字符串中不同单词出现的次数
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<map>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
void func(string str)
{
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
if (str[i] == '.')
{
str[i] = ' ';
}
}
map<string, int>m;
char str1[200];
strcpy(str1, str.c_str());
char* str2 = strtok(str1, " ");
while (str2)
{
m[str2]++;
str2 = strtok(NULL, " ");
}
for (auto i = m.begin(); i != m.end(); i++)
{
cout << left << setw(10) << i->first << ":" << i->second << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
string str = "This is a world.This is a girl.";
func(str);
return 0;
}
2023
参考这位同学的题目和答案,添加一些自己的思考
看程序写结果
1、指针引用
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void fun1(char* s1, char* s2) {
int i = 0;
for (; *s1 == *s2; s1++, s2++) {
i++;
}
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << i << endl;
}
void fun2(char* &s1, char* &s2) {
int i = 0;
for (; *s1 == *s2; s1++, s2++) {
i++;
}
*(s1 - 1) = '\0';
*(s2 - 1) = '\0';
}
int main() {
char string1[] = "I love Nanjing";
char string2[] = "I love Southeast University";
char* p1 = string1;
char* p2 = string2;
fun1(p1, p2);
cout << p1 << endl;
cout << p2 << endl;
cout << string1 << endl;
cout << string2 << endl;
fun2(p1, p2);
cout << p1 << endl;
cout << p2 << endl;
cout << string1 << endl;
cout << string2 << endl;
return 0;
}Nanjing
7
I love Nanjing
I love Southeast University
I love Nanjing
I love Southeast University
Nanjing
Southeast University
I love
I love涉及到指针引用
for语句先判断再执行括号里的语句
fun1()cout<<s1,此时si指向的不是string1[0],而是string1[7],要注意
fun2()使用了指针引用,所以在main函数里指针的位置已经改变了,不是指向string2[0],而是string2[7]
下面是fun2无&的情况
void fun1(char* s1, char* s2) {
int i = 0;
for (; *s1 == *s2; s1++, s2++) {
i++;
}
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << i << endl;
}
void fun2(char* s1, char* s2) {
int i = 0;
for (; *s1 == *s2; s1++, s2++) {
i++;
}
*(s1 - 1) = '\0';
*(s2 - 1) = '\0';
}
int main() {
char string1[] = "I love Nanjing";
char string2[] = "I love Southeast University";
char* p1 = string1;
char* p2 = string2;
fun1(p1, p2);
cout << p1 << endl;
cout << p2 << endl;
cout << string1 << endl;
cout << string2 << endl;
fun2(p1, p2);
cout << p1 << endl;
cout << p2 << endl;
cout << string1 << endl;
cout << string2 << endl;
return 0;
}Nanjing
7
I love Nanjing
I love Southeast University
I love Nanjing
I love Southeast University
I love
I love
I love
I love2、静态数据成员,继承
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Student{
public:
Student(){
num++;
}
~Student(){num--;}
static int num;
private:
string name;
};
int Student::num = 0;
class Undergraduate: public Student{
public:
Undergraduate(int i = 0, float s = 100){
id = i;
score = s;
num++;
}
~Undergraduate(){num--;}
static int num;
private:
int id;
float score;
};
int Undergraduate::num = 0;
class Postgraduate: public Student{
public:
Postgraduate(string s = "UNDK", string n = "KDS"){
sa = s;
na = n;
num++;
}
~Postgraduate(){num--;}
static int num;
private:
string sa, na;
};
int Postgraduate::num = 0;
int num = 100;
Undergraduate ug(1);
Postgraduate p;
int main(){
int num = 0;
// 这里所有的输出都简写了,因为记不得,其实原题是有部分英文的
// 诸如 "There are" << num << "students" 之类的,不影响考点
cout << num << endl;
cout << ::num << endl;
cout << ug.num << endl;
cout << p.num << endl;
cout << Student::num << endl;
{
Undergraduate u1;
Postgraduate p1;
cout << u1.num << endl;
cout << p1.num << endl;
cout << Student::num << endl;
}
Undergraduate *u = new Undergraduate;
cout << Undergraduate::num << endl;
// cout << Postgraduate::num << endl;
cout << Student::num << endl;
delete u;
cout << Undergraduate::num << endl;
// cout << Postgraduate::num << endl;
cout << Student::num << endl;
}
0
100
1
1
2
2
2
4
2
3
1
2这里构造函数num++,析构函数num--,在程序结束后会自动调用析构函数。
想到了学过的虚函数,把析构函数设置成虚函数。这种情况下往往是派生类对象赋值给基类的指针,在释放空间的时候先释放派生类再释放基类。如果不设置成虚析构函数,在释放空间的时候只能释放基类的空间。
int main() {
int num = 0;
// 这里所有的输出都简写了,因为记不得,其实原题是有部分英文的
// 诸如 "There are" << num << "students" 之类的,不影响考点
cout << num << endl;
cout << ::num << endl;
cout << ug.num << endl;
cout << p.num << endl;
cout << Student::num << endl;
cout << endl;
Student* u = new Undergraduate;
cout << Undergraduate::num << endl;
// cout << Postgraduate::num << endl;
cout << Student::num << endl;
delete u;
cout << Undergraduate::num << endl;
// cout << Postgraduate::num << endl;
cout << Student::num << endl;
}0
100
1
1
2
2
3
2
2
Student* u = new Undergraduate;这里修改一下,最后输出Undergraduate::num应该是1,因为不是虚析构函数,所以派生类析构函数没有被调用,结果是2
3、静态函数成员的访问
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test{
public:
Test(){
num++;
}
~Test(){num--;}
static void print(){
cout << "T count: " << num << endl;
}
private:
static int num;
};
int Test::num = 0;
void fun(Test *p){
Test m3;
p = new Test[5];
p->print();
delete[] p;
p = nullptr;
}
Test t1;
int main(){
t1.print();
Test t2;
Test *ptr = nullptr;
ptr->print();
fun(ptr);
ptr = new Test;
ptr->print();
delete ptr;
Test::print();
return 0;
}
T count: 1
T count: 2
T count: 8
T count: 3
T count: 2静态成员函数的访问
4、简单题,for循环
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n = 13;
for(int i = 0 ;i < n;i++){
if(i%5==0) continue;
cout << i << ' ';
if(i%2==0) cout << endl;
if(i%10==0) break;
}
}
1 2
3 4
6
7 8
9 11 125、异常处理
#include <iostream>
#include <stdexcept>
using namespace std;
class ErrorA: public runtime_error{
public:
ErrorA():runtime_error{"errorA"}{
}
};
class ErrorB: public runtime_error{
public:
ErrorB():runtime_error{"errorB"}{
}
};
class ErrorC: public ErrorA{
public:
ErrorC(){
runtime_error{"errorC"};
}
};
int main(){
for(int i = 0 ;i < 4; i++){
try{
switch(i){
case 0: throw runtime_error{"runtime_error"}; break;
case 1: throw ErrorA();
case 2: throw ErrorB();
case 3: throw ErrorC();
}
}catch(ErrorA &err){
cout << err.what() << endl;
}catch(ErrorB &err){
cout << err.what() << endl;
}catch(ErrorC &err){
cout << err.what() << endl;
}catch(runtime_error &err){
cout << err.what() << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
runtime_error
errorA
errorB
errorA有问题的是case 3: throw ErrorC();这里,先调用A的构造函数,再调用C的构造函数。
这里不太确定,我想的是先抛出ErrorA,那么就直接进到catch块里,后面的ErrorC就直接跳过了 ,只要找到一个匹配的异常类型,后面的异常处理都将被忽略。
填空
1、随机数排序
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <ctime> // 这一行是自己加的,原题没有
using namespace std;
void genterator(int* arr, int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
arr[i] = rand() % 100;// 设空
}
}
void bubble(int* arr, int size) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
bool flag = false;
for (int j = 0; j < size-1-i; j++) { // size-1-i设空
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
flag = true;
}
if (flag == false) break;
}
}
}
string transform(int num) {
string s;
if (num == 0)
s = string("0");
while (num != 0) {
int d = num % 16;
if (d<=9) { // 设空
s = char(d + '0') + s;
}
else {
d -= 10; // 空
s = char(d + 'A') + s;
}
num = num / 16; // 空
}
return s;
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); // 这一行是自己加的,原题没有
const int size = rand() % 20;
int *a=new int[size];// 这一行是自己加的,原题没有,不然会报错
genterator(a, size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)cout << a[i]<< endl;// 这一行是自己加的,原题没有,更方便看程序
bubble(a, size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
cout << transform(a[i]) << endl;
}
delete a;
