六十七.-def reduce[A1 >: A](op: (A1, A1) ⇒ A1): A1
六十七.-def reduceLeft[B >: A](op: (B, T) ⇒ B): B
-def reduceRight[B >: A](op: (T, B) ⇒ B): B
-def reduceLeftOption[B >: A](op: (B, T) ⇒ B): Option[B]
-def reduceRightOption[B >: A](op: (T, B) ⇒ B): Option[B]
六十九.-def reverseIterator: collection.Iterator[T]
七十.-def reverseMap[B](f: (A) ⇒ B): Array[B]
七十一.-def sameElements(that: GenIterable[A]): Boolean
-def scanLeft[B, That](z: B)(op: (B, T) ⇒ B)(implicit bf: CanBuildFrom[Array[T], B, That]): That
-def scanRight[B, That](z: B)(op: (T, B) ⇒ B)(implicit bf: CanBuildFrom[Array[T], B, That]): That
七十三.-def segmentLength(p: (T) ⇒ Boolean, from: Int): Int
七十四.-def seq: collection.mutable.IndexedSeq[T]
七十五.-def slice(from: Int, until: Int): Array[T]
七十六.-def sliding(size: Int): collection.Iterator[Array[T]]
-def sliding(size: Int, step: Int): collection.Iterator[Array[T]]
七十七.-def sortBy[B](f: (T) ⇒ B)(implicit ord: math.Ordering[B]): Array[T]
七十八.-def sortWith(lt: (T, T) ⇒ Boolean): Array[T]
七十九.-def sorted[B >: A](implicit ord: math.Ordering[B]): Array[T]
八十.-def span(p: (T) ⇒ Boolean): (Array[T], Array[T])
八十一.-def splitAt(n: Int): (Array[T], Array[T])
八十二.-def startsWith[B](that: GenSeq[B], offset: Int): Boolean
-def startsWith[B](that: GenSeq[B]): Boolean
八十三.-def subSequence(start: Int, end: Int): CharSequence
八十六.-def take(n: Int): Array[T]
八十七.-def takeRight(n: Int): Array[T]
八十八.-def takeWhile(p: (T) ⇒ Boolean): Array[T]
-def toBuffer[A1 >: A]: Buffer[A1]
-def toIndexedSeq: collection.immutable.IndexedSeq[T]
-def toIterable: collection.Iterable[T]
-def toIterator: collection.Iterator[T]
-def toStream: collection.immutable.Stream[T]
九十.-def transpose[U](implicit asArray: (T) ⇒ Array[U]): Array[Array[U]]
九十一.-def union(that: collection.Seq[T]): Array[T]
九十三.-def update(i: Int, x: T): Unit
九十四.-def view(from: Int, until: Int): IndexedSeqView[T, Array[T]]
九十五.-def withFilter(p: (T) ⇒ Boolean): FilterMonadic[T, Array[T]]
九十六.-def zip[B](that: GenIterable[B]): Array[(A, B)]
九十七.-def zipAll[B](that: collection.Iterable[B], thisElem: A, thatElem: B): Array[(A, B)]
九十八.-def zipWithIndex: Array[(A, Int)]
四十六.-def isTraversableAgain: Boolean
判断序列是否可以反复遍历,该方法是GenTraversableOnce中的方法,对于 Traversables 一般返回true,对于 Iterators 返回 false,除非被复写
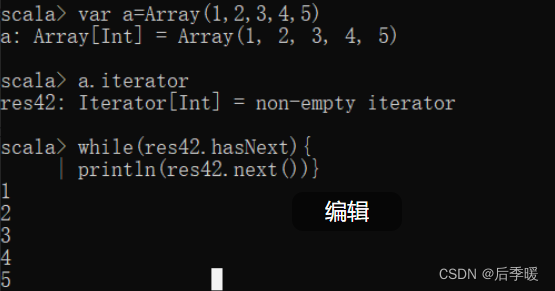
四十七.-def iterator: collection.Iterator[T]
对序列中的每个元素产生一个 iterator 该迭代器只能迭代一次 下一次需要重新定义迭代器
四十八.-def last: T
取得序列中最后一个元素

