前言
本篇主要介绍双链表,简易的讲就是你知道你前面的地址和你后面的地址,本篇涉及知识和上篇单链表一样,但是双链表在实现上比单链表要简单,抽象度不高,容易掌握。
一、双链表是什么?
1.双链表的引入是为了来弥补单链表的部分缺陷,在单链表插入删除时,总是要进行遍历,时间复杂度相对较高。对此,我们采取以空间换时间的策略引入双链表。
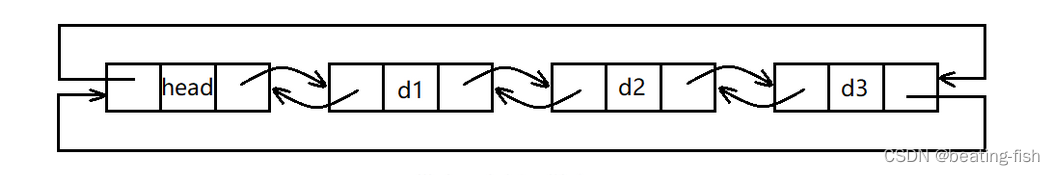
- 带头双向循环链表:结构最复杂,一般用在单独存储数据。实际中使用的链表数据结构,都
是带头双向循环链表。另外这个结构虽然结构复杂,但是使用代码实现以后会发现结构会带
来很多优势,实现反而简单了。
二、双链表的具体实现?
1、函数接口介绍
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include<cassert>
using namespace std;
typedef int DateType;
struct Node
{
DateType value;
struct Node* prev;
struct Node* next;
};
Node* Init();
Node* BuyNode(DateType x);
void Push_back(Node* phead,DateType x);
void Push_front(Node* phead,DateType x);
void Pop_back(Node* phead);
void Pop_front(Node* phead);
Node* Find(Node* phead, DateType x);
void Erase(Node* pos);
void Insert(Node* pos, DateType x);
void Print(Node* phead);
2、函数具体实现
#include "Double_Linklist.h"
Node* Init()
{
Node* phead = BuyNode(-1);
phead->next = phead;
phead->prev = phead;
return phead;
}
void Push_back(Node* phead, DateType x)
{
//Node* newnode = BuyNode(x);
//Node* tail = phead->prev;
//tail->next = newnode;
//newnode->prev = tail;
//newnode->next = phead;
//phead->prev = newnode;
Insert(phead->prev,x);
}
void Push_front(Node* phead, DateType x)
{
//Node* newnode = BuyNode(x);
//newnode->next = phead->next;
//phead->next->prev = newnode;
//newnode->prev = phead;
//phead->next = newnode;
Insert(phead, x);
}
Node* BuyNode(DateType x)
{
Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (node == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
node->value = x;
node->next = NULL;
node->prev = NULL;
return node;
}
void Pop_back(Node* phead)
{
assert(phead->next != phead);
//Node* tmp = phead->prev;
//tmp->prev->next = phead;
//phead->prev = tmp->prev;
//free(tmp);
Erase(phead->prev);
}
void Pop_front(Node* phead)
{
//assert(phead->next!=phead);
//Node* tmp = phead->next;
//phead->next = tmp->next;
//tmp->next->prev = phead;
//free(tmp);
Erase(phead->next);
}
void Insert(Node* pos, DateType x)//在pos后面插入
{
assert(pos);
Node* newnode = BuyNode(x);
pos->next->prev = newnode;
newnode->next = pos->next;
newnode->prev = pos;
pos->next = newnode;
}
void Erase(Node* pos)
{
assert(pos);
Node* tmp = pos->prev;
tmp->next = pos->next;
pos->next->prev = pos->prev;
free(pos);
}
Node* Find(Node* phead, DateType x)
{
Node* cur = phead->next;
while (cur!=phead)
{
if (cur->value == x)
return cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}
void Print(Node* phead)
{
assert(phead);
Node* cur = phead->next;
while (cur != phead)
{
cout << cur->value << " ";
cur = cur->next;
}
}
三、总结
双链表在具体实现的时最主要的是要搞清四条链接线,修改时注意顺序(在没有另设变量保存时),其他的和单链表相比还稍微简单一丢丢哦!
注:作者水平有限,如有错误,敬请指正!!!






















 9759
9759











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