return 0;
}一共产生10个数字
1
21
66
57
93
58
43
56
46
40
1
15
42
39
5D
3A
2B
38
2E
282、逆序处理
使用的是递归,但是不好想,一般是递归从大到小,这里是从小到大。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; // 空
void reverString(char* a, int b); // 空
int main() {
char str[] = "Hello this is my Cyber S&E!!";
cout << str << endl; // 空
reverString(str, 0); // 空
return 0;
}
void reverString(char* a, int b) { // b设空
static int chars = 0;
if (chars==18||a[b]=='\0') // 空
return;
if (a[b] != ' ')
chars++; // 空
reverString(a, b+1); // b+1设空
if (a[b] != ' ') // 空
cout << a[b];
}Hello this is my Cyber S&E!!
rebyCymsisihtolleH编程
1、动态规划,不会,想不通是怎么运行的
2、<< 重载只能使用友元函数
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Pet {
public:
Pet() { cout << "new pet," << endl; }
virtual ~Pet() { cout << "delete pet" << endl; }
};
class Cat :public Pet {
private:
char* name;
public:
Cat(const char* n=NULL)
{
if (n) {
name = new char[strlen(n) + 1];
strcpy(name, n);
cout << "cat:" << name << ",new" << endl;
}
else {
name = NULL; cout << "cat:~~" << endl;
}
}
~Cat() {
if (name != NULL)
{
cout << "leave cat," << name << endl;
delete[] name;
}
else cout << "leave cat" << endl;
}
Cat(Cat& c) {
name = new char[strlen(c.name) + 1];
strcpy(name, c.name);
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os,Cat& c)
{
if (c.name)
{
os << "Cat:" << c.name << ",miaomiao~~" << endl;
}
else { os << "~~" << endl; }
return os;
}
};
class Dog :public Pet {
private:
char* name;
public:
Dog(const char* n=NULL)
{
if (n) {
name = new char[strlen(n) + 1];
strcpy(name, n);
cout << "dog:" << name << ",new" << endl;
}
else {
name = NULL; cout << "!!" << endl;
}
}
~Dog()
{
if (name != NULL)
{
cout << "leave dog," << name << endl;
delete[] name;
}
else cout << "leave dog" << endl;
}
Dog(Dog &d) {
if (d.name) {
name = new char[strlen(d.name) + 1];
strcpy(name, d.name);
cout << "copy pet," << endl;
}
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, Dog& d)
{
if (d.name)
{
os << "Dog:" << d.name << ",wawa!!" << endl;
}
else { os << "!!" << endl; }
return os;
}
void eat()
{
cout << "Dog:" << name << ",eat bone!!" << endl;
}
};
void feed(Dog dog) {
dog.eat();
}
int main() {
Pet* pets[5];
cout << "=========================coming=========================" << endl;
pets[0] = new Dog("wangcai");
pets[1] = new Dog("dahuang");
pets[2] = new Cat("xiaomao");
pets[3] = new Cat("huhu");
pets[4] = new Cat(NULL);
cout << "=========================crying=========================" << endl;
cout << *dynamic_cast<Dog*>(pets[0]) ;
cout << *dynamic_cast<Dog*>(pets[1]);
cout << *dynamic_cast<Cat*>(pets[2]);
cout << *dynamic_cast<Cat*>(pets[3]);
cout << *dynamic_cast<Cat*>(pets[4]);
cout << "=========================feed=========================" << endl;
feed(*dynamic_cast<Dog*>(pets[0]));
cout << "=========================leave=========================" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
delete pets[i];
}
return 0;
}=========================coming=========================
new pet,
dog:wangcai,new
new pet,
dog:dahuang,new
new pet,
cat:xiaomao,new
new pet,
cat:huhu,new
new pet,
cat:~~
=========================crying=========================
Dog:wangcai,wawa!!
Dog:dahuang,wawa!!
Cat:xiaomao,miaomiao~~
Cat:huhu,miaomiao~~
~~
=========================feed=========================
new pet,
copy pet,
Dog:wangcai,eat bone!!
leave dog,wangcai
delete pet
=========================leave=========================
leave dog,wangcai
delete pet
leave dog,dahuang
delete pet
leave cat,xiaomao
delete pet
leave cat,huhu
delete pet
leave cat
delete pet2019
看程序写结果
1、switch嵌套,没有break的情况
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 4, c = 0, b = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
switch ((--a) > 0)
{
case 0:switch (c++)
{
case 0:cout << "%";
case 1:cout << "#";
}break;
case 1:switch (b)
{
case 0:cout << "*"; --b; break;
case 1:cout << "@"; --b; break;
}
default:cout << "&";
}
cout << "!" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
2、for语句
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void funcc(int a)
{
cout << a << endl;
}
int main()
{
int i = 0, k = 2;
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; ++i)
{
funcc(i * k);
}
cout << i << " " << k << endl;
return 0;
}
3、交换数据
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void func(int* p, int* q)
{
int* c;
c = p;
p = q;
q = c;
}
int main()
{
int a = 7, b = 19;
int* pa = &a, * pb = &b;
cout << *pa << " " << *pb << endl;
func(pa, pb);
cout << *pa << " " << *pb << endl;
return 0;
}
4、交换数据
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void func(int* p, int* q)
{
int* c;
c = p;
p = q;
q = c;
}
int main()
{
int a = 7, b = 19;
int* pa = &a, * pb = &b;
cout << *pa << " " << *pb << endl;
func(pa,pb);
cout << *pa << " " << *pb << endl;
return 0;
}
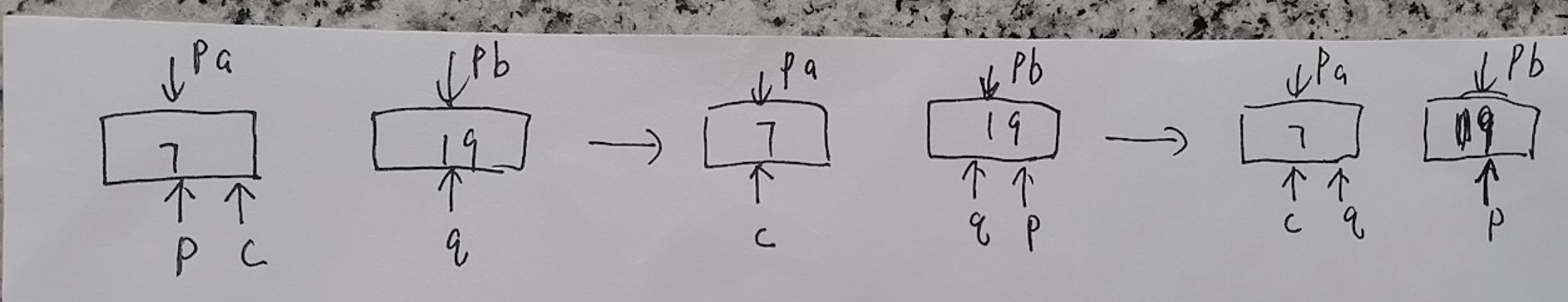
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void func(int* p, int* q)
{
int c;
c = *p;
*p = *q;
*q = c;
}
void func(int* &p, int* &q)//这种也是可以交换数据的
{
int c;
c = *p;
*p = *q;
*q = c;
}
int main()
{
int a = 7, b = 19;
int* pa = &a, * pb = &b;
cout << *pa << " " << *pb << endl;
func(pa,pb);
cout << *pa << " " << *pb << endl;
return 0;
}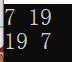
上面的代码的结果之所以没有调换,是因为交换的是指针变量,而下面代码交换的是指针变量的值,所以可以实现交换的功能。
5、全局对象、全局静态变量、静态局部对象、栈对象构造与析构
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
private:
int xx;
public:
A(int x) :xx(x) { cout << "A()" << xx << endl; }
~A() { cout << "~A" << xx << endl; }
};
A a(1);
int main()
{
A b(2);
static A c(3);
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
private:
int xx;
public:
A(int x) :xx(x) { cout << "A()" << xx << endl; }
~A() { cout << "~A" << xx << endl; }
};
A a(1);
static A d(4);
int main()
{
A b(2);
static A c(3);
return 0;
}A()1
A()4
A()2
A()3
~A2
~A3
~A4
~A1全局静态对象和全局对象析构顺序按照构造时候的反顺序来
主要注意局部静态对象和局部对象析构的顺序
6、引用,复制构造函数
class Ccc
{
private:
int xx;
int yy;
public:
Ccc(int x,int y):xx(x),yy(y){}
friend Ccc operator++(Ccc);
void print()
{
cout << xx << "," << yy << endl;
}
};
Ccc operator++(Ccc c)
{
++c.xx;
++c.yy;
return c;
}
int main()
{
Ccc aa(10, 20);
aa.print();
for (int i= 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
++aa;
}
aa.print();
Ccc b = ++aa;
b.print();
return 0;
}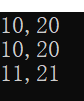
在以上代码中,++aa并没有改变值,是因为Ccc operator++(Ccc c)形参不是对象的引用,离开了作用域不会对aa产生变化。而Ccc b = ++aa;,是因为++aa有一个临时无名对象作为返回值,调用默认复制构造函数,赋给b
Ccc& operator++(Ccc c)
{
++c.xx;
++c.yy;
return c;
}
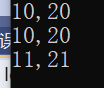
Ccc operator++(Ccc& c)
{
++c.xx;
++c.yy;
return c;
}
int main()
{
Ccc aa(10, 20);
aa.print();
for (int i= 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
++aa;
}
aa.print();
Ccc b = ++aa;
b.print();
return 0;
}
7、虚函数、赋值兼容规则
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
A() { cout << "A()" << endl; }
virtual void print()const { cout << "I am A" << endl; }
~A() { cout << "~A()" << endl; }
};
class B :public A
{
public:
B() { cout << "B()" << endl; }
void print()const { cout << "I am B" << endl; }
~B() { cout << "~B()" << endl; }
};
int main()
{
A* pa = new B();
pa->print();
delete pa;
return 0;
}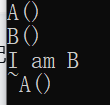
A* pa = new B();先对B进行初始化,调用B构造函数之前,先调用A构造函数。print()是虚函数,delete pa,只释放~A,是因为,析构函数不是虚函数
改错