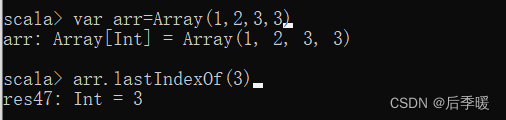
四十九.-def lastIndexOf(elem: T): Int
取得序列中最后一个等于 elem 的元素的位置
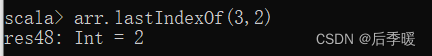
五十.-def lastIndexOf(elem: T, end: Int): Int
取得序列中最后一个等于 elem 的元素的位置,可以指定在 end 之前(包括)的元素中查找
前面的indexOf方法 两个参数 第二参数是从哪开始找 和这边不一样!
五十一.-def lastIndexOfSlice[B >: A](that: GenSeq[B]): Int
判断当前序列中是否包含序列 that,并返回最后一次出现该序列的位置处的索引
val a = Array(1, 4, 2, 3, 4, 5, 1, 4)
val b = Array(1, 4)
println(a.lastIndexOfSlice(b)) // return 6五十二.-def lastIndexOfSlice[B >: A](that: GenSeq[B], end: Int): Int
val a = Array(1, 4, 2, 3, 4, 5, 1, 4)
val b = Array(1, 4)
println(a.lastIndexOfSlice(b,4)) // return 0五十三.-def lastIndexWhere(p: (T) ⇒ Boolean): Int
返回当前序列中最后一个满足条件 p 的元素的索引
val a = Array(1, 4, 2, 3, 4, 5, 1, 4)
val b = Array(1, 4)
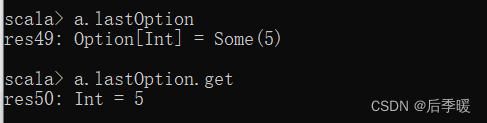
println(a.lastIndexWhere( {x:Int => x<2})) // return 6五十四.-def lastOption: Option[T]
返回当前序列中最后一个对象
五十五.-def length: Int
-def size: Int
都是返回长度
五十六.-def lengthCompare(len: Int): Int
就是返回两个序列长度的差值 如果小于括号里的序列则返回负数

五十七.-def max: A
返回序列中最大的元素
五十八.-def minBy[B](f: (A) ⇒ B): A
-def maxBy[B](f: (A) ⇒ B): A
找出符合条件的集合中的最大值和最小值
val map = Map[String,Int]("a"->10, "b"->99 , "c"->88)
// map默认按照key排序获取最大和最小数据
// 指定map排序 按照value排序
map.maxBy(x=>x._2) //(b,99)
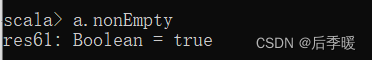
map.minBy(x=>x._2) //(a,10)五十九.-def nonEmpty: Boolean
判断序列不是空
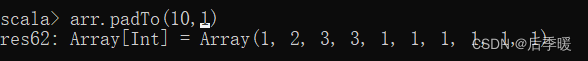
六十.-def padTo(len: Int, elem: A): Array[A]
后补齐序列,如果当前序列长度小于 len,那么新产生的序列长度是 len,多出的几个位值填充 elem,如果当前序列大于等于 len ,则返回当前序列
六十一.-def par: ParArray[T]
返回一个并行实现,产生的并行序列,不能被修改
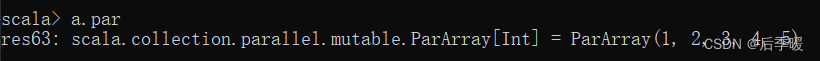
六十二.-def partition(p: (T) ⇒ Boolean): (Array[T], Array[T])
按条件将序列拆分成两个新的序列,满足条件的放到第一个序列中,其余的放到第二个序列
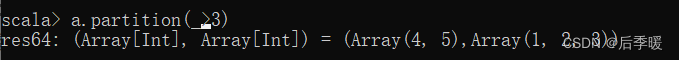
六十三.-def patch(from: Int, that: GenSeq[A], replaced: Int): Array[A]
批量替换,从原序列的 from 处开始,后面的 replaced 数量个元素,将被替换成序列 that
val a = Array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
val b = Array(3, 4, 6)
val c = a.patch(1,b,2)
println(c.mkString(",")) // return 1,3,4,6,4,5
/**从 a 的第二个元素开始,取两个元素,即 2和3 ,这两个元素被替换为 b的内容*/六十四.-def permutations: collection.Iterator[Array[T]]
排列组合,他与combinations不同的是,组合中的内容可以相同,但是顺序不能相同,combinations不允许包含的内容相同,即使顺序不一样
val a = Array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
val b = a.permutations.toList // b 中将有120个结果,知道排列组合公式的,应该不难理解吧
/**如果是combinations*/
val b = a.combinations(5).toList // b 中只有一个,因为不管怎样排列,都是这5个数字组成,所以只能保留第一个六十五.-def prefixLength(p: (T) ⇒ Boolean): Int
给定一个条件 p,返回一个前置数列的长度,这个数列中的元素都满足 p
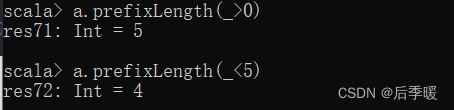
六十六.-def product: A
返回所有元素乘积的值
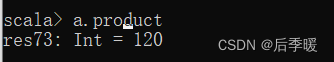
六十七.-def reduce[A1 >: A](op: (A1, A1) ⇒ A1): A1
同 fold,不需要初始值
(1 to 9).reduceLeft( _ * _) //相当于1 * 2 * 3 * 4 * 5 * 6 * 7 * 8 * 9
(1 to 9).reduceLeft( _ + _) //相当于1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 + 9
(1 to 9).reduce(_ + _) //默认是reduceLeft
六十七.-def reduceLeft[B >: A](op: (B, T) ⇒ B): B
从左向右计算
-def reduceRight[B >: A](op: (T, B) ⇒ B): B
从右向左计算
-def reduceLeftOption[B >: A](op: (B, T) ⇒ B): Option[B]
计算Option,参考reduceLeft
-def reduceRightOption[B >: A](op: (T, B) ⇒ B): Option[B]
计算Option,参考reduceRight

