1.链表的概念及结构
概念:链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续,非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。

注意:
1.从上图可以看出,链式结构在逻辑上是连续的,但是在物理上不一定连续。
2.现实中的节点一般都是从堆上申请出来的。
3.从堆上申请的空间,是按照一定的策略来分配的,两次申请的空间可能连续,也可能不连续。
2.链表的分类
实际中链表的结构非常多样,以下情况组合起来就有8种链表结构:
1.单向或者双向
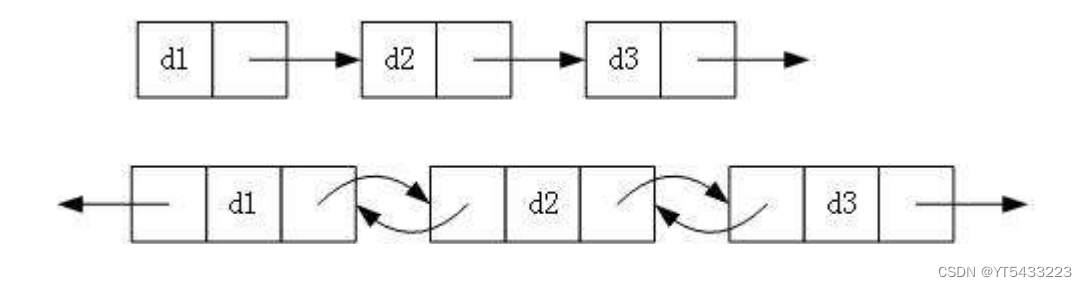
2.带头或者不带头
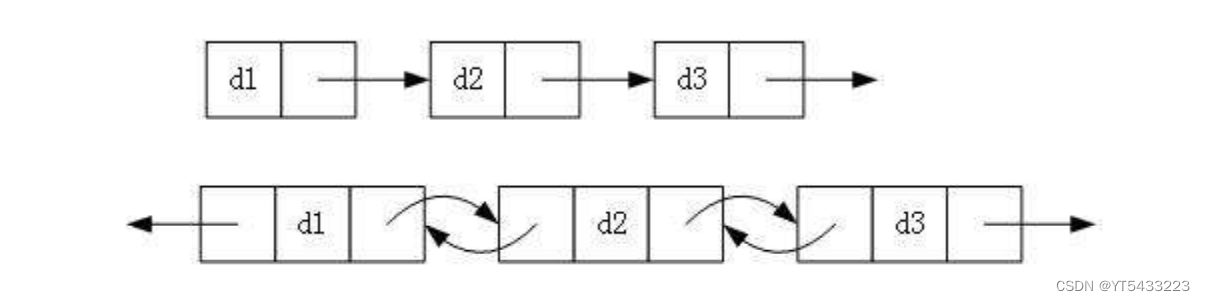
3.循环或者非循环