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Acc
{
char cc = '0';
public:
Acc(char c) :cc(c) {}
char& rise()
{
return ++cc;
}
};
int main()
{
Acc aa('w');
char result=aa.rise();
cout << result;
return 0;
}int main()
{
cout << 'a' + 1 << endl;
char c = 'a';
c += 1;
cout << c;
return 0;
}98
b编程
1、
先用随机函数(rand)按列优先初始化一个3行4列的数组(数组中元素的范围是【1,9】),然后判断该数组中是否有鞍点(即是否存在既是行上最大又是列上最小的元素)
1、rand()不需要参数,它会返回一个从0到最大随机数的任意整数,最大随机数的大小通常是固定的一个大整数。
2、如果要产生0~99这100个整数中的一个随机整数,可以表达为:int num = rand() % 100;
这样,num的值就是一个0~99中的一个随机数了。
3、如果要产生1~100,则是这样:int num = rand() % 100 + 1;
4、总结来说,可以表示为:int num = rand() % n +a;
其中的a是起始值,n-1+a是终止值,n是整数的范围。
-
一般性:rand() % (b-a+1)+ a ; 就表示 a~b 之间的一个随机整数。
http://t.csdn.cn/L6RVH
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[3][4];
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
for (j = 0; j < 4; j++)
a[i][j] = rand() % 9 + 1;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 4; j++)
cout << a[i][j] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
int num = 0;
for (j = 1; j < 4; j++)
{
if (a[i][j] >= a[i][num]) { num = j; }
}
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
if (a[j][num] < a[i][num]) break;
}
if (j == 4)cout << "yes" << endl;
else cout << "no" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
不存在
2、
(递归)写一个函数模板完成二分查找的功能,是在数组中查找该数组中的元素是有序的,必须使用递归实现。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
int Binarysearch(T a[], T key, int left, int right)
{
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (left > right)
return -1;
else if (a[mid] == key)
return mid;
else if (a[mid] > key)
Binarysearch(a, key, 0, mid - 1);
else
Binarysearch(a, key, mid + 1, 8);
}
int main()
{
int a[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
int ans = Binarysearch(a, 2, 0, 8);
if (ans == -1)
{
cout << "cannot found" << endl;
}
else
cout << ans << " is the position" << endl;
return 0;
}3、
实现一个selfString 类,要求至少包含构造函数和新构函数,构造函数功能从文件里读取一行英文字符串,也得有一个功能函数,该功能函数实现在两个字符串中找到他们的公共单词,要求必须是长度最长的公共单词,selfString有两个私有数据成员一个是字符数组,一个是Length,每个英文单词之间用空格分隔开,最后一点要求:不允许使用标准模板库。
参考别人的代码
使用动态规划
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class selfString {
private:
char* dataStr;
int Length;
public:
selfString() {
dataStr = NULL;
Length = 0;
}
selfString(const char str[]) {
Length = strlen(str);
dataStr = new char[Length + 1];
strcpy(dataStr, str);
}
selfString(const selfString& str) {
Length = str.Length;
dataStr = new char[Length + 1];
strcpy(dataStr, str.dataStr);
}
~selfString() {
if (dataStr != NULL) {
delete[] dataStr;
dataStr = NULL;
Length = 0;
}
}
void show()
{
cout << dataStr << endl;
}
friend selfString longestCommonWord(const selfString& str1, const selfString& str2);
};
selfString longestCommonWord(const selfString& str1, const selfString& str2) {
int len1 = str1.Length;
int len2 = str2.Length;
char* word1 = new char[len1 + 1];
char* word2 = new char[len2 + 1];
int i = 0, j = 0, maxLen = 0, maxStart = 0;
while (i < len1 && j < len2) {
if (str1.dataStr[i] == ' ') {
i++;
continue;
}
if (str2.dataStr[j] == ' ') {
j++;
continue;
}
int start1 = i, start2 = j;
while (i < len1 && str1.dataStr[i] != ' ') {
word1[i - start1] = str1.dataStr[i];
i++;
}
word1[i - start1] = '\0';
while (j < len2 && str2.dataStr[j] != ' ') {
word2[j - start2] = str2.dataStr[j];
j++;
}
word2[j - start2] = '\0';
if (strcmp(word1, word2) == 0) {
int len = strlen(word1);
if (len > maxLen) {
maxLen = len;
maxStart = start1;
}
}
}
delete[] word1;
delete[] word2;
return selfString(str1.dataStr + maxStart);
}
int main() {
ifstream fin("input.txt");
char buffer[1000];
fin.getline(buffer, 1000);
selfString str1(buffer);
fin.getline(buffer, 1000);
selfString str2(buffer);
fin.close();
selfString commonWord = longestCommonWord(str1, str2);
cout << "The longest common word is: "; commonWord.show() ;
return 0;
}2017
编程
1、
格式转换,从一个文件中读取日期07/21/2016,转换为以下格式July 21,2016并输出到屏幕上
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<string>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ifstream file("data.txt");
if (!file) { cout << "文件不能打开" << endl; }
string str;
string month[] = {" ","Junary","Fabuary","March","April","May","June","July","August","September",
"October","November","December" };
while (getline(file, str))
{
string str1(str, 0, 2);
int m = stoi(str1);
string str2(str, 3, 2);
string str3(str, 6, 4);
cout << left<<setw(10) << setfill(' ') << month[m] <<str2 << ',' << str3 << endl;
}
}