六十八.-def reverse: Array[T]
反转序列
六十九.-def reverseIterator: collection.Iterator[T]
反向生成迭代
七十.-def reverseMap[B](f: (A) ⇒ B): Array[B]
同 map 方向相反
val a = Array(1,2,3,4,5)
val b = a.reverseMap( {x:Int => x*10} )
println(b.mkString(",")) // 50,40,30,20,10七十一.-def sameElements(that: GenIterable[A]): Boolean
判断两个序列是否顺序和对应位置上的元素都一样
val a = Array(1,2,3,4,5)
val b = Array(1,2,3,4,5)
println(a.sameElements(b)) // true
val c = Array(1,2,3,5,4)
println(a.sameElements(c)) // false七十二.-def scan[B >: A, That](z: B)(op: (B, B) ⇒ B)(implicit cbf: CanBuildFrom[Array[T], B, That]): That
用法同 fold,scan会把每一步的计算结果放到一个新的集合中返回,而 fold 返回的是单一的值
val a = Array(1,2,3,4,5)
val b = a.scan(5)(seqno)
println(b.mkString(",")) // 5,6,8,11,15,20-def scanLeft[B, That](z: B)(op: (B, T) ⇒ B)(implicit bf: CanBuildFrom[Array[T], B, That]): That
从左向右计算
-def scanRight[B, That](z: B)(op: (T, B) ⇒ B)(implicit bf: CanBuildFrom[Array[T], B, That]): That
从右向左计算
七十三.-def segmentLength(p: (T) ⇒ Boolean, from: Int): Int
从序列的 from 处开始向后查找,所有第一个满足 p 的条件的连续元素的长度
val a = Array(1,2,3,1,1,1,1,1,4,5)
val b = a.segmentLength( {x:Int => x < 3},3) // 5七十四.-def seq: collection.mutable.IndexedSeq[T]
产生一个引用当前序列的 sequential 视图

