OpenCV—模糊处理与高斯模糊,二值化
模糊处理常用的可以分为三种:
1、均值模糊(均值滤波)
均值滤波是典型的线性滤波算法,它是指在图像上对目标像素给一个模板,该模板包括了其周围的临近像素(以目标像素为中心的周围8个像素,构成一个滤波模板,即去掉目标像素本身),再用模板中的全体像素的平均值来代替原来像素值。
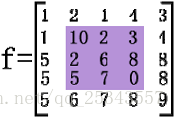
其缺点也显而易见:
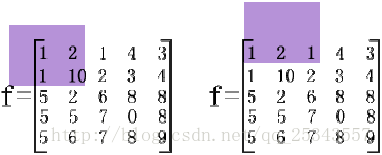
由于图像边框上的像素无法被模板覆盖,所以不做处理。
这当然造成了图像边缘的缺失 。
2、中值模糊(滤波)
中值,中间值,将数据从小到大排序后的中间值 ,中值滤波使用一个围绕当前像素的矩形,查找区域内像素的中值,并用该中值替换矩形区域内的其它像素点。
3、高斯模糊
针对图像中的每一个点与高斯内核进行卷积计算,并将计算结果相加,输出到目标图像中。
均值与中值模糊代码
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
def blur_demo(img):
dst1 = cv.blur(img, (5, 5)) # 均值模糊,(5,5)代表坐标
cv.imshow("blur_demo", dst1)
def median_blur_demo(img):
dst2 = cv.medianBlur(img, 9) # 中值模糊 有去椒盐的功能(去噪)值得注意的是,ksize的位置必须是整型奇数!
cv.imshow("medianBlur_demo", dst2)
中值滤波处理椒盐噪声效果显著
自定义模糊
注意要做防止溢出处理
def custom_demo(img):
kernel = np.ones([5, 5], np.float32)/25
dst3 = cv.filter2D(img, -1, kernel=kernel) # 自定义模糊
cv.imshow("custom_demo", dst3)
自定义锐化操作:
def custom_demo(img):
# kernel = np.ones([5, 5], np.float32)/25
kernel = np.array([[1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1]], np.float32)/9
dst3 = cv.filter2D(img, -1, kernel=kernel) # 自定义模糊
cv.imshow("custom_demo", dst3)
高斯模糊
其在opencv官网的各个参数的说明图
dst = cv2.GaussianBlur(src, ksize, sigmaX, sigmaY)
#ksize,滤波器卷积核的尺寸,必须为元组
#sigmaX:double型,表示高斯核函数在X方向的的标准偏差
#sigmaY:double型,示高斯核函数在Y方向的的标准偏差。若sigmaY为零,就将它设为sigmaX

# 将范围定义在0-255之间
def clamp(pv):
if pv > 255:
return 255
elif pv < 0:
return 0
else:return pv
# 定义高斯噪声函数
def gaussian_demo(img): #高斯模糊
h, w, c = img.shape #高,宽,通道数
for row in range(0, h, 1):
for col in range(0, w, 1):
s = np.random.normal(0, 20, 3)
b = img[row, col, 0] # blue
g = img[row, col, 1] # green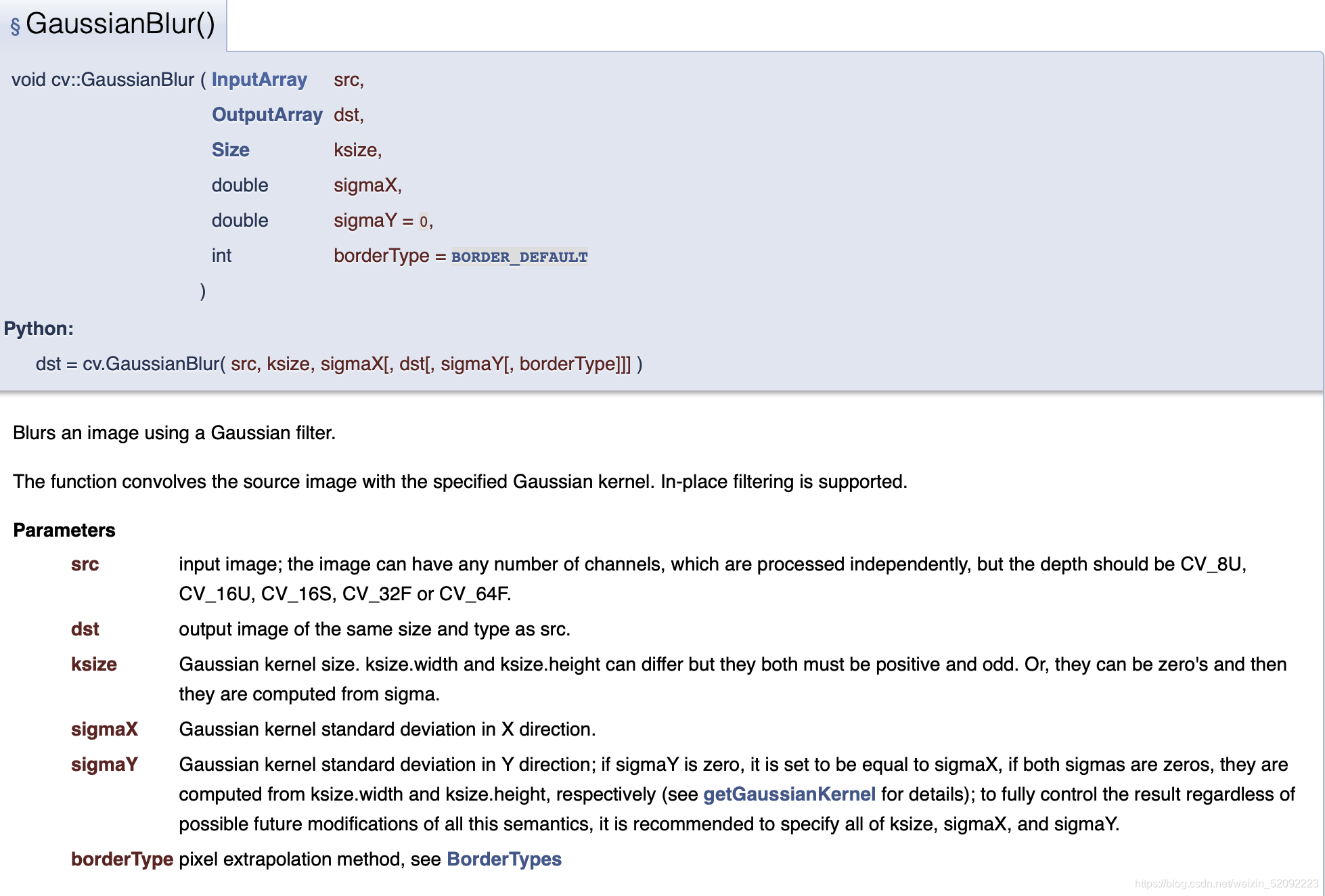
r = img[row, col, 2] # red
img[row, col, 0] = clamp(b + s[0])
img[row, col, 1] = clamp(g + s[1])
img[row, col, 2] = clamp(r + s[2])
cv.imshow("gaussian_demo", img)
二值化