2016
编程
1、输入一行文本,求文本中每个单词的长度

#include <iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char a[] = "This is a flower";
char* str;
cout << left << setw(10) << "word" << "length" << endl;
str = strtok(a, " ");
while (str)
{
cout << left << setw(10) << str << strlen(str) << endl;
str = strtok(NULL, " ");
}
}
str = strtok(a, " ");
while (str)
{
cout << left << setw(10) << str << strlen(str) << endl;
str = strtok(NULL, " ");
}
第一次调用,第一个参数为字符串,后面调用必须为NULL。strtok参数为char*
参考别人的方法
#include <iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
// 方法一 使用string类的成员函数
void split1(const string& inStr) {
int pos = 0; // 记录上次分割的位置
for (size_t i = 0; i < inStr.size(); ++i) {
if (inStr[i] == ' ') { // 找到分割记号
cout << inStr.substr(pos, i - pos) << ": " << i - pos << endl;
pos = i + 1; // 更新下一次开始的地方,需要跳过一个' '
}
else if (i == inStr.size() - 1) // 处理最后一个单词
cout << inStr.substr(pos, i - pos + 1) << ": " << i - pos + 1 << endl;
}
}
// 方法二 使用C语言类型的字符串处理函数
void split2(const string& inStr) {
char str[100] = { 0 };
char* temPtr;
inStr.copy(str, inStr.size()); // 转换成char*类型
temPtr = strtok(str, " "); // 不断按照分隔符取一段单词
while (temPtr) {
cout << temPtr << ": " << strlen(temPtr) << endl; // 输出单词及其长度
temPtr = strtok(nullptr, " ");
}
}
// 方法三 最无脑的解法,直接将输入和输出结合起来
void getAns() {
string str;
while (cin >> str) {
cout << str + ": " << str.size() << endl;
}
}
int main() {
getAns();
string inStr;
getline(cin, inStr);
split1(inStr);
cout << endl << endl;
split2(inStr);
return 0;
}2、使用字符数组存储一段字符,判断是否是回文字符串(需要判断并忽略空格)
#include <iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void Str(const char* a)
{
int len = strlen(a);
char* str=new char[len];
int num = 0;
int i, j;
for ( i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (a[i] != ' ')
{
str[num++] = a[i];
}
}
for ( i = 0, j = num - 1; i <= num / 2; i++, j--)
{
if (str[i] != str[j])
{
cout << "no" << endl; break;
}
}
if (i == num / 2 + 1) cout << "yes" << endl;
}
int main()
{
Str("abc dec ba");
return 0;
}

int main()
{
char a[80],b[80];
cin.getline(a, 80);
int len = strlen(a);
int num = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (a[i] != ' ')
{
b[num++] = a[i];
}
}
int i, j;
for (i = 0, j = num - 1; i < j; i++, j--)
{
if (b[i] != b[j])
{
cout << "no" << endl;
break;
}
}
if (i >= j) { cout << "yes" << endl; }
return 0;
}w tt w
yes2015
编程
1、求e^x