七十五.-def slice(from: Int, until: Int): Array[T]
取出当前序列中,from 到 until 之间的片段
val a = Array(1,2,3,4,5)
val b = a.slice(1,3)
println(b.mkString(",")) // 2,3七十六.-def sliding(size: Int): collection.Iterator[Array[T]]
从第一个元素开始,每个元素和它后面的 size - 1 个元素组成一个数组,最终组成一个新的集合返回,当剩余元素不够 size 数,则停止(每次切三个)
val a = Array(1,2,3,4,5)
val b = a.sliding(3).toList
for(i<-0 to b.length - 1){
val s = "第%d个:%s"
println(s.format(i,b(i).mkString(",")))
}
/**
第0个:1,2,3
第1个:2,3,4
第2个:3,4,5
*/-def sliding(size: Int, step: Int): collection.Iterator[Array[T]]
从第一个元素开始,每个元素和它后面的 size - 1 个元素组成一个数组,最终组成一个新的集合返回,当剩余元素不够 size 数,则停止
该方法,可以设置步进 step,第一个元素组合完后,下一个从 上一个元素位置+step后的位置处的元素开始
val a = Array(1,2,3,4,5)
val b = a.sliding(3,2).toList //第一个从1开始, 第二个从3开始,因为步进是 2
for(i<-0 to b.length - 1){
val s = "第%d个:%s"
println(s.format(i,b(i).mkString(",")))
}
/**
第0个:1,2,3
第1个:3,4,5
*/七十七.-def sortBy[B](f: (T) ⇒ B)(implicit ord: math.Ordering[B]): Array[T]
按指定的排序规则排序

七十八.-def sortWith(lt: (T, T) ⇒ Boolean): Array[T]
自定义排序方法 lt
val a = Array(3,2,1,4,5)
val b = a.sortWith(_.compareTo(_) > 0) // 大数在前
println(b.mkString(",")) // 5,4,3,2,1七十九.-def sorted[B >: A](implicit ord: math.Ordering[B]): Array[T]
使用默认的排序规则对序列排序
val a = Array(3,2,1,4,5)
val b = a.sorted
println(b.mkString(",")) // 1,2,3,4,5八十.-def span(p: (T) ⇒ Boolean): (Array[T], Array[T])
分割序列为两个集合,从第一个元素开始,直到找到第一个不满足条件的元素止,之前的元素放到第一个集合,其它的放到第二个集合
和partition不一样 partition是每个元素都和条件比较 这个是从第一个开始比较 不满足就结束
和prefixLength有点类似 但是prefixLength返回的是满足的长度(从第一个开始) 而不是分组
takeWhile也是从第一个开始 满足条件的取出来
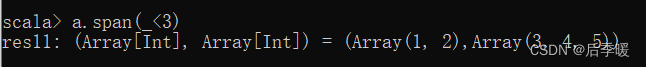
八十一.-def splitAt(n: Int): (Array[T], Array[T])
从指定位置开始,把序列拆分成两个集合
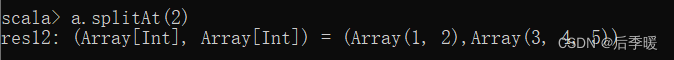
八十二.-def startsWith[B](that: GenSeq[B], offset: Int): Boolean
从指定偏移处,是否以某个序列开始

-def startsWith[B](that: GenSeq[B]): Boolean
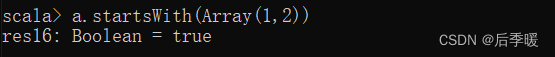
八十三.-def subSequence(start: Int, end: Int): CharSequence
返回 start 和 end 间的字符序列 前闭后开
val chars = Array('a','b','c','d')
val b = chars.subSequence(1,3)
println(b.toString) // bc八十四.-def sum: A
序列求和,元素需为Numeric[T]类型
val a = Array(1,2,3,4,5)
val b = a.sum // 15八十五.-def tail: Array[T]
返回除了当前序列第一个元素的其它元素组成的序列
val a = Array(1,2,3,4,5)
val b = a.tail // 2,3,4,5八十六.-def take(n: Int): Array[T]
返回当前序列中前 n 个元素组成的序列
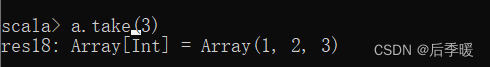
八十七.-def takeRight(n: Int): Array[T]
返回当前序列中,从右边开始,选择 n 个元素组成的序列

八十八.-def takeWhile(p: (T) ⇒ Boolean): Array[T]
返回当前序列中,从第一个元素开始,满足条件的连续元素组成的序列
span是返回两个序列 这边是返回一个

