技巧一:复用组件逻辑
具体而言,高阶组件是参数为组件,返回值为新组件的函数
const EnhancedComponent = higherOrderComponent(WrappedComponent);
For example:
参数复用
const withSize = (Component) => {
return class toSize extends Component {
state = {
xPos: document.documentElement.clientWidth,
yPos: document.documentElement.clientHeight
}
getPos = () => {
this.setState({
xPox: document.documentElement.clientWidth,
yPos: document.documentElement.clientHeight
})
}
componentDidMount(){
window.addEventListener('resize', this.getPos)
}
componentWillUnmount(){
window.removeEventListener('resize', this.getPos)
}
render() {
return <Component {...this.state}/>
}
}
}
class Foo extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<p>x:{ this.props.xPos} -- y: {this.props.yPos} </p>
</div>
)
}
}
class Sub extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<button>x:{ this.props.xPos} -- y: {this.props.yPos} </button>
</div>
)
}
}
const SubWithSize = withSize(Sub)
const FooWithSize = withSize(Foo)
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<SubWithSize />
<FooWithSize />
</div>
)
}
}
函数逻辑复用
// PhotoList.js
import React from 'react'
import withFetch from '../withFetch'
const url = 'https://www.abc.com/photos?_limit=5
const PhotoList = ({ list }) => {
return (
<ul>
{list.map((photo) => {
return <li key={photo.id}> 图片URL:{photo.url}</li>
})}
</ul>
)
}
export default withFetch(PhotoList, url)
// UserList.js
import React from 'react'
import withFetch from '../withFetch'
const url = 'https://www.abc.com/users?_limit=5
const UserList = ({ list }) => {
return (
<ul>
{list.map((user) => {
return <li key={user.id}> 用户名:{user.name}</li>
})}
</ul>
)
}
export default withFetch(UserList, url)
import React from 'react'
import axios from 'axios'
const withFetch = (Component, url) => {
return class WithFetchComponent extends React.Component {
state = {
list: []
}
async componentDidMount() {
const { data: list } = await axios.get(url)
this.setState({
list
})
}
render() {
return <Component {...this.props} list={this.state.list} /}
}
}
}
技巧二:组件的异步加载
利用lazy、suspense来实现组件的异步加载
- 1、lazy引入异步组件
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
import React, { Component, lazy, Suspense } from 'react'
const sub = lazy(() => import('./Sub'))
2、suspense调用组件
class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
/*fallback的作用是在异步加载的空档中填充一些内容让页面可以正常渲染 */
<Suspense fallback = { <div>loading</div> }>
<Sub />
</Suspense>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(
<App />,
document.getElementById('rroot')
)
技巧三:组件的生命周期
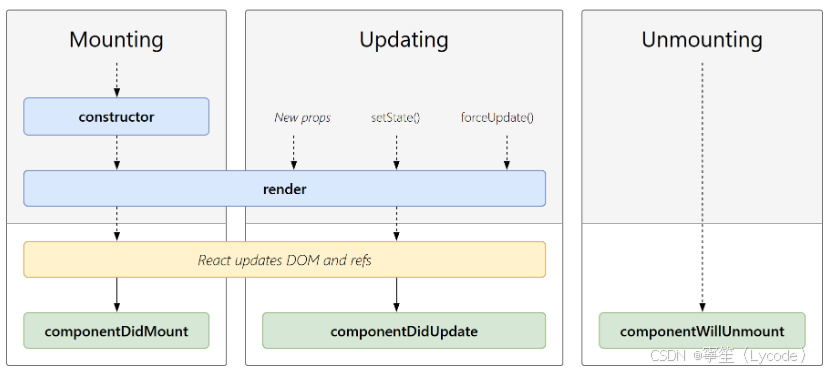
Mounting(挂载)
- constructor(): 在 React 组件挂载之前,会调用它的构造函数。
- getDerivedStateFromProps(): 在调用 render 方法之前调用,并且在初始挂载及后续更新时都会被调用。
- render(): 唯一必须实现的纯函数;
- componentDidMount(): 在组件挂载后(插入 DOM 树中)立即调用。
Updating(更新)
- componentDidUpdate(): 在组件更新后立即调用
Unmounting(卸载)
- componentWillUnmount(): 在组件卸载后理解调用
For example:
class App extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = { count: 0 }
console.log('cons');
}
onclick = () => {
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1
})
}
componentDidMount(){
console.log('did mount');
}
componentDidUpdate(){
console.log('did update');
}
componentWillUnmount(){
console.log('will unmount');
}
return() {
console.log('render')
return (
<div>
<p> {this.state.count} </p>
<button onclick={this.onclick}>add</button>
</div>
)
}
// 执行顺序:()
// cons -> render -> did mount (mounting阶段)
// -> render -> did update (updating阶段)
// -> will unmount (unmounting阶段)
技巧四:组件的优化
- 避免无数据更新的自组件反复更新

import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
import React, { Component, PureComponent, memo } from 'react'
//组件的优化一: 类组件
class Sub extends Component //方法二:替换成PureComponent {
// 方法一
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState){
if (nextProps.name === this.props.name) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
render() {
console.log('sub render');
return (
<div>
sub
</div>
)
}
}
//组件的优化二: 函数组件
const Sub = memo((params) => {
console.log('sub render');
return (
<div>
sub
</div>
)
})
class App extends Component {
state = {
count: 0
}
onclick = () => {
this.setState({
count: this.state.count + 1
})
}
callback = () => {
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<Sub name="zhangsan" />
// 函数同理
<Sub func={this.callback} />
<p> {this.state.count} </p>
<button onclick={this.onclick}>add</button>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(
<App />,
document.getElementById('rroot')
)

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