#include <iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int func1(int n)
{
if (n == 1) return 1;
else {
return n * func1(n - 1);
}
}
double func(int x)
{
double sum = 1;
int i = 1;
double tmp;
do
{
tmp = double(pow(x, i)) / func1(i);
sum += tmp;
i++;
} while (tmp > 1e-7);
return sum;
}
int main()
{
cout << fixed << setprecision(7) << func(3);
}参考别人的做法,更简洁
#include <iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
double myExp(double x) {
double ans=1,tmp;
int k=1, n=1;
do {
tmp = pow(x, k) / n;
ans += tmp;
k++;
n = n * k;
} while (tmp > 1.0e-7);
/*
按题源应该是while(fabs(tem1 - tem2) <= acc),但是这样计算精确度很低,偏差大
精度低的原因:试考虑取x=3,当n=3时,x^n/x! 与 x^(n-1)/(n-1)! 的值相同
*/
return ans;
}
int main() {
cout << fixed << setprecision(7) << myExp(3) << endl;
return 0;
}2、(递归)编写一个递归函数,其功能为:输入一个字符串,字符间都有空格,输出一个整型值。例如:输入“1 x 2 y z 3 d h 4 g 5”输出为54321。
不用递归
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s = "1 x 2 y z 3 d h 4 g 5";
string s1;
for (int i = s.size()-1; i >=0; i--)
{
if (s[i] != ' ' && s[i] >= '0' && s[i] <= '9')
{
s1.push_back(s[i]);
}
}
cout << s1;
}使用递归
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void func(string s)
{
if (s.size() != 0)
{
func(s.substr(1));
//s = string(s, 1);
if (s[0] != ' ' && s[0] >= '0' && s[0] <= '9') cout << s[0];
}
}
int main() {
string s = "1 x 2 y z 3 d h 4 g 5";
func(s);
}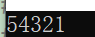
void func(char* a, int size)
{
if (size == 1)
{
if (*a != ' ' && *a >= '0' && *a <= '9') cout << *a;
}
else
{
func((a + 1), size - 1);
if (*a != ' ' && *a >= '0' && *a <= '9') cout << *a;
}
}
int main()
{
char a[] = "1 x 2 y z 3 d h 4 g 5";
func(a, strlen(a));
return 0;
}543213、使用随机数函数 srand()和time()生成随机数,来模拟掷骰子。
(1)分别投掷两次,将两次所得的值,求出其和值,并写入二维数组A,数组的行存放第一次投掷的结果,数组的列存放第二次投掷的结果。
(2)如果投掷1000次,将其和值出现的次数写入二维数组B。编写函数完成以上功能。
不太理解题目意思,参考别人的
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
// 数组大小可以更改,只需更改数组大小后,掷骰子的次数会随之更改
// 函数功能为:首行与首列为随机掷骰子的点数,中间交叉行列则为两
// 边界线的数的和
void flip1(unsigned val[][2], unsigned row, unsigned col) {
for (unsigned i = 1; i < col; ++i) // 初始化首行
val[0][i] = 1 + rand() % 6;
for (unsigned j = 1; j < row; ++j) // 初始化首列
val[j][0] = 1 + rand() % 6;
for (unsigned i = 1; i < row; ++i) { // 计算交叉行列的和
val[i][i] = val[0][i] + val[i][0];
}
}
// 随机掷骰子times次,并将出现的点数的次数记录在数组中
void flip2(unsigned val[7], unsigned times) {
for (unsigned i = 0; i < times; ++i)
val[1 + rand() % 6]++;
}
int main() {
srand(time(0));
const int row = 2;
const int col = 2;
unsigned A[row][col] = { 0 };
unsigned B[7] = { 0 };
flip1(A, row, col);
flip2(B, 1000);
cout << "The array of A:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < row; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < col; ++j)
cout << left<<setw(5) << A[i][j];
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl << "The array of B:" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i < 7; ++i)
cout << left<<setw(5) << B[i];
return 0;
}自己理解的B数组
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
//投掷两次的值
unsigned flip1() {
unsigned val[2][2] = { 0 };
val[0][1] = rand() % 6 + 1; // 初始化首列
val[1][0] = rand() % 6+1;
val[1][1] = val[0][1] + val[1][0];
return val[1][1];
}
// 随机掷骰子times次,并将出现的点数的次数记录在数组中
void flip2(unsigned val1[13],unsigned times)
{
for (unsigned i = 0; i < times; ++i)
val1[flip1()]++;
}
int main() {
srand(time(0));
unsigned B[13] = { 0 };
flip2(B, 500);
cout << endl << "The array of B:" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i < 13; ++i)
cout << left<<setw(5) << B[i];
return 0;
}4、编写FindRepStr()函数
此函数功能为,在字符串str中查找目的字符串findStr,并用repalceStr来替换,最后输出替换后的字符串str。函数原型为:void FindRepStr( char str[], const char findStr[], const replaceStr[])
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include<string>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
void FindRepStr(char str[], const char findStr[], const char replaceStr[])
{
string s1(str);
string s2(findStr);
string s3(replaceStr);
int n=s1.find(s2);
s1.replace(n, s2.size(), s3);
cout << s1;
}
int main() {
char str[] = "Hello world!";
const char findStr[] = "world";
const char replaceStr[] = "girl";
FindRepStr(str, findStr, replaceStr);
return 0;
}char a[80];
void FindRepStr(char str[], const char findStr[], const char replaceStr[])
{
char* p = strstr(str, findStr);
int len = strlen(findStr);
int len2 = strlen(replaceStr);
char* p1 = p + len, * p2 = str;
int num = 0;
while (p2 != p) { a[num++] = *p2++; }
for (int i = 0; i < len2; i++) { a[num++] = replaceStr[i]; }
while (*p1 != '\0') { a[num++] = *p1++; }
a[num++] = '\0';
cout << a << endl;
}
int main() {
char str[] = "Hello world!";
const char findStr[] = "world";
const char replaceStr[] = "girl";
FindRepStr(str, findStr, replaceStr);
return 0;
}Hello girl!5、编写一个Teacher类,要求类含有教师编号,姓名,性别,出生年月,入职年月。以及以下成员函数:
(1)带有默认参数的构造函数(默认出生年月为1900-00-00),复制构造函数。
(2) 2016年进行新一轮聘用,男教师满55岁,女教师满60岁,则到退休年龄,编写函数输出应退休的教师姓名和编号。
(3)如果满退休年龄的女教师入职时间未满35年,则继续聘用,编写函数输出应继续聘用的满退休年龄的女教师的姓名和编号。
(4)编写main 函数来测试你所设计的类。
此代码有问题,待改
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include<string>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
class Teacher
{
char* num;
char* name;
char* sex;
int birth;
int emp;
public:
Teacher(const char* n, const char* na, const char* s, int b = 19000000, int e = 19000000)
{
num = new char[strlen(n) + 1];
strcpy(num, n);
name = new char[strlen(na) + 1];
strcpy(name, na);
sex = new char[strlen(s) + 1];
strcpy(sex, s);
birth = b;
emp = e;
}
Teacher(Teacher& t)
{
if (t.num) { name = new char[strlen(num) + 1]; strcpy(num, t.num); }
birth = t.birth;
emp = t.emp;
if (t.name) { name = new char[strlen(name) + 1]; strcpy(name, t.name); }
if (t.sex) { sex = new char[strlen(sex) + 1]; strcpy(sex, t.sex); }
}
void Retire()
{
if ((sex=="男"&&(2016 - birth / 10000) >= 55))
{
cout << left << setw(10) << name << left << setw(6) << num << '\t';
cout << "退休" << endl;
}
else if (sex=="女"&&((2016 - birth / 10000) >= 60))
{
cout << left << setw(10) << name << left << setw(6) << num << '\t';
cout << "退休" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << left << setw(10) << name << left << setw(6) << num << '\t';
cout << "不能退休" << endl;
}
}
void NoRetire()
{
if (sex == "女"&& (2016 - emp / 10000) <= 35)
{
cout << left << setw(10) << name << left << setw(6) << num << "\t";
cout << "继续聘用" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << left << setw(10) << name << left << setw(6) << num << "\t";
cout << "退休" << endl;
}
}
void show()
{
cout << left << setw(10) << name << left << setw(6) << num << endl;
}
};
int main() {
Teacher t1("123", "x", "男", 19750203, 19950506);
Teacher t2("456", "y", "女", 19550923, 19730622);
t1.show();
t2.show();
cout << "可以退休:" << endl;
cout << left << setw(10) << "姓名" << left << setw(6) << "编号" << endl;
t1.Retire();
t2.Retire();
cout << "继续工作:" << endl;
cout << left << setw(10) << "姓名" << left << setw(6) << "编号" << endl;
t1.NoRetire();
t2.NoRetire();
return 0;
}2014
阅读题
1、