import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('scratch.png', 0)
# global thresholding
ret1, th1 = cv2.threshold(img, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# Otsu's thresholding
th2 = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(img, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY, 11, 2)
# Otsu's thresholding
# 阈值一定要设为 0 !
ret3, th3 = cv2.threshold(img, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY + cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
# plot all the images and their histograms
images = [img, 0, th1, img, 0, th2, img, 0, th3]
titles = [
'Original Noisy Image', 'Histogram', 'Global Thresholding (v=127)',
'Original Noisy Image', 'Histogram', "Adaptive Thresholding",
'Original Noisy Image', 'Histogram', "Otsu's Thresholding"
]
# 这里使用了 pyplot 中画直方图的方法, plt.hist, 要注意的是它的参数是一维数组
# 所以这里使用了( numpy ) ravel 方法,将多维数组转换成一维,也可以使用 flatten 方法
# ndarray.flat 1-D iterator over an array.
# ndarray.flatten 1-D array copy of the elements of an array in row-major order.
for i in range(3):
plt.subplot(3, 3, i * 3 + 1), plt.imshow(images[i * 3], 'gray')
plt.title(titles[i * 3]), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(3, 3, i * 3 + 2), plt.hist(images[i * 3].ravel(), 256)
plt.title(titles[i * 3 + 1]), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(3, 3, i * 3 + 3), plt.imshow(images[i * 3 + 2], 'gray')
plt.title(titles[i * 3 + 2]), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from skimage.data import page
from skimage.filters import (threshold_otsu, threshold_niblack,
threshold_sauvola)
matplotlib.rcParams['font.size'] = 9
image = page()
binary_global = image > threshold_otsu(image)
window_size = 25
thresh_niblack = threshold_niblack(image, window_size=window_size, k=0.8)
thresh_sauvola = threshold_sauvola(image, window_size=window_size)
binary_niblack = image > thresh_niblack
binary_sauvola = image > thresh_sauvola
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 7))
plt.subplot(2, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
plt.title('Original')
plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(2, 2, 2)
plt.title('Global Threshold')
plt.imshow(binary_global, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(2, 2, 3)
plt.imshow(binary_niblack, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
plt.title('Niblack Threshold')
plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(2, 2, 4)
plt.imshow(binary_sauvola, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
plt.title('Sauvola Threshold')
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
-
opencv 简单阈值 cv2.threshold
-
opencv 自适应阈值 cv2.adaptiveThreshold (自适应阈值中计算阈值的方法有两种:mean_c 和 guassian_c ,可以尝试用下哪种效果好)
附:现记录几种计算阀值的方法供以后参考

1、双峰法

2、P参数法

3、大津法


4、最大熵阀值法


5、迭代法
























 1628
1628











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