虽然有很多种链表结构,但是最常用的还是两种结构:
1.无头单项非循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其它数据结构的子结构,如哈希桶,图的邻接表等等。
2.带头双向循环链表:结构复杂,一般用在单独存储数据。实际中使用的链表数据结构,都是带头双向循环链表。虽然结构复杂,但是使用代码实现会发现结构带来很多优势,实现反而更简单。
3.链表的实现
分为三个文件头文件实现,头文件,函数实现文件,测试文件
头文件
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
//结构体声明
typedef struct lianbiao
{
int data;
struct lianbiao* next;
}lb;
//动态申请一个节点声明
lb* BuySListNode(int x);
//单链表打印声明
void lbprint(lb* phead);
//单链表头插声明
void lbpushfront(lb** pphead, int x);
//单链表尾插声明
void lbpushback(lb** pphead, int x);
//单链表尾删声明
void lbpopback(lb** pphead);
//单链表头删声明
void lbpopfront(lb** pphead);
//单链表查找声明
lb* lbFind(lb* phead, int x);
//单链表在pos位置之后插入声明
void lbinsertafter(lb* pos, int x);
//单链表在pos位置之前插入声明
void lbinsertbefore(lb** pphead, lb* pos, int x);
//单链表删除在pos位置之后的节点声明
void lberaseafter(lb* phead);
//单链表删除pos位置之前的节点函数实现
void lberasebefore(lb** pphead, lb* pos);
//单链表的销毁声明
void lbdestroy(lb** phead);函数实现文件
#include"lianbiao.h"
//动态申请节点函数实现
lb* BuySListNode(int x)
{
lb* newnode = (lb*)malloc(sizeof(lb));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fial");
return;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
//单链表打印函数实现
void lbprint(lb* phead)
{
assert(phead);
lb* tail = phead;
while (tail != NULL)
{
printf("%d->", tail->data);
tail = tail->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
//单链表的头插函数实现
void lbpushfront(lb** pphead, int x)
{
assert(pphead);
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
*pphead = BuySListNode(x);
}
else
{
lb* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
newnode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newnode;
}
}
//单链表尾插
void lbpushback(lb** pphead, int x)
{
assert(pphead);
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
lb* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
*pphead = newnode;
}
else
{
lb* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
lb* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
tail->next = newnode;
}
}
//单链表尾删函数实现
void lbpopback(lb** pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
lb* tail = *pphead;
if (tail->next==NULL)
{
*pphead = NULL;
}
else
{
while (tail->next->next != NULL)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail->next);
tail->next = NULL;
}
}
//单链表头删函数实现
void lbpopfront(lb** pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
lb* delnode = *pphead;
*pphead = delnode->next;
free(delnode);
}
//单链表查找函数实现
lb* lbFind(lb* phead, int x)
{
if (phead == NULL)
{
printf("链表为空!\n");
return;
}
else
{
lb* pos = phead;
while (pos != NULL)
{
if (pos->data == x)
{
return pos;
}
else
{
pos = pos->next;
}
}
printf("未查找到该节点!\n");
return NULL;
}
}
//单链表在pos位置之后插入声明
void lbinsertafter(lb* pos, int x)
{
assert(pos);
lb* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
newnode->next = pos->next;
pos->next = newnode;
}
//单链表在pos位置之前插入声明
void lbinsertbefore(lb** pphead, lb* pos, int x)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
assert(pos);
lb* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
lb* tail = *pphead;
if (pos == *pphead)
{
newnode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newnode;
}
else if (pos->next == NULL)
{
pos->next = newnode;
}
else
{
while (tail->next != NULL)
{
if (tail->next == pos)
{
newnode->next = tail->next;
tail->next = newnode;
return;
}
tail = tail->next;
}
}
}
//单链表删除在pos位置之后的节点实现
void lberaseafter(lb* pos)
{
assert(pos);
lb* delnode = pos->next;
pos->next = delnode->next;
free(delnode);
}
//单链表删除pos位置之前的节点函数实现
void lberasebefore(lb** pphead, lb* pos)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
assert(pos);
if (pos == *pphead)
{
printf("pos节点之前没有可删除的节点!\n");
}
else if (pos == (*pphead)->next)
{
lb* delnode = *pphead;
*pphead = pos;
free(delnode);
}
else
{
lb* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next->next != pos)
{
tail = tail->next;
}
lb* delnode = tail->next;
tail->next = pos;
free(delnode);
}
}
//单链表的销毁声明
void lbdestroy(lb** pphead)
{
lb* cur = *pphead;
lb* next;
while (cur != NULL)
{
next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
*pphead = NULL;
}测试文件
#include"lianbiao.h"
void testpushfront()
{
lb* phead = NULL;
lbpushfront(&phead, 1);
lbpushfront(&phead, 2);
lbpushfront(&phead, 3);
lbpushfront(&phead, 4);
lbprint(phead);
lbdestroy(&phead);
}
void testpushback()
{
lb* phead = NULL;
lbpushback(&phead, 1);
lbpushback(&phead, 2);
lbpushback(&phead, 3);
lbpushback(&phead, 4);
lbpushfront(&phead, 5);
lbprint(phead);
lbdestroy(&phead);
}
void testpopback()
{
lb* phead = NULL;
lbpushback(&phead, 1);
lbpushback(&phead, 2);
lbpushback(&phead, 3);
lbpushback(&phead, 4);
lbprint(phead);
lbpopback(&phead);
lbprint(phead);
lbdestroy(&phead);
}
void testpopfront()
{
lb* phead = NULL;
lbpushback(&phead, 1);
lbpushback(&phead, 2);
lbpushback(&phead, 3);
lbpushback(&phead, 4);
lbprint(phead);
lbpopfront(&phead);
lbprint(phead);
lbdestroy(&phead);
}
void testfind()
{
lb* phead = NULL;
lbpushback(&phead, 1);
lbpushback(&phead, 2);
lbpushback(&phead, 3);
lbpushback(&phead, 4);
lbprint(phead);
lb* result = lbFind(phead, 5);
if (result == NULL)
{
return;
}
else
{
printf("值为%d的节点的地址为:%p\n", result->data, result);
}
lbdestroy(&phead);
}
void testinsertafter()
{
lb* phead = NULL;
lbpushback(&phead, 1);
lbpushback(&phead, 2);
lbpushback(&phead, 3);
lbpushback(&phead, 4);
lbprint(phead);
lb* result = lbFind(phead, 2);
lbinsertafter(result, 5);
lbprint(phead);
lbdestroy(&phead);
}
void testlbinsertbefore()
{
lb* phead = NULL;
lbpushback(&phead, 1);
lbpushback(&phead, 2);
lbpushback(&phead, 3);
lbpushback(&phead, 4);
lbprint(phead);
lb* result = lbFind(phead, 1);
lbinsertbefore(&phead, result, 5);
lbprint(phead);
result = lbFind(phead, 4);
lbinsertbefore(&phead, result, 6);
lbprint(phead);
lbdestroy(&phead);
}
void testeraseafter()
{
lb* phead = NULL;
lbpushback(&phead, 1);
lbpushback(&phead, 2);
lbpushback(&phead, 3);
lbpushback(&phead, 4);
lbprint(phead);
lb* result = lbFind(phead, 2);
lberaseafter(result);
lbprint(phead);
lbdestroy(&phead);
}
void testerasebefore()
{
lb* phead = NULL;
lbpushback(&phead, 1);
lbpushback(&phead, 2);
lbpushback(&phead, 3);
lbpushback(&phead, 4);
lbprint(phead);
lb* result = lbFind(phead, 2);
lberasebefore(&phead, result);
lbprint(phead);
lbdestroy(&phead);
}
void testlbdestroy()
{
lb* phead = NULL;
lbpushback(&phead, 1);
lbpushback(&phead, 2);
lbpushback(&phead, 3);
lbpushback(&phead, 4);
lbdestroy(&phead);
}
//int main()
//{
// /*testpushfront();
// testpushback();
// testpopback();
// testpopfront();
// testfind();
// testinsertafter();
// testlbinsertbefore();
// testeraseafter();
// testerasebefore();
// testlbdestroy();*/
//
//
//
// return 0;
//}





















 3320
3320











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