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void f(int* p)
{
if(p)
{
*p *= 100;
cout << *p << endl;
}
}
void main()
{
int p = 10;
int* ptr = &p;
f(ptr);
}10002、

题目不全

str[13]=str[length]='\0',所以从str【13】开始的的字符都无法输出
3、


void fun(int i, int j, int* a)
{
*a = j - i;
}
void main()
{
int a, b, c;
fun(20, 9, &a);
fun(9, a, &b);
fun(a, b, &c);
cout << a << "," << b << "," << c << endl;
}
4、输出结果
class A {
public:
virtual void print()
{
cout << "A::print" << endl;
}
};
class B :public A
{
public:
void print()
{
cout << "B::print" << endl;
}
};
class C :public B
{
public:
void print()
{
cout << "C::print" << endl;
}
};
void main()
{
B b;
C c;
A* a;
a = &c;
a->print();
a = &b;
a->print();
}
编程
1、(递归)用递归编程

#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int ack(int m, int n)
{
if (m == 0)return n + 1;
else if (n == 0) return m + 1;
return ack(m - 1, n - 1);
}
void main()
{
cout << ack(1, 2);
}2、写一个IntToStr(int a)函数将一个整形数转换为字符串
方法一:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
void IntToStr(int a)
{
string str = to_string(a);
cout << str << endl;
}
void main()
{
IntToStr(123);
}方法二
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
void IntToStr(int a)
{
char s[30] = { 0 };
int count = 0;
while (a) {
s[count++] = a % 10 + '0';
a = a / 10;
}
s[count] = '\0';
for (int i = 0, j = count - 1; i < count / 2; i++)
{
char tmp = s[i]; s[i] = s[j]; s[j] = tmp;
}
cout << s;
}
void main()
{
IntToStr(123);
}
3、写一个swap(int a[], int m, int n )使得数组的前m项和后n项交换位置
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
void Reverse(int a[], int low, int high)
{
for (int i = low, j = high; i <= (low + high) / 2; i++, j--)
{
int tmp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = tmp;
}
}
void Swap(int a[],int m,int n)
{
Reverse(a, 0, m-1);
Reverse(a, m, m + n - 1);
Reverse(a, 0, m + n - 1);
}
void main()
{
int a[] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
Swap(a, 2, 3);
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]); i++)
{
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
}这里默认长度为m+n,否则不好写代码
void swap(int a[], int m, int n,int size)
{
int len = size;
int* p1 = a;
int* p2 = p1 + m, * p5 = p2;
int* p3 = p1+(len - n), * p4 = p3;
int b[80]; int num=0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { b[num++] = *p3++; }
while (p2 != p4) { b[num++] = *p2++; }
while (p1 != p5) { b[num++] = *p1++; }
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)cout << b[i] << " ";
}
void main()
{
int a[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
swap(a, 3, 2,9);
}8 9 4 5 6 7 1 2 34、写一个日期Date类
(1)成员有年月日,成员函数有无参数构造函数、设置年月日的函数setDate还有一个打印函数display 3个
(2)第二个类是员工类Employee,成员有工号、姓名、身份证号、出生日期、受聘日期聘用年限、月薪
成员函数要有构造函数、改变出生日期函数、改变聘用年限函数、改变月薪函数、续聘函数(要求当续聘后的年龄大于60时给提示不能续聘)
还有展示函数display,需要有工号、姓名、身份证号、出生日期、聘用到期时间、聘用年限、年薪
注意第二个类会有Date类或其指针作为成员
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
int year, month, day;
public:
Date(int y,int m,int d):year(y),month(m),day(d){}
void setDate(int y, int m, int d)
{
year = y; month = m; day = d;
}
int getYear() { return year; }
void display()
{
cout << year << "年" << month << "月" << day << "日" ;
}
};
class Employee
{
int num;
char* name;
int ID;
Date birth;
Date emp;
int yearx;
int money;
public:
Employee(int n, const char* na, int i, Date d1,Date d2,int y, int my):birth(d1),emp(d2)
{
num = n; ID = i; yearx = y, money = my;
name = new char[strlen(na) + 1]; strcpy(name, na);
}
void SetDay(int y, int m, int d) { birth.setDate(y, m, d); }
void SetEmp(int y, int m, int d) { emp.setDate(y, m, d); }
void YearX(int y)
{
if (2023 - birth.getYear() > 60) { cout << "不能续聘" << endl; }
else { y = yearx; }
}
void SetMoney(int n) { money = n; }
void show()
{
cout << num << " " << name << " " << ID << " ";
birth.display(); cout << "\t"; emp.display();
cout <<" "<< yearx << " " << money << endl;
}
};
void main()
{
Date d1(1974, 02, 23); Date d2(1992, 06, 19);
d1.display();
cout << endl;
d2.display();
cout << endl;
Employee t(123, "Mike", 142123, d1, d2, 10, 20000);
t.show();
}