八十九.转换函数
-def toArray: Array[A]
转换成 Array 类型
-def toBuffer[A1 >: A]: Buffer[A1]
转换成 Buffer 类型
-def toIndexedSeq: collection.immutable.IndexedSeq[T]
转换成 IndexedSeq 类型
-def toIterable: collection.Iterable[T]
转换成可迭代的类型
-def toIterator: collection.Iterator[T]
同 iterator 方法
-def toList: List[T]
同 List 类型
-def toMap[T, U]: Map[T, U]
同 Map 类型,需要被转化序列中包含的元素是Tuple2 类型数据
val chars = Array(("a","b"),("c","d"),("e","f"))
val b = chars.toMap
println(b) //Map(a -> b, c -> d, e -> f)-def toSeq: collection.Seq[T]
同 Seq 类型
-def toSet[B >: A]: Set[B]
同 Set 类型
-def toStream: collection.immutable.Stream[T]
同 Stream 类型
-def toVector: Vector[T]
同 Vector 类型
九十.-def transpose[U](implicit asArray: (T) ⇒ Array[U]): Array[Array[U]]
矩阵转换,二维数组行列转换

九十一.-def union(that: collection.Seq[T]): Array[T]
联合两个序列,同操作符 ++
九十二.-def unzip[T1, T2](implicit asPair: (T) ⇒ (T1, T2), ct1: ClassTag[T1], ct2: ClassTag[T2]): (Array[T1], Array[T2])
将数组元素是两个元素的这种数组,把它们的第一个元素取出组成一个序列,第二个元素组成一个序列

-def unzip3[T1, T2, T3](implicit asTriple: (T) ⇒ (T1, T2, T3), ct1: ClassTag[T1], ct2: ClassTag[T2], ct3: ClassTag[T3]): (Array[T1], Array[T2], Array[T3])
将数组元素是三个元素的这种数组,第一个元素都取出组成一个序列,第二个元素组成一个序列,第三个元素组成一个序列
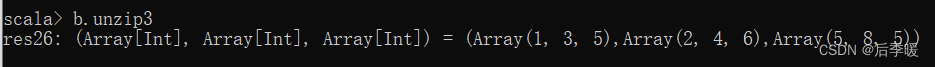
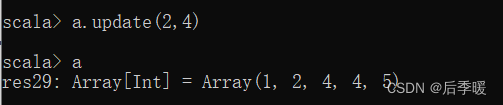
九十三.-def update(i: Int, x: T): Unit
九十四.-def view(from: Int, until: Int): IndexedSeqView[T, Array[T]]
返回 from 到 until 间的序列,不包括 until 处的元素
val a = Array(1,2,3,4,5)
val b = a.view(1,3)
println(b.mkString(",")) //2,3九十五.-def withFilter(p: (T) ⇒ Boolean): FilterMonadic[T, Array[T]]
根据条件 p 过滤元素

九十六.-def zip[B](that: GenIterable[B]): Array[(A, B)]
val a = Array(1,2,3,4,5)
val b = Array(5,4,3,2,1)
val c = a.zip(b)
println(c.mkString(",")) //(1,5),(2,4),(3,3),(4,2),(5,1)九十七.-def zipAll[B](that: collection.Iterable[B], thisElem: A, thatElem: B): Array[(A, B)]
同 zip ,但是允许两个序列长度不一样,不足的自动填充,如果当前序列端,空出的填充为 thisElem,如果 that 短,填充为 thatElem
后面的短填充后面那个参数 前面的短填充前面的参数
val a = Array(1,2,3,4,5,6,7)
val b = Array(5,4,3,2,1)
val c = a.zipAll(b,9,8) //(1,5),(2,4),(3,3),(4,2),(5,1),(6,8),(7,8)
val a = Array(1,2,3,4)
val b = Array(5,4,3,2,1)
val c = a.zipAll(b,9,8) //(1,5),(2,4),(3,3),(4,2),(9,1)九十八.-def zipWithIndex: Array[(A, Int)]
序列中的每个元素和它的索引组成一个序列
val a = Array(10,20,30,40)
val b = a.zipWithIndex
println(b.mkString(",")) //(10,0),(20,1),(30,2),(40,3) Scala数组函数详解
Scala数组函数详解





















 557
557

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