2013
编程
1、编写程序,计算1~20000之间的质数,输出时要求每行10个数.
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int sushu(int n)
{
if (n == 2) return 1;
else
{
for (int i = 2; i <= sqrt(n); i++)
{
if (n % i == 0) return 0;
}
return 1;
}
}
void main()
{
int num = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < 2000; i++)
{
if (sushu(i))
{
if (num <= 10)
{
cout <<left<<setw(5)<< i << " ";
num++;
}
else
{
num = 1;
cout << endl;
cout << left << setw(5) << i << " ";
num++;
}
}
}
}2、编写简单的加密,解密程序.
在main()函数中接收需要加密的字符串,进行加密。加密时,将字符指针+1,Encrpy的参数为字符指针。解密时将字符指针-1,Decrpy的参数亦为字符指针。
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
char* Encrpy(const char* str,int size)
{
char* str1 = new char[size+1];
strcpy(str1, str);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
str1[i] = str[(i+1)%size];
}
return str1;
}
char* Dncrpy(const char* str, int size)
{
char* str1 = new char[size + 1];
strcpy(str1, str);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
str1[i] = str[(i +size- 1) % size];
}
return str1;
}
void main()
{
char s[]="abcd";
cout << s << endl;
const char*s1= Encrpy(s, strlen(s));
cout << s1 << endl;
const char* s2 = Dncrpy(s1, strlen(s));
cout << s2 << endl;
}我理解的意思是字符往后移,比如abcd,变为bcda;
3、编写如下算法:1.选择排序 2.桶排序
void SelectSort(int* a, int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
int index = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < size; j++)
{
if (a[j] < a[index]) index = j;
}
swap(a[i], a[index]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) cout << a[i] << " ";
}
int b[100] = { 0 };
void TongSort(int* a, int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) b[a[i]]++;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
if (b[i] != 0)
{
while(b[i]>0)
{
cout << i << " ";
b[i]--;
}
}
}
}
void main()
{
int a[] = { 6,3,7,1,5 };
//SelectSort(a, 5);
TongSort(a, 5);
}4、对应于ASCII字符中33~126之间的字符,将其转化为10进制,8进制,16进制,以及ACII码输出到文件,在该文件中依次输出四张ASCII表格。
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ofstream file("table.dat");
file << setw(6) << "ASCII" << setw(4) << "dec"
<< setw(4) << "oct" << setw(4) << "hex" << endl;
for (int i = 33; i <= 126; ++i) {
file << setw(6) << char(i)
<< setw(4) << dec << i
<< setw(4) << oct << i
<< setw(4) << hex << i << endl;
}
return 0;
}
5、处理字符串(025)87234865-987,用strtok处理,以“区号 电话 分机号”的格式输出。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
char str[] = "(025)87234865-987";
cout << "分区" << "\t" << "电话" << "\t\t" << "分机号" << endl;
char* str1 = strtok(str+1, ")");
cout << str1 << "\t";
str1 = strtok(NULL, "-");
cout << str1 << "\t";
str1 = strtok(NULL, "");
cout << str1;
}6、已知:Person类包含3个数据成员(name,nationality,sex)和三个成员函数(构造函数,printName函数和printNationality函数),其中name的数据类型为Name类。Name类包含三个数据成员(first,middle,last)和两个成员函数(构造函数和printName函数)
定义Person类和Name类,并编写程序测试这两个类的所有接口。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Name
{
char* first;
char* middle;
char* last;
public:
Name(const char* f,const char* m,const char* l)
{
first = new char[strlen(f) + 1]; strcpy(first, f);
middle = new char[strlen(m) + 1]; strcpy(middle, m);
last = new char[strlen(l) + 1]; strcpy(last, l);
}
void printName()
{
cout << first << " " << middle << " " << last << endl;
}
};
class Person
{
Name name;
char* nationality;
char* sex;
public:
Person(Name na,const char* n,const char* s) :name(na)
{
nationality = new char[strlen(n) + 1]; strcpy(nationality, n);
sex = new char[strlen(s) + 1]; strcpy(sex, s);
}
void printName() { name.printName(); }
void printNationality() { cout << nationality << endl; }
};
void main()
{
Name n("a", "b", "c");
Person p(n, "中国", "女");
p.printName();
p.printNationality();
}2012
编程
1、编写程序,求最小公倍数。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int yueshu(int a, int b)
{
int r;
while (b)
{
r = a % b;
a = b;
b = r;
}
return a;
}
int beishu(int a, int b)
{
int x = yueshu(a, b);
return a / x * b;
}
void main()
{
cout << beishu(6, 9) << endl;
}2、编写程序,计算一系列整数之和。
假定:输入的第一个整数为继续输入整数的个数。【要求每条输入语句仅读取一个整数】
例如:输入5,101,213,325,437,549,表明输入五个整数分别是101,213,325,437,549.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
int n,sum=0,t;
cin >> n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
cin.ignore(); // 忽略逗号
cin >> t;
sum += t;
}
cout << sum;
}void main()
{
char a[100];
cin.getline(a, 100);
char* str = strtok(a, ",");
int n = atoi(str);
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
str = strtok(NULL,",");
sum += atoi(str);
}
cout << n << '\t' << sum;
}5,1,2,3,4,5
5 153、编写程序,读入几行文本,并打印一个表格,显示每个不同单词在文本中出现的次数。
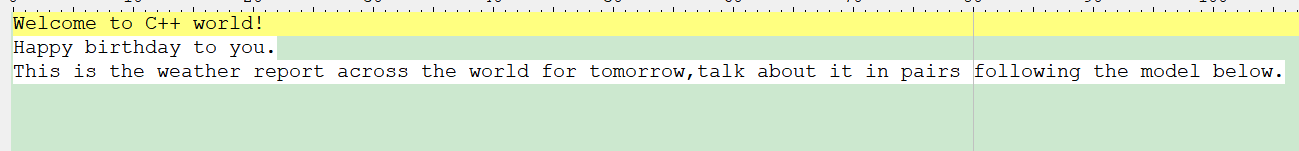
例如输入: Welcome to C++ world ! Happy birthday to you .This is theweather report across the world for tomorrow , talk about it in pairsfollowing the model below.结果为Welcome出现1次,to出现2次,C++出现1次等。
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<string>
#include<map>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ifstream file("input.txt");
string str;
string str1;
while (getline(file, str1))
{
str += str1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
if (str[i] == '.'||str[i]==','||str[i]=='!')
{
str.replace(i, 1, " ");
}
}
char ch[200];
strcpy(ch, str.c_str());
char* str2 = strtok(ch," ");
map<string, int> m;
while (str2)
{
m[str2]++;
str2 = strtok(NULL, " ");
}
for (map<string, int>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++)
{
cout <<left<<setw(10)<< it->first << " : " << it->second << endl;
}
return 0;
}

4、已知:Person类包含3个数据成员(name , nationality 和 sex)和三个成员函数(构造函数,printName函数和printNationality 函数),其中 name的数据类型为Name类。Name类包含三个数据成员(first , middle和 last)和两个成员函数(构造函数和printName函数)。
定义Person类和Name 类,并编写程序测试这两个类的所有接口。
已写过
2011
编程
1、编写一个程序,利用下面的公式计算e^x的值,精确到10^-10

#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
double fun(int x)
{
double sum = 1;
int i=1, k=1;
double tmp;
do
{
tmp = double(pow(x, i)) / k;
sum += tmp;
i++;
k = k * i;
} while (tmp >= 1e-10);
return sum;
}
int main()
{
cout << fixed << setprecision(10) << fun(1);
return 0;
}
2、编写一个程序,利用下面的公式计算Π的值,要求小数点后的位数为计算机可表达的最大范围。
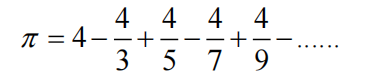
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
double fun()
{
double sum = 4;
int i=1,k=3;
double tmp;
do
{
tmp = double(4) / k;
if (i % 2 == 1)
{
sum -= tmp;
}
else if (i % 2 == 0)
{
sum += tmp;
}
i++;
k = k+2;
} while (tmp >= 1e-5);
return sum;
}
int main()
{
cout << fixed << setprecision(10) << fun();
return 0;
}

3、(递归)编写一个递归函数模板,从一个数组中找出最小值,并返回该值的数组元素下标。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
T Min(T* a, int first,int last)
{
static int index=0;
if (first<=last)
{
if (a[first] < a[index])
{
index = first;
}
Min(a, first + 1, last);
}
return index;
}
int main()
{
int a[] = { 5,2,4,6 };
cout<<Min(a, 0, 3);
return 0;
}4、编写两个函数SortOne和SortTow,分别对字符串数组实现插入排序和选择排序
void SortOne(char* a, int size)
{
int index;
char insert;
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++)
{
index = i - 1;
insert = a[i];
while (index >= 0 && a[index] > insert)
{
a[index + 1] = a[index];
index--;
}
a[index + 1] = insert;
}
}
void SortTwo(char* b, int size)
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
int index = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < size; j++)
{
if (b[index]>b[j])
{
index = j;
}
}
char temp;
temp = b[i];
b[i] = b[index];
b[index] = temp;
}
}
int main(void)
{
char a[] = { 'd','c','b','a' };
SortOne(a, 4);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) cout << a[i]<<" ";
cout << endl;
char b[] = { 'd','c','b','a' };
SortTwo(b, 4);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) cout << b[i] << " ";
}
5、对于一个数组Array类的chess对象通过调用运算符重载函数(),可实现chess(row,column)代替 chess[row][column]。
请完成:
(1)、Array类的基本定义,包括构造函数、析构函数、拷贝构造函数和基本数据成员;
(2)、运算符重载函数()的定义。
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<iomanip>
using namespace std;
class Array
{
int row;
int column;
public:
int* array;
Array(int r, int c) :row(r), column(c)
{
array = new int[row * column];
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < column; j++)
{
array[i*column+j] = 0;
}
}
}
int getr() { return row; }
int getc() { return column; }
Array(Array& a)
{
array = new int[a.row * a.column];
row = a.row; column = a.column;
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < column; j++)
{
array[i * column + j] = a.array[i * column + j];
}
}
}
~Array() { delete[] array; }
int operator()(int r,int c)
{
if (r > row || c > column) return -1;
else return array[r * column + c];
}
friend void operator>> (istream& input, Array& a);
friend void operator<< (ostream& output, Array& a);
};
void operator>> (istream& input, Array& a)
{
for (int i = 0; i < a.row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < a.column; j++)
{
input >> a.array[i * a.column + j];
}
}
}
void operator<< (ostream& output, Array& a)
{
for (int i = 0; i < a.row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < a.column; j++)
{
output << a.array[i * a.column + j];
}
}
}
int main()
{
Array a(2, 3);
cin >> a;
cout << a(1, 1);
return 0;
}
6、定义一个具有多态性的基类Shape,派生出三个类:圆Circle(坐标点和半径),矩形Rec类(两点不同坐标),三角形Tri类(三个不同坐标),每个类中至少有一个计算面积的函数。
编写程序,从文件 file.txt中读取数据来创建各类的对象,并放在 Shape指针向量中,最后循环处理每个对象并输出面积。
【假设file.txt中的数据如下:C:123,5,40;T:1,2,32,50,60,3;R:6,8,8,100 】
海伦公式:p=(a+b+c)/2
s=√(p(p-a)(p-b)(p-c))
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Shape
{
public:
virtual void print() {};
};
class Circle:public Shape
{
int x;
int y;
int radius;
public:
Circle(int x, int y, int r) :radius(r)
{
this->x = x; this->y = y;
}
void print()
{
cout << 3.14 * radius * radius << endl;
}
};
class Tri :public Shape
{
int x1,y1;
int x2,y2;
int x3,y3;
public:
Tri(int x1, int y1, int x2,int y2,int x3,int y3)
{
this->x1 = x1; this->x2 = x2; this->x3=x3;
this->y1 = y1; this->y2 = y2; this->y3=y3;
}
void print()
{
int a = sqrt(pow((x2-x1),2)+pow((y2-y1),2));
int b = sqrt(pow((x3 - x2), 2) + pow((y3 - y2), 2));
int c = sqrt(pow((x3 - x1), 2) + pow((y3 - y1), 2));
int p = (a + b + c) / 2;
cout << sqrt(p * (p - a) * (p - b) * (p - c)) << endl;
}
int get() { return x3; }
};
class Rect :public Shape
{
int x1, y1;
int x2, y2;
public:
Rect(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2)
{
this->x1 = x1; this->x2 = x2;
this->y1 = y1; this->y2 = y2;
}
void print()
{
cout << abs(x2 - x1) * abs(y2 - y1) << endl;
}
};
//C:1,3,1;T:0,0,3,0,0,4;R:6,8,8,9
int main()
{
Shape* s;
fstream output("file.txt");
int c[3];
int t[6];
int r[4];
string str;
getline(output, str);
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++)
{
if (str[i] == ':' || str[i] == ',' || str[i] == ';')
str[i] = ' ';
}
str.erase(str.find('C'),1);
str.erase(str.find('T'), 1);
str.erase(str.find('R'), 1);
int num = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
if (str[i] != ' '&&num<=2)
{
c[num++] = str[i]-'0';
}
else if (str[i] != ' ' && num >= 3&&num<=8)
{
t[num-3]= str[i]-'0';
num = num++;
}
else if (str[i] != ' ' && num >= 9 && num <= 12)
{
r[num - 9] = str[i]-'0';
num = num++;
}
}
Circle circle(c[0], c[1], c[2]);
Tri tri(t[0], t[1], t[2], t[3], t[4], t[5]);
Rect rect(r[0], r[1], r[2], r[3]);
s = &circle; s->print();
s = &tri; s->print();
s = ▭ s->print();
return 0;
}

2010
编程
1、输入n个十进制数转换成二进制写到文件,n是随机得到
#include<iostream>
#include<iomanip>
#include<fstream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
string binary(int x)
{
int a[200];
string str;
int n;
while (x)
{
n = x % 2;
str += to_string(n);
x = x / 2;
}
reverse(str.begin(), str.end());
return str;
}
int main()
{
ofstream file("abc.txt");
int n = rand()%4+1;
int x;
cout << n << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> x;
file << binary(x) << endl;
}
return 0;
}


2、(递归)写两个函数模板:插入排序的迭代实现和递归实现
template<class T>
void SortOne(T* a, int size)
{
int index;
T insert;
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++)
{
index = i-1;
insert = a[i];
while (index >= 0 && a[index] > insert)
{
a[index + 1] = a[index];
index--;
}
a[index + 1] = insert;
}
}
template<class T>
void SortTwo(T* b, int size)
{
if (size > 1)
{
SortTwo(b, size - 1);
int index = size - 2;
T insert = b[size - 1];
while (index >= 0 && insert < b[index])
{
b[index + 1] = b[index];
index--;
}
b[index + 1] = insert;
}
}
int main(void)
{
char a[] = { 'd','c','b','a' };
SortOne(a, 4);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) cout << a[i]<<" ";
cout << endl;
char b[] = { 'd','c','b','a' };
SortTwo(b, 4);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) cout << b[i] << " ";
}
3、文件中有类似的一行行字符串“(010)(15012345678)|123|(430070)”,按以下格式输出: “区号| 电话号码| 城市编号| 邮编”
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//(010)(15012345678)|123|(430070)
//区号| 电话号码| 城市编号| 邮编
int main()
{
char str[] = "(010)(15012345678)|123|(430070)";
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(str); i++)
{
if (str[i] == '(' || str[i] == ')' || str[i] == '|')
{
str[i] = ' ';
}
}
cout << "区号| 电话号码| 城市编号| 邮编" << endl;
char* str1 = strtok(str+1, " ");
while (str1)
{
cout << str1<<'|';
str1 = strtok(NULL, " ");
}
return 0;
}
4、设计一个多项式类Polynomial(包括构造函数、复制构造函数、析构函数、赋值函数、实现两个多项式相加)
5、几个类(Vehicle类 Car类 Streetwheel类 Brake类)有着必然的联系,设计类与实现
6、一个基类Shape,在基类的基础上继承写一个二维图形类,再继承写一个三维图形类,设计与实现







 本文通过C++代码示例展示了字符串中单词计数的方法,探讨了指针引用与静态数据成员在类继承中的应用,提供了二进制转换及文件操作的解决方案,介绍了递归排序算法的实现,并设计了多项式类与相关类结构,最后涉及随机数生成与动态规划思想的应用。
本文通过C++代码示例展示了字符串中单词计数的方法,探讨了指针引用与静态数据成员在类继承中的应用,提供了二进制转换及文件操作的解决方案,介绍了递归排序算法的实现,并设计了多项式类与相关类结构,最后涉及随机数生成与动态规划思想的应用。
















 5198
5198

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








